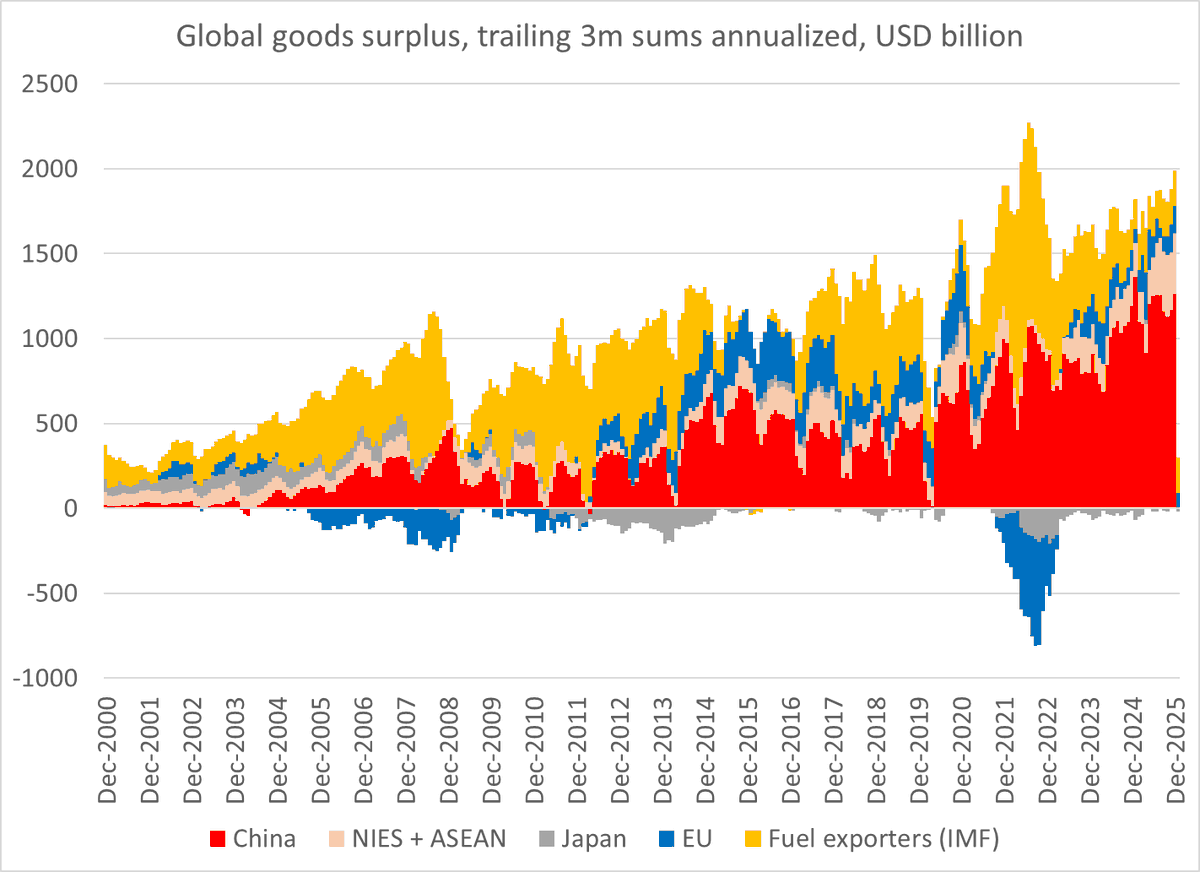
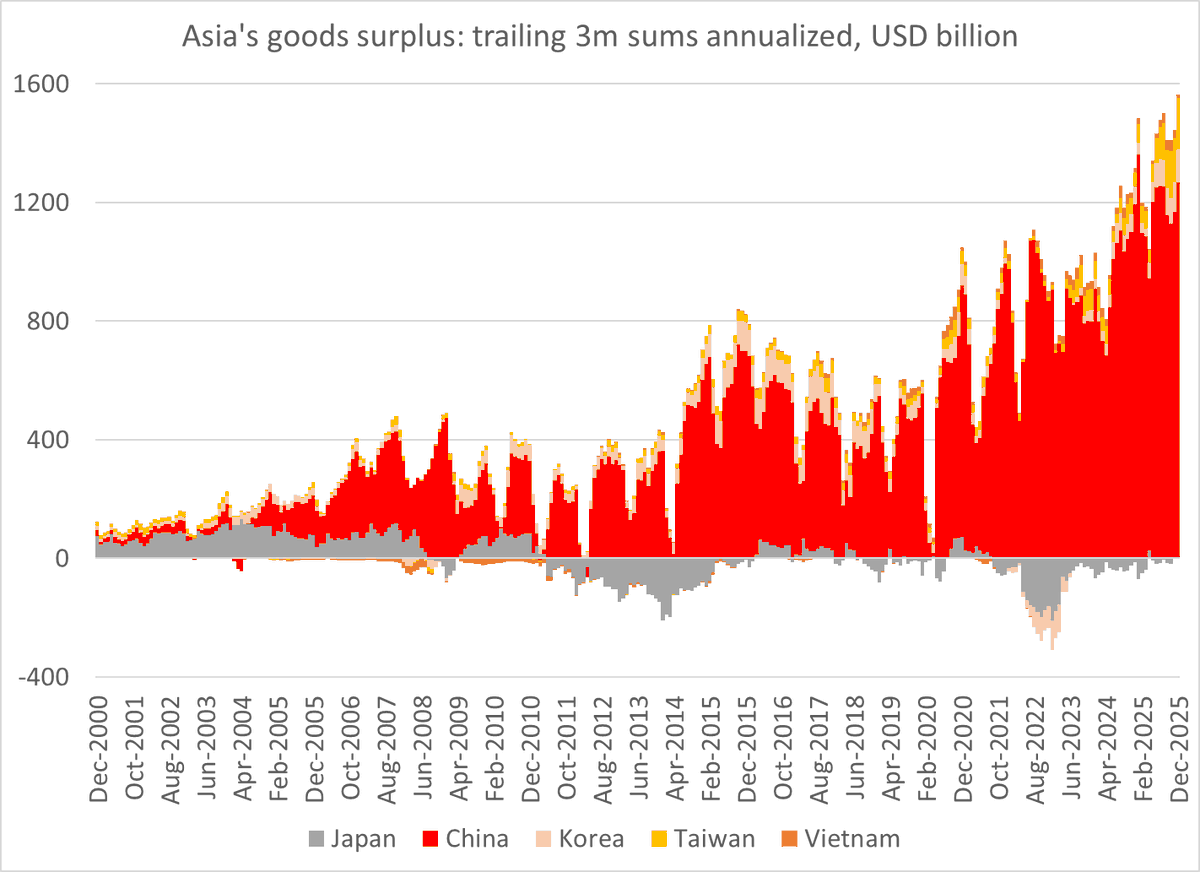
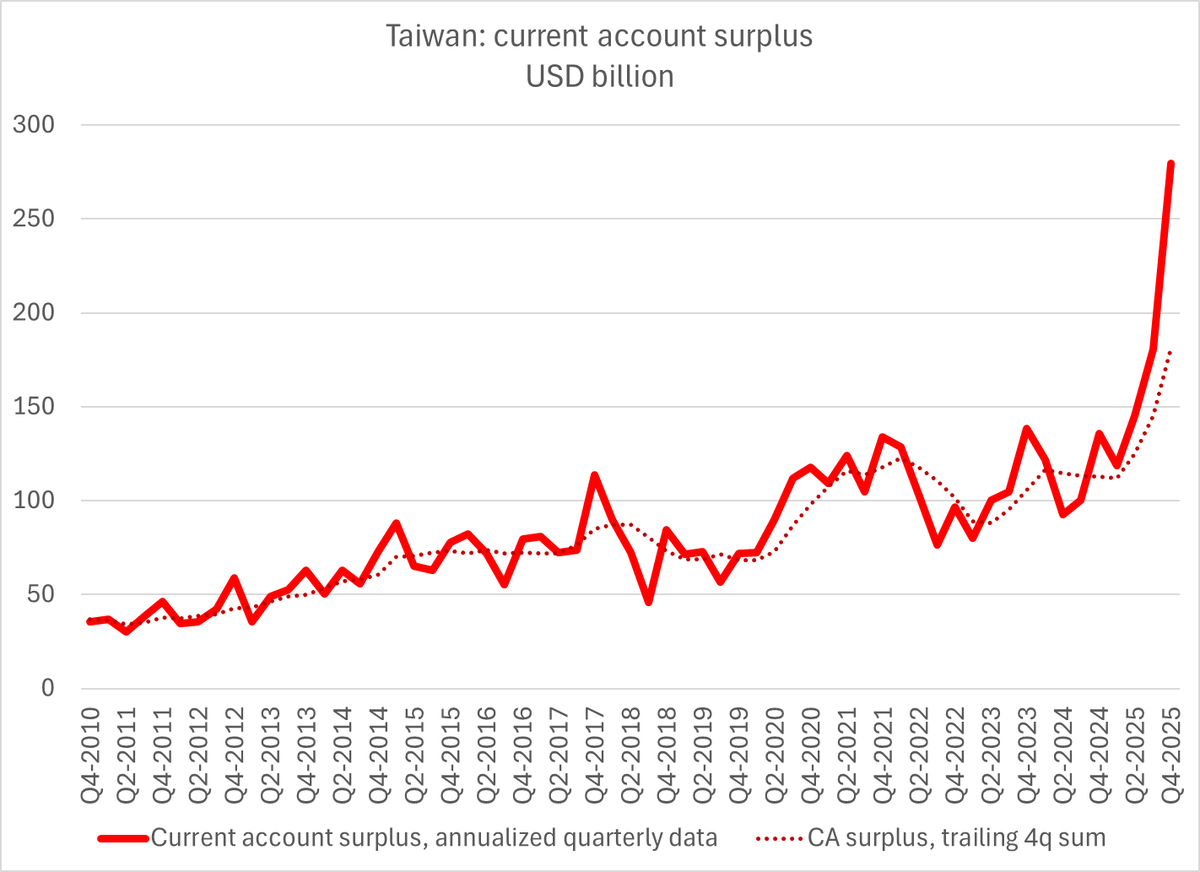
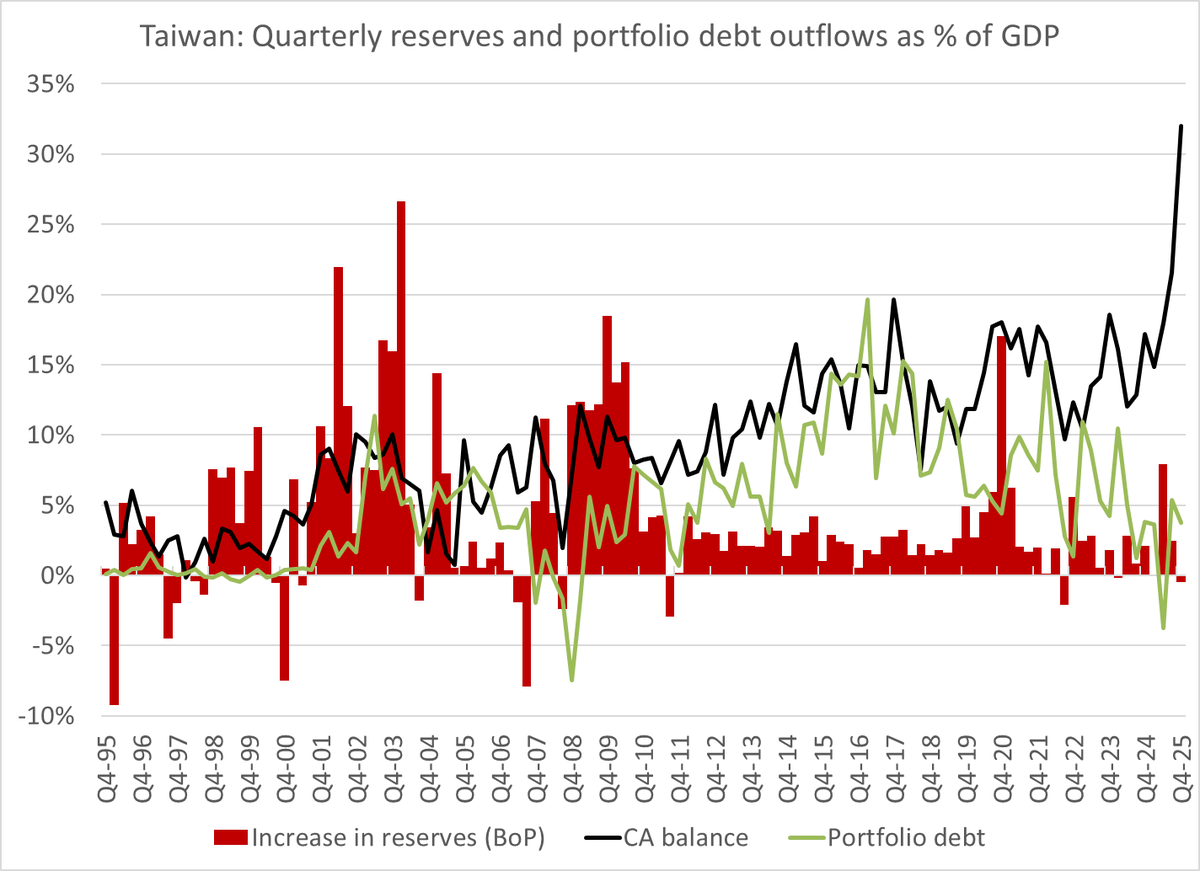
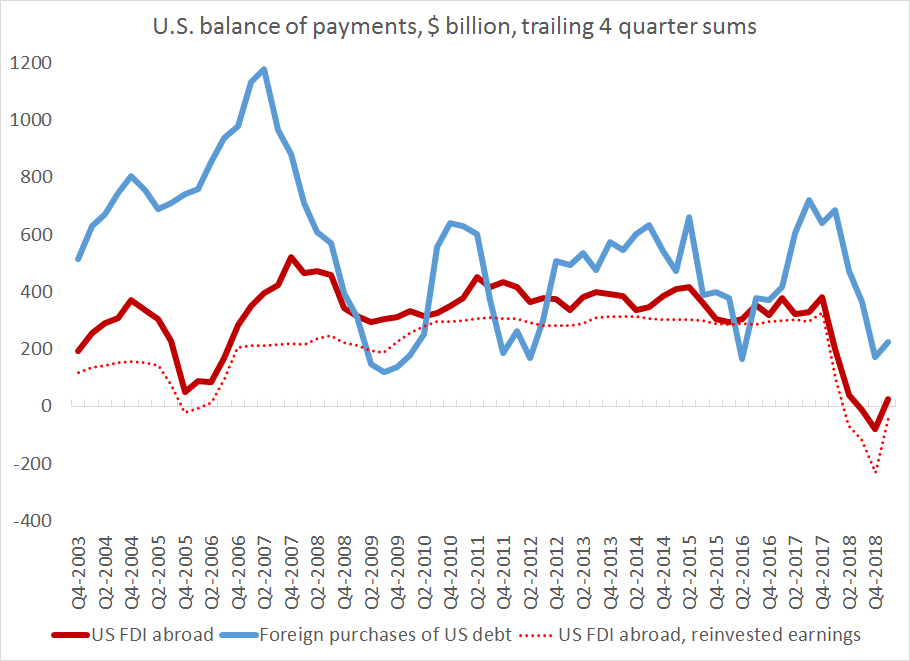
There will be a lot written about financial deglobalization when folks pour over the 2018 data. But it is a mistake to fit last year's financial deglobalization into a Trump trade driven narrative.
It is basically a function of the shift in U.S. tax policy.
(thread)
1/x
It is basically a function of the shift in U.S. tax policy.
(thread)
1/x

The fall in U.S. outward FDI is entirely a function of a fall in U.S. direct investment in the world's tax havens; there was not real change in the pattern of investment in other economies.
(under the old law profits reinvested abroad could defer paying US tax)
2/x
(under the old law profits reinvested abroad could defer paying US tax)
2/x

The fall in U.S. FDI "reinvested" abroad in low havens had a host of other effects - firms building up assets in low tax jurisdictions were buying U.S. debt, inflating gross flows in both ways.
(there is actually a good fit in the BoP data here,using flows over last 4qs)
3/x
(there is actually a good fit in the BoP data here,using flows over last 4qs)
3/x
E.g. a lot of US FDI abroad was in practice the rising "cash" of a Techco (Ireland or Bermuda) sub, and a lot of foreign demand for US debt was coming from the same Techcos (or Pharmacos) offshore subs
4/x
4/x
I think I have found this in the BoP - the fall in cumulative FDI in a set of tax havens was mirrored by a fall in the cumulative purchases of U.S. debt of a slightly different set of tax havens
(cumulative flows = proxy for the stock" of offshore claims)
5/x
(cumulative flows = proxy for the stock" of offshore claims)
5/x

The match here isn't "pure." The debt holdings line for example includes Russia (which moved its reserves out of the US). But other Europe is the breakdown in the US data alas. & I couldn't include the Caribbean's holdings of U.S. debt b/c that was picking up something else ...
but I don't think it is totally spurious. here is the same plot for the set of EA countries that includes Ireland.
Both US FDI in Ireland & Irish holdings of US debt have gone into reverse (the fall in FDI tho is just a fall in the cash held by the Irish subs of US firms)
6/x
Both US FDI in Ireland & Irish holdings of US debt have gone into reverse (the fall in FDI tho is just a fall in the cash held by the Irish subs of US firms)
6/x

and since so much of this involved or touched a euro area country, it has similar implications for the euro area's balance of payments. FDI into the EA fell (US firms were "reinvesting" less in tax havens) and European demand for US debt fell ...
7/7
7/7
p.s. will do a blog on this too, but likely not til after labor day ...
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh