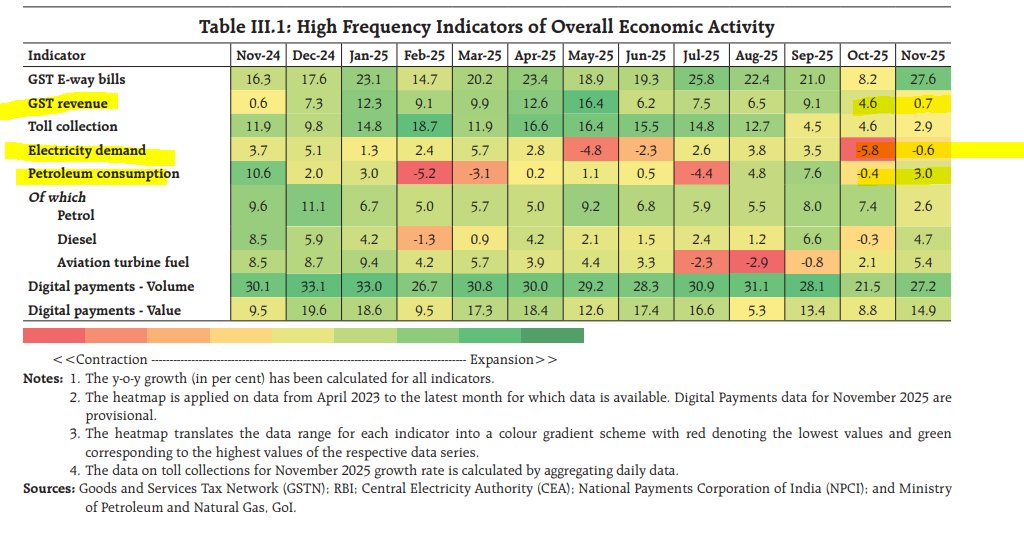
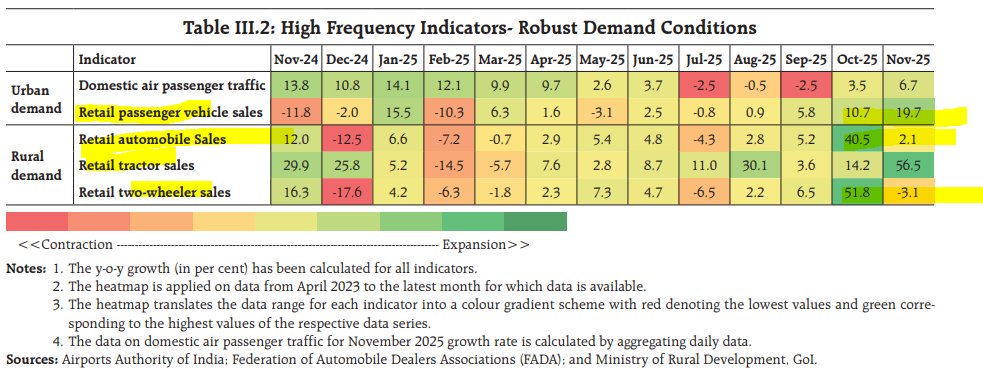
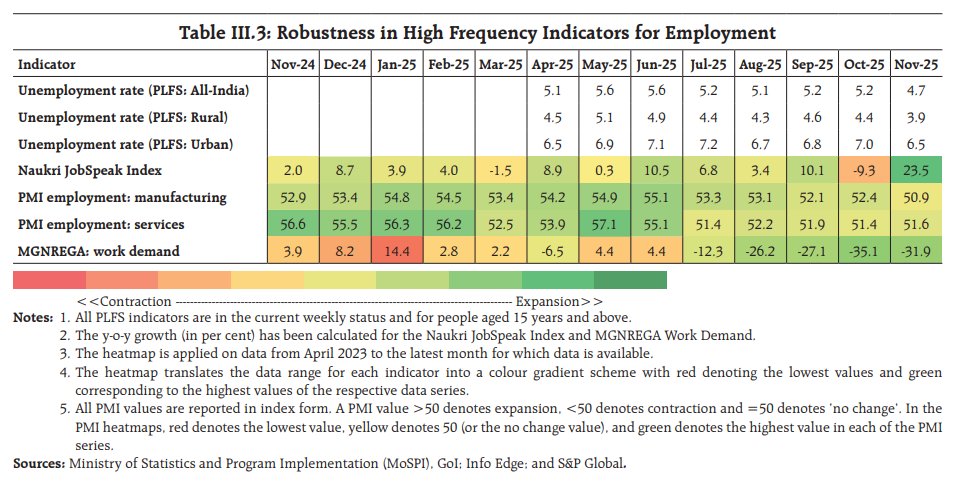
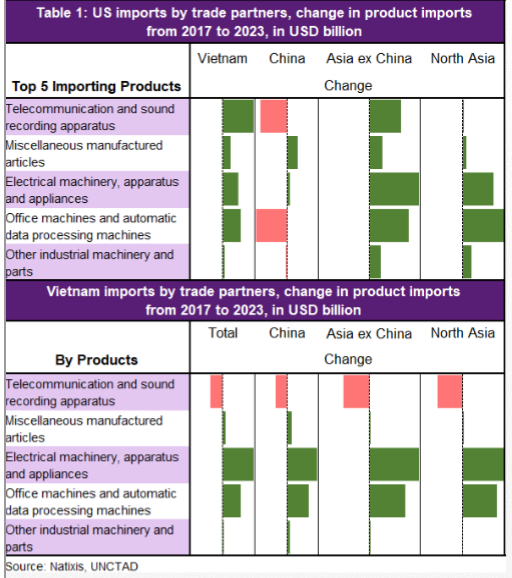
Good morning🌞- another hot & hazy Thursday in 🇭🇰. After a Trump Tweet meets a weaker Yuan fix, Asian central banks didn't stand by & slashed🔪rates (RBNZ -50bps, RBI-35bps, BOT-25bps). Today, we got the BSP & expect a 25bps cut w/ a RRR cut to add extra liquidity.
#CurrencyWar
#CurrencyWar

China July trade data is out & expectations of a sharper contraction of imports & exports weak.
Note this: China using the current account as a 1st line of defense is boosting its trade surplus via REDUCTION OF IMPORTS & that is bad news for traders 👇🏻.
Note this: China using the current account as a 1st line of defense is boosting its trade surplus via REDUCTION OF IMPORTS & that is bad news for traders 👇🏻.
https://twitter.com/Trinhnomics/status/1158881235776593922?s=20
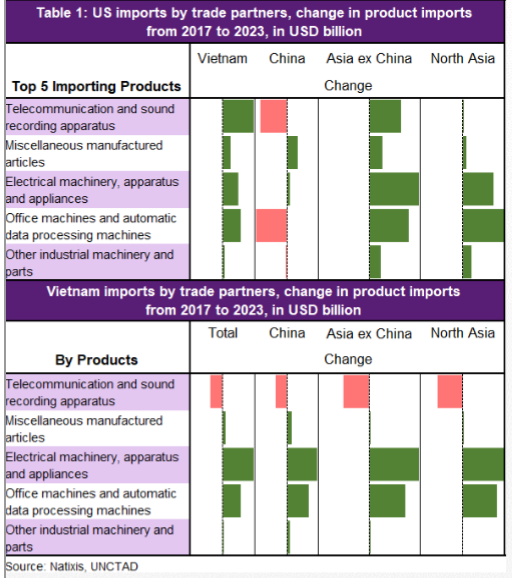
Trade relationship between the US and China & the amounts w/ tariffs so far (45bn left to retaliate) & the amount not yet by the US on China (300bn left) 👇🏻. Notice the asymmetric relationship & also the last tranche mostly consumer & capital goods so Trump'll tread gently. 

Another way to look at it & decomposed by manufacturing & non. Notice the massive manufacturing bias for China vs the US & also remember that manufacturing PMIs for China are still contracting. Escalated tensions likely to impact China July export figures in USD. 

Because China has only 45bn left to retaliate (it knows this). And because its retaliation so far trails the US imposition of tariffs (110bn vs 250bn) & b/c the relationship is asymmetric, it is using the CURRENT ACCOUNT AS A LINE OF DEFENSE.
What does that mean? IMPORTS DOWN👇🏻
What does that mean? IMPORTS DOWN👇🏻

Why imports? Let's go back to this concept of a J-curve. The idea is that if you DEPRECIATE your currency (the yuan) then, depending on elasticity of demand, your weaker currency should help w/ pricing power.
But that theory ignores one fact - MOST GLOBAL TRADE INVOICED IN USD👇🏻
But that theory ignores one fact - MOST GLOBAL TRADE INVOICED IN USD👇🏻

China's use of the RMB for trade invoicing PEAKED in Q1 2015, roughly ~65 of total merchandise trade. And do u remember what happened in August 2015? Yes, depreciation of RMB vs USD. Since then, usage of USD trade invoicing has risen to ~85-90%. This's important & pay attention. 

Let's pretend u are a manufacturer in Guangdong. Ready?
Costs are: Fixed & variable & in CNY. May import some inputs for production but China uses mostly domestic goods except commodities (Trump's beef is that as China expands it export market globally, it imports less from RoW).
Costs are: Fixed & variable & in CNY. May import some inputs for production but China uses mostly domestic goods except commodities (Trump's beef is that as China expands it export market globally, it imports less from RoW).
Price in USD to ur foreign customers.
Scenario1: CNY depreciates by 10% & tariffs go up say 10%.
Costs in CNY goes up by less b/c ur import content not so high but there is upward costs to fixed costs such as rent etc by 5%. Translates this into USD & costs of production cheaper
Scenario1: CNY depreciates by 10% & tariffs go up say 10%.
Costs in CNY goes up by less b/c ur import content not so high but there is upward costs to fixed costs such as rent etc by 5%. Translates this into USD & costs of production cheaper
BUT, don't forget that u gain 10% in FX since last yr, but ur inputs in CNY don't stay constant & they go up say 5% so ur net is only up 5% & so in USD ur costs of production goes down by 5%. But tariffs are up 10% on the USD prices. To be competitive u have to discount in USD!
Tariffs are paid by importers (Americans & they are ur BIGGEST CUSTOMER 16-20% of market). But the importers VIEW UR PRODUCTS AS 10% more expensive vs. the others if prices same as last year in USD. Input costs lower but output has to be DISCOUNTED EVEN MORE & margin squeezed!
So the way Chinese manufacturers cope is by DISCOUNTING THEIR PRICES IN USD & passing on the SAVINGS to their American customers (this is why you don't see PCE in the US going higher). In the process, the margin they make on these products are LOWER despite savings in input costs
The DEPRECIATION OF THE CNY is helpful to lower INPUT COSTS & that means that if there weren't any tariffs, a Chinese exporter can get a boost if there aren't any tariff & may choose to either pass on the savings to be competitive or not but the savings less than FX depreciation.
This is why the Chinese government wants to expand usage of RMB in trade invoicing. But the fact is that MOST TRADE IS INVOICED IN USD. And that has implications in the PASS-THROUGH OF FX to the economy. Note that I haven't even touched trade financing, which is also in USD.
What is the macroeconomic implication of the dominance of the USD in trade-invoicing in China? The PASS-THROUGH OF FX IS THROUGH IMPORTS.
A 10% weaker CNY (not to mention a multitude of tax incentives passed recently to help w/ domestic market) means LESS IMPORT FROM WORLD.
A 10% weaker CNY (not to mention a multitude of tax incentives passed recently to help w/ domestic market) means LESS IMPORT FROM WORLD.

You will see this today for the July figure & we already know that from the year-to-date figure of sharper contraction of imports (exports not doing great but domestic producers being helped by less competition).
Something else - the RMB REER is much lower than in 2015. So?
Something else - the RMB REER is much lower than in 2015. So?

What is a REER? It is a summation of a trade-weighted FX (so say CNYUSD, CNYEUR, CNYKRW, etc) that is deflated by relative CPI. FX strategists/economists use this as a more comprehensive valuation of FX as USD just shows vs USD not other partners.
USD/CNY shows USD appreciating
USD/CNY shows USD appreciating

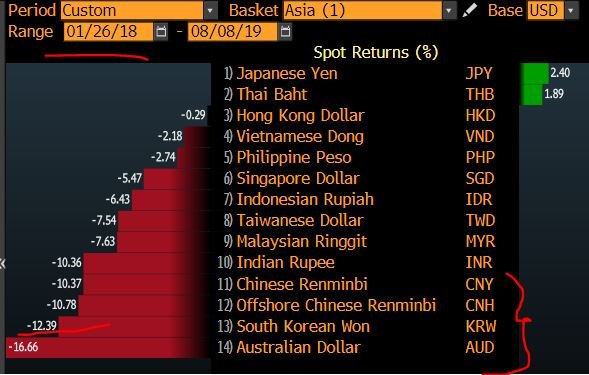
Are you ready? This is the implication of China sheltering its economy through the current account (imports down): Asian exports are DOWN, especially key traders like South Korea.
Why are they down? Because South Korea depends on China for demand & that market is SHRINKING👇🏻
Why are they down? Because South Korea depends on China for demand & that market is SHRINKING👇🏻

So the FX policy implication of this, and this is OLD NEWS, is that the Won can't appreciate against the YUAN (I wrote a report on this in 2016) & why you see the KRW DEPRECIATING MORE THAN THE CNY.
Why? Because it can't stand idly by & just watch its external market shrinking.
Why? Because it can't stand idly by & just watch its external market shrinking.
The mid-rate fix is 7.0039 today (lowest since 2008) & that means max it can weaken onshore is 7.143 (+2% & -2%). Okay, what do you think the trade figure will be? My guess is NOT PRETTY & watch the IMPORTS.
#CurrencyWar
#CurrencyWar

The winner of Japan-Korea tensions, US-China tensions, weak domestic demand thanks to Moonomics & high household debt & low fiscal stimulus, weak global growth, China sheltering its domestic market using the current account as a 1st line of defense (fiscal + FX) is:
BOND🙇🏻♀️🥇💪🏻💪🏻
BOND🙇🏻♀️🥇💪🏻💪🏻

China July exports +3.3% vs expectations of -1% from -1.3% in June & IMPORTS CONTRACTED -5.6%YoY in USD.
Yes, trade surplus ballooning on weaker imports. With the CNY weaker, don't expect import demand to rise.
Yes, trade surplus ballooning on weaker imports. With the CNY weaker, don't expect import demand to rise.
My guess is a lot of front-loading before the remainder of the tariffs go up (+300bn tariffs 1 September) & that is a key driver of the higher surplus with the US.
Front-loading will be even more intense in August, before the 1 September deadline of 10% of 300bn goods.
Details of China contraction of imports (-5.6%YoY) by destination:
USA -19.1% 🥶
Canada -23.6%🥶
Japan -13%🥶
South Korea -20.1%🥶
Singapore -2.9%🥶
EU -3.3%🥶
UK -22.4%🥶
Germany -7.5%🥶
Hong Kong up +19.9%
USA -19.1% 🥶
Canada -23.6%🥶
Japan -13%🥶
South Korea -20.1%🥶
Singapore -2.9%🥶
EU -3.3%🥶
UK -22.4%🥶
Germany -7.5%🥶
Hong Kong up +19.9%

Details of China EXPANSION of exports (+3.3%YoY):
USA -6.5% (down but not as much as imports by China of American products)
Canada +6.5% (note that Chinese demand of Canadian is DOWN)
Japan -4.1%
South Korea +9.3%
Taiwan +19.9%
Singapore +11.6%
EU+6.5%
UK +9.1%
Germany +5.8%
USA -6.5% (down but not as much as imports by China of American products)
Canada +6.5% (note that Chinese demand of Canadian is DOWN)
Japan -4.1%
South Korea +9.3%
Taiwan +19.9%
Singapore +11.6%
EU+6.5%
UK +9.1%
Germany +5.8%

Putting this together:
a) China exports to the USA contracts but by less than US exports to China as Chinese exporters likely discounted products (thanks to a weaker CNY) to offset tariffs
b) China exports to RoW rise as a weaker CNY helps w/ input costs
c) China IMPORTS CONTRACT

a) China exports to the USA contracts but by less than US exports to China as Chinese exporters likely discounted products (thanks to a weaker CNY) to offset tariffs
b) China exports to RoW rise as a weaker CNY helps w/ input costs
c) China IMPORTS CONTRACT
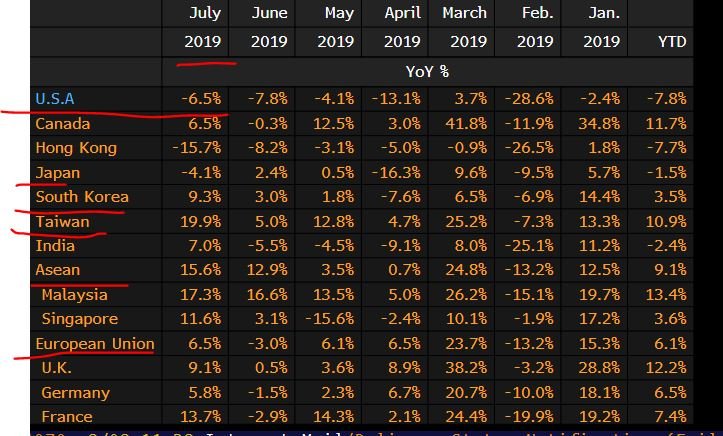

The big story of the year is:
China using the current account as a first line of defense & that story is especially more salient as the CNY weakness quickens. This has global implication b/c the stabilization of China comes at a great costs to exporters (less Chinese demand)👆🏻
China using the current account as a first line of defense & that story is especially more salient as the CNY weakness quickens. This has global implication b/c the stabilization of China comes at a great costs to exporters (less Chinese demand)👆🏻
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh