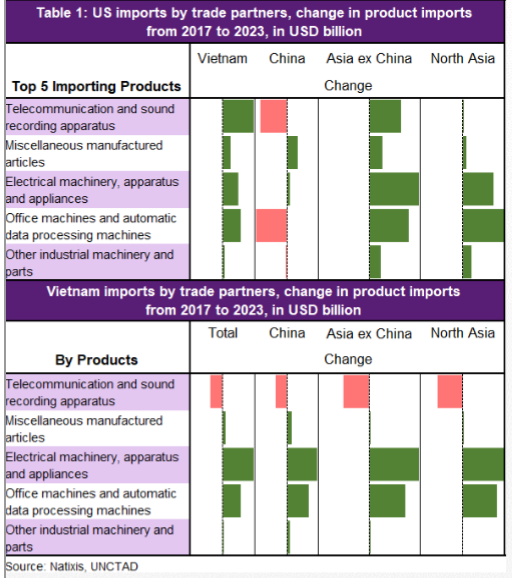
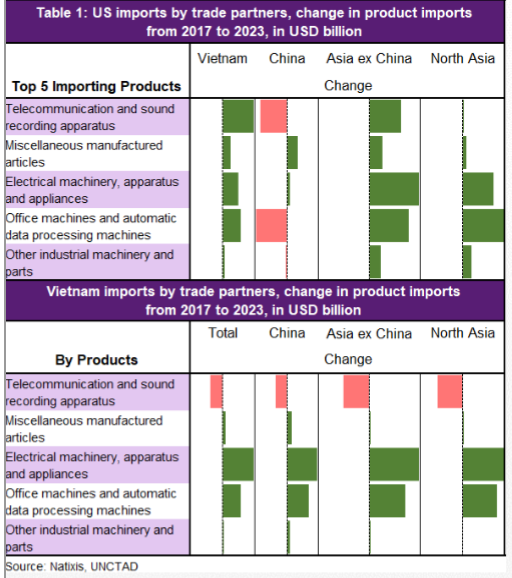
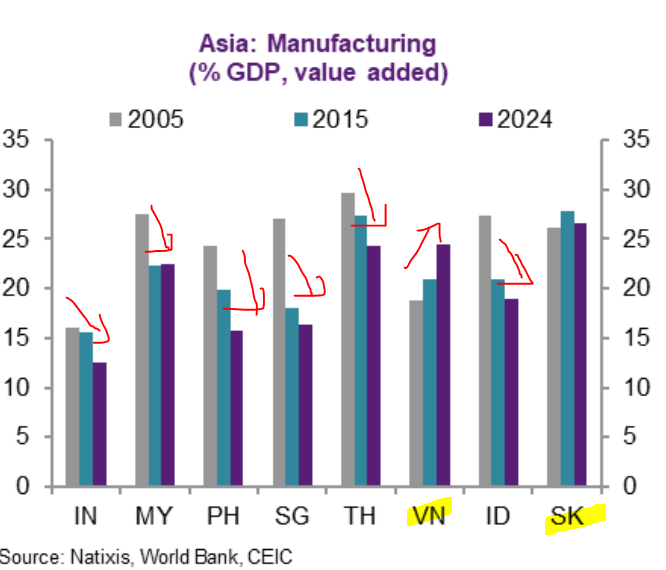
Let's dive right into this discussion of negative interest rates policy (NIRP). Before we talk about the impact, let's talk about this paper issued by the IMF on:
Enabling Deep Negative Rates to Fight Recessions: A guide
I will read this w/ u & cover key topics like money.
Enabling Deep Negative Rates to Fight Recessions: A guide
I will read this w/ u & cover key topics like money.
https://twitter.com/Trinhnomics/status/1161433761273143296
As a rule, before I read a paper, I glance at the title, abstract, authors, & the organization publishing. The IMF - led by a European & multilateral - responsible for helping countries w/ fiscal management & capacity building. Legarde was head & now will be the ECB head.
How u read an academic paper: Skim through the title, abstract, look for thesis, look at table of content, go to the back and read the conclusion & then the body. W/o reading the entire paper, the thesis👉🏻 is TO ENABLE DEEP NEGATIVE RATES TO MAINTAIN THE POWER OF MONETARY POLICY. 

We already know that: this is not a discussion of WHETHER one should ENABLE NEGATIVE RATES but A GUIDE OF HOW TO ENABLE NEGATIVE RATES. They made that decision already & this is just how to make it palatable for the public.
Now u know what WON'T BE in the paper & what will be.
Now u know what WON'T BE in the paper & what will be.
So to actively read we must know the WHY to understand the HOW they will show u & what they WON'T SHOW U.
Okay, let's go. How is an academic paper structured? Usually abstract, after executive summary & then literature review to show that this is not coming out of left field.
Okay, let's go. How is an academic paper structured? Usually abstract, after executive summary & then literature review to show that this is not coming out of left field.

The table summarizes neatly the literature review. Their review is sparse w/ NO ACADEMIC cited advocating what they are saying but some area related but not exactly. Eisler wrote in 1932 & then nothing & a bunch of people on abolishing cash lately. But used anyway for legitimacy. 

Btw, if u think the literature review is sparse (qualitative legitimacy), then the paper has NO quantitative evidence on why this needs to be enabled or why anything they argue is empirically true.
But they tell u what this is - a GUIDE to ENABLE NIRP to MAINTAIN POWER OF CBs👈🏻
But they tell u what this is - a GUIDE to ENABLE NIRP to MAINTAIN POWER OF CBs👈🏻

And they are not hiding the WHY of this paper: POLITICS. This word is used so often in the piece. Read the highlighted part about why this needs to happen (has nothing to do w/ effectiveness but politics): THE USE OF DEEP NEGATIVE RATES FOR A SHORT TIME HAS POLITICAL ADVANTAGES 

So the WHY is here in plain sight: TO HELP CALM THE POLITICS OF NEGATIVE RATES. Yes, they wrote that. They made the decision before discussing whether NIRP & now publishing a GUIDE on how to CALM THE MASS & NORMALIZE NIRP. 

Here are the steps to MITIGATE THE POLITICAL COSTS of implementing NIRP (yes, they wrote this):
a) Measuring markets' perception
b) Making the market aware of CB tools & can help manage associated side effects
c) CONVINCE MARKETS that the CB willing to use new tools.
Digest that
a) Measuring markets' perception
b) Making the market aware of CB tools & can help manage associated side effects
c) CONVINCE MARKETS that the CB willing to use new tools.
Digest that

So after 6 pages of ranting, the authors have 4 charts on rates going down & the only charts u'll get for a while. No discussion of output, wealth, employment, wages. Nothing.
Then this on p8. Political costs are repeated in 2 paragraphs. Politics. This is what this is about.
Then this on p8. Political costs are repeated in 2 paragraphs. Politics. This is what this is about.

History of thought on NIRP (there's none):
a) Gesell in 1916 - proposed requiring stamps to be purchased to paper money periodically
b) Goodfriend 2000 on stamped paper currency
c) Eisler depreciation mechanism for paper currency
d) Rogoff on ban cash
Authors then cite BLOGS!😱
a) Gesell in 1916 - proposed requiring stamps to be purchased to paper money periodically
b) Goodfriend 2000 on stamped paper currency
c) Eisler depreciation mechanism for paper currency
d) Rogoff on ban cash
Authors then cite BLOGS!😱

Before we proceed to discuss approaches to ENABLE NIRP to maintain the power of monetary policy, let's talk about something important & key for everyone to understand: HOW MONEY IS CREATED & the role of central banks & banks so u know why EVERYONE should care (scared) about NIRP.
Pay attention. This part is key to the why NIRP will impact you.
Central banks need BANKS to transmit their policy objective to the real eco(households, firms). Do this 3 ways: set the price of money (interest rates), quantity (quantity of assets they purchase), & regulations.
Central banks need BANKS to transmit their policy objective to the real eco(households, firms). Do this 3 ways: set the price of money (interest rates), quantity (quantity of assets they purchase), & regulations.

Central banks can only INFLUENCE & can't force banks to lend according to their policy/political objectives (some do through window guidance eg PBOC & SBV). This is what economists like to call rule-based approach & should be based on some sort of inflation or employment rules.
Let's use the Fed: has a price target & stable employment. If it is below that target for a long period of time, the Fed can say it'll help via loosening financial condition by: loosen regulations, lower rates & buy assets
When the Fed cuts rates by 25bps to 2.25% that impacts u
When the Fed cuts rates by 25bps to 2.25% that impacts u
When the Fed sets rates high, pays banks more to park $ & when it sets rate low, wants reduce banks' incentive to hold cash
Ur deposit at the bank is the banks' liabilities (banks borrow from u). When banks lend u $, that is a bank's assets. Diff is net interest income for banks
Ur deposit at the bank is the banks' liabilities (banks borrow from u). When banks lend u $, that is a bank's assets. Diff is net interest income for banks

CBs can only influence via their toolbox & up for banks to allocate based on risk appetite. Why did the ECB lower deposit rates to -0.1% in 2014 (now -0.4%)? Frustrated w/ Euro banks not taking enuff risks & firms in Europe depend on banks for funding (US equity & bonds more key)
Markets expect deposit rates to turn even more negative & that means the ECB making it very expensive for banks to park cash w/ the ECB & so in the process forcing banks to take risks to improve profitability because banks CAN'T fully PASS ON NEGATIVE RATES TO RETAIL depositors.
Now that we roughly covered key ideas important for you to understand, let's get back to the paper. I will cover their 1st approach soon - the CLEAN APPROACH (trust me, not clean & they know it & call for more research to make it clean as some law prohibits it). 

Notice that no where in this paper they call for more research on the effectiveness of NIRP or anything they propose. Words are just thrown out as if they are facts. No reason to hide the agenda either -> here to ENABLE NIRP to EMPOWER MONETARY POLICY.
Okay, clean approach. haha
Okay, clean approach. haha
Clean approach = tax on holding paper currency vs electronic currency. Basically a tax on CASH or putting a negative interest rate on paper currency interest rate (PCIR). Example: Fed set PCIR at -1%. That means that after 1 yr, that 100 cash is worth only 99. DEPRECIATES CASH
👇🏻
👇🏻

Now u know what the clean approach is, u may ask, well, how does that help u losing $ on holding cash? Well, just does! Duh! Author said in 1 sentence: Negative PCIR makes it possible to stimulate investment & net exports as much as needed to revive the economy!
Just like that👌🏻
Just like that👌🏻

No empirical evidence. No charts. No studying of other countries that are without cash. Just like that. 1 sentence.
What about SIDE EFFECTS of the clean approach? Let me tell u, there are many! Author found 5! Yep! Lots of side effects & no support for why negative PCIR works👌🏻
What about SIDE EFFECTS of the clean approach? Let me tell u, there are many! Author found 5! Yep! Lots of side effects & no support for why negative PCIR works👌🏻

We'll move on to the RENTAL FEE APPROACH (RFA). Let's not forget that the CLEAN APPROACH (CA) is a misnomer & actually NOT LEGAL. And so author says:
If central banks can find a legal way, then CA, but if THERE ARE LEGAL BARRIERS, then the RFA to enable deep negative rates🤗.Yep
If central banks can find a legal way, then CA, but if THERE ARE LEGAL BARRIERS, then the RFA to enable deep negative rates🤗.Yep

Will continue with this thread tomorrow as I got morning meeting bright & early at 8am & need to hike the peak now. We're on page 20 btw in case u want to get a head start.
Thanks for reading w/ me📖🤓
Thanks for reading w/ me📖🤓
Ready? Let's go, hope u're caught up w/ the Clean Approach & how that isn't actually clean 😬(legal issues, small detail 🤗).
Rental Fee Approach is a RENT payment on paper currency. Imagine Fed has -1% PCIR = Fed charges the banks 1% for taking paper currency from cash window👇🏻
Rental Fee Approach is a RENT payment on paper currency. Imagine Fed has -1% PCIR = Fed charges the banks 1% for taking paper currency from cash window👇🏻

Examples of Rent Approach:
a) Swiss National Bank (SNB) in 2014 NIRP imposes a charge on banks for excess paper currency withdrawals. Put it another way, imposes a negative rate only on the portion of the bank's reserves at the SNB that exceeds a certain threshold 👈🏻
b) BOJ
a) Swiss National Bank (SNB) in 2014 NIRP imposes a charge on banks for excess paper currency withdrawals. Put it another way, imposes a negative rate only on the portion of the bank's reserves at the SNB that exceeds a certain threshold 👈🏻
b) BOJ
BOJ in 2016 followed the SNB & adjusts up the portion of bank reserves to which negative rates apply 1-for-1 when bank exchanges its CB reserves for cash. The BOJ only subjects the bank's own holding of paper currency but not include paper currency the bank passes on to customer.
Notice that the authors see this as a short-coming & said: THERE IS NO REASON IT NEEDS TO STOP THERE!
Because the there would be: NO LIMIT TO HOW LOW THE MARGINAL PAPER CURRENCY INTEREST COULD GO😱
Yep, wrote that. No explanation. Next, we got PAGES OF SIDE EFFECT. True story
Because the there would be: NO LIMIT TO HOW LOW THE MARGINAL PAPER CURRENCY INTEREST COULD GO😱
Yep, wrote that. No explanation. Next, we got PAGES OF SIDE EFFECT. True story

What u've learned so far:
a) Authors don't bother to argue WHETHER NIRP is needed but rather we need to ENABLE NIRP to empower monetary policy
b) DON'T HAVE (care to) EVIDENCE WHY NIRP SHOULD BE ENABLED
c) But defo knows plenty of side effects. Pages & pages of side effects 😱👇🏻
a) Authors don't bother to argue WHETHER NIRP is needed but rather we need to ENABLE NIRP to empower monetary policy
b) DON'T HAVE (care to) EVIDENCE WHY NIRP SHOULD BE ENABLED
c) But defo knows plenty of side effects. Pages & pages of side effects 😱👇🏻

The 3 side effects of RFA:
a) BANK PROFITABILITY PROBLEM😱
b) Cash-rental-fee-pass-through problem (yep mouthful) but means BANKS CAN'T PASS ON NEGATIVE RATES TO RETAIL DEPOSITORS w/o risking them taking $ out😱
c) the 'Gresham's Law' Problem😱
Don't worry, they have "solutions"
a) BANK PROFITABILITY PROBLEM😱
b) Cash-rental-fee-pass-through problem (yep mouthful) but means BANKS CAN'T PASS ON NEGATIVE RATES TO RETAIL DEPOSITORS w/o risking them taking $ out😱
c) the 'Gresham's Law' Problem😱
Don't worry, they have "solutions"

Let's go through these "solutions" (by that I mean either wishful thinking or bending reality or proposing solutions that are HORRIBLE FOR THE AVERAGE PERSON & the only people benefiting are, gosh I don't know who benefits).
Ready? I promise it is good & worth u reading w/ me.
Ready? I promise it is good & worth u reading w/ me.

"Solutions" of NIRP:
*Somehow banks' profitability improves due to the valuation effect of banks w/ a positive maturity gap experience capital gains as long-term assets have capital gains? Urgh🧙🏻♀️
*DEFAULT CHANNEL - NIRP improves firms' profitability & improves NPL 🧙🏻♀️
Yay!!! 🥳
*Somehow banks' profitability improves due to the valuation effect of banks w/ a positive maturity gap experience capital gains as long-term assets have capital gains? Urgh🧙🏻♀️
*DEFAULT CHANNEL - NIRP improves firms' profitability & improves NPL 🧙🏻♀️
Yay!!! 🥳

*Fees & commission income channel - AUTHORS THINK THAT WHEN INTEREST RATES ARE LOWER, FEES & COMMISSION INCOME TEND TO RISE & IMPROVES BANK'S PROFITABILITY
Wuat?😮
*Net interest income channel - authors didn't have anything good to say & concede NIRP is bad. But didn't stop there
Wuat?😮
*Net interest income channel - authors didn't have anything good to say & concede NIRP is bad. But didn't stop there

Authors think NIRP improves banks' profitability (3 channels ex 1, which their wishful thinking couldn't ignore that fact that it doesn't work).
Conclude: EMPIRICAL LITERATURE (as opposed to FACTS that banks' profitability is DOWN) shows BENIGN EFFECTS OF NEGATIVE RATES ON BANKS
Conclude: EMPIRICAL LITERATURE (as opposed to FACTS that banks' profitability is DOWN) shows BENIGN EFFECTS OF NEGATIVE RATES ON BANKS

Wait, but I haven't gotten to their "solutions", which should frighten u. Ready? They propose:
Banks modify existing deposit contracts to CHARGE FEES & INHIBIT CONVERSION OF ELECTRONIC $ TO CASH.
Charge a fee for a cash withdrawals at ATM machines. Put a limit on withdrawal 😱
Banks modify existing deposit contracts to CHARGE FEES & INHIBIT CONVERSION OF ELECTRONIC $ TO CASH.
Charge a fee for a cash withdrawals at ATM machines. Put a limit on withdrawal 😱

Instead of going through all, let's look at this table on the SIDE-EFFECTS of RFA & tools to manage the side effect. Notice that the benefits FEW & the side effects plenty:
Bank profitability😱
Cash arbitrage😱
Pass-through of RFA😱
Reduced CIRCULATION OF $ 😱
To name a few.
Bank profitability😱
Cash arbitrage😱
Pass-through of RFA😱
Reduced CIRCULATION OF $ 😱
To name a few.

Food for thought & all here in the table. To ENABLE DEEP NEGATIVE RATES, the RFA have 5 problems & 5 BAD SOLUTIONS that are very bad for HOUSEHOLDS
To achieve the political agenda & we're only 31/89 here, authors have identified a lot of problems & proposed few good solutions👌🏻.
To achieve the political agenda & we're only 31/89 here, authors have identified a lot of problems & proposed few good solutions👌🏻.

Notice that nowhere here where they PAUSE a second WHETHER NIRP is worth the costs. This paper entire objective is:
Enabling Deep Negative Rates to Fight Recessions: A Guide
Don't bother to discuss the impact on households - ORDINARY PEOPLE who don't understand NIRP anyway 👇🏻
Enabling Deep Negative Rates to Fight Recessions: A Guide
Don't bother to discuss the impact on households - ORDINARY PEOPLE who don't understand NIRP anyway 👇🏻

Read the comments for this FT article. Not a single person is applauding the ECB's NIRP. Many of the comments are very astute. The review for the ECB effort is overwhelmingly NEGATIVE & so the ECB will:
DOUBLE DOWN thanks to support from the IMF et al👌🏻
ft.com/content/9d7d46…
DOUBLE DOWN thanks to support from the IMF et al👌🏻
ft.com/content/9d7d46…
Draghi in July '12, "Within our mandate, the ECB is ready to do whatever it takes to preserve the euro. And believe me, it will be enough."
7 yrs later: CPI 1%, GDP weak, risks piling as the ECB force banks to take more risks to preserve profitability..
That's not the worst part
7 yrs later: CPI 1%, GDP weak, risks piling as the ECB force banks to take more risks to preserve profitability..
That's not the worst part
The worst part about this is: the central bank is about to DOUBLE DOWN on this. People are now expecting deposit rates to go LOWER. The ECB to introduce tiering to help w/ the side-effects it created. And the ECB will have to change its 33% cap on ownership of govies to raise APP
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh