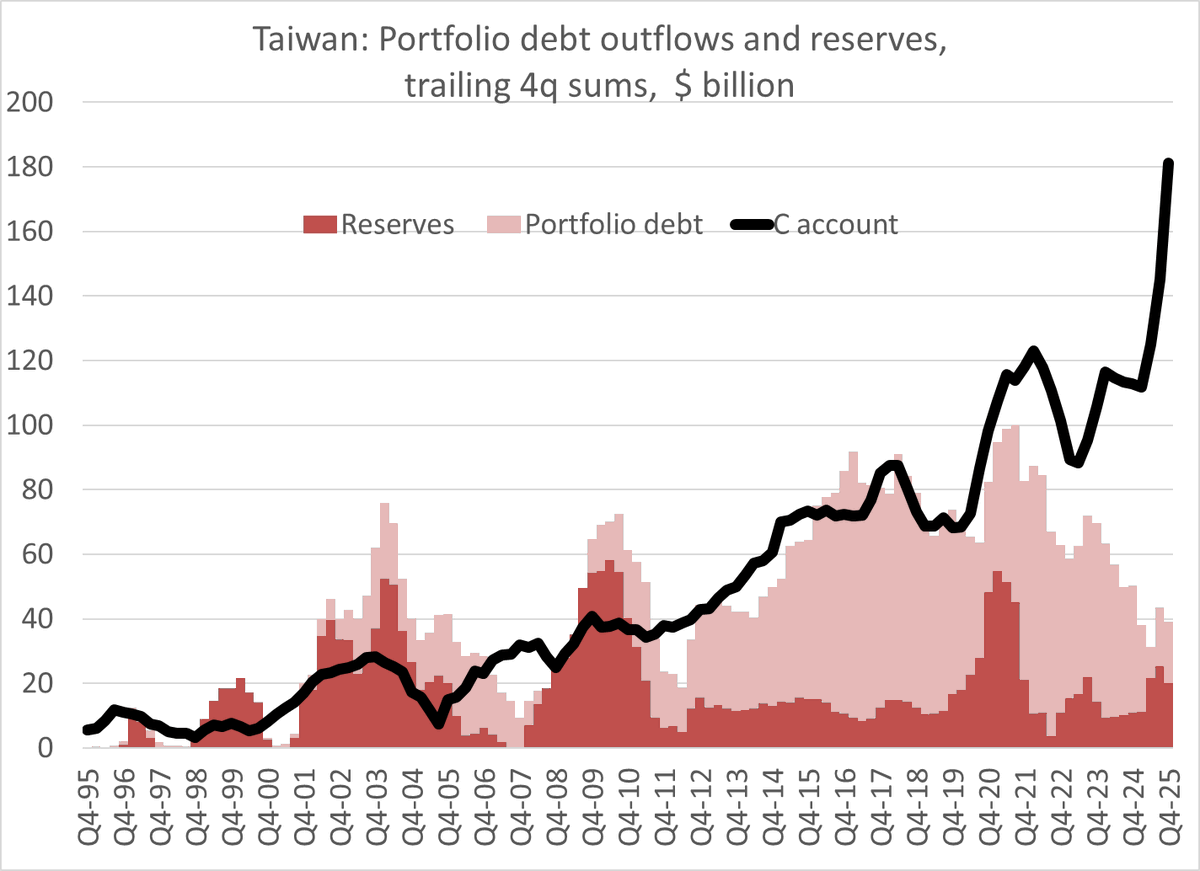
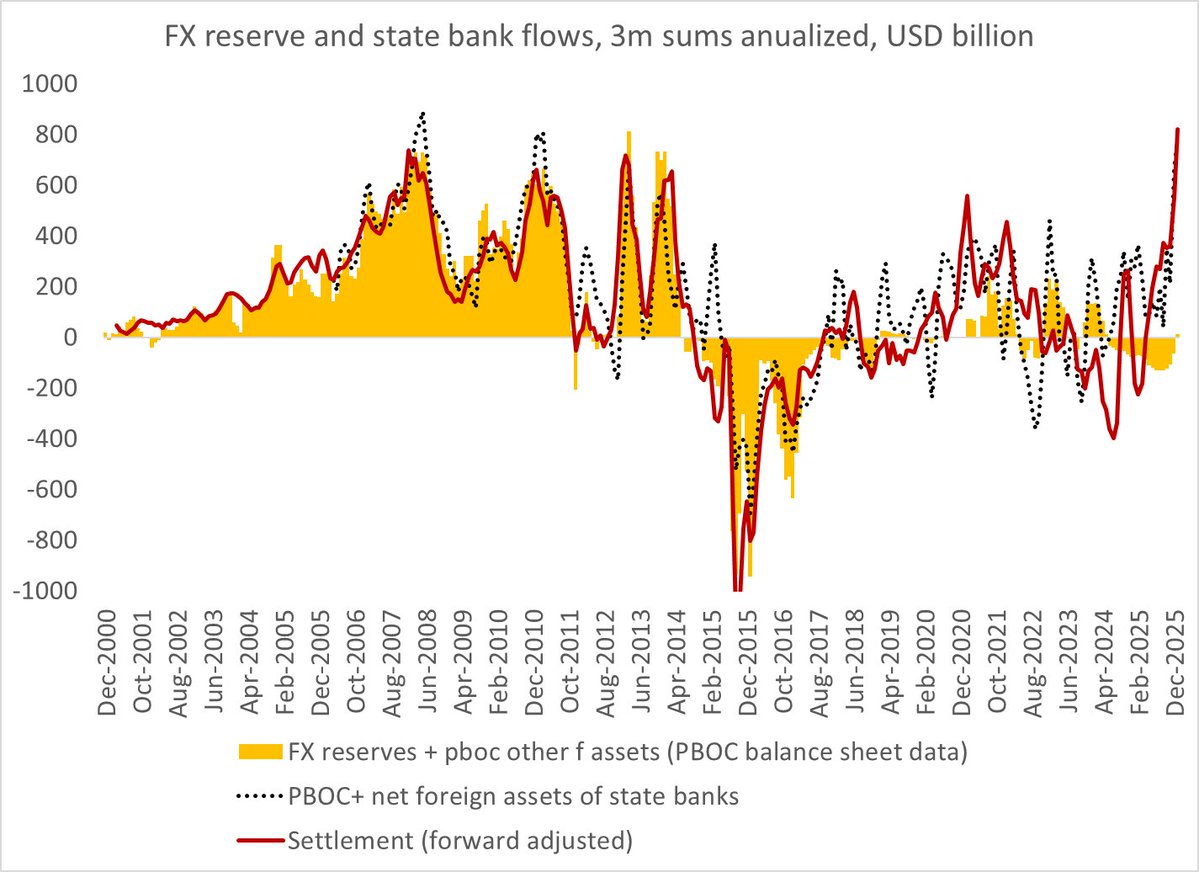
I am among those trying to figure out Trump’s China trade strategy.
Like most I am confused. Trump’s latest escalation was formally a response to China’s latest round of tariffs. But China’s tariffs, in my view, basically confirmed that China has run out of good targets.
1/x
Like most I am confused. Trump’s latest escalation was formally a response to China’s latest round of tariffs. But China’s tariffs, in my view, basically confirmed that China has run out of good targets.
1/x
The incremental costs to the U.S. of the trade war right now are essentially coming from Trump’s own tariffs. And I suspect that undermines the United States' leverage.
2/x
2/x
https://twitter.com/niubi/status/1166042563721269250
UBS thinks that China added about $10b in new products to its tariff lists, so its tariffs now cover $100b rather than say $90b of its $150b in imports from the U.S. (based the Chinese number for imports from the U.S.)
3/x
3/x
China also raised the tariff rate a bit, but that’s largely irrelevant. China has already proved, tariff or no tariff, it can shut down certain U.S. imports if it wants to.
(Crude supposedly wasn't hit by tariffs last fall ... )
4/x
(Crude supposedly wasn't hit by tariffs last fall ... )
4/x

Remember that in 3 of the 4 largest goods exporting sectors, the market for U.S. exports is essentially China’s state. The state airlines. The state oil and gas companies. And the old state ag and oilseed import monopoly. Gives China some unique tools (like it or not)
5/x
5/x
Autos are the exception: they are sold to private buyers. & China did raise its tariffs there – but that cannot have surprised the Trump administration.
China lifted the auto tariffs it imposed last fall to help facilitate the negotiations. They were an obvious target.
6/x
China lifted the auto tariffs it imposed last fall to help facilitate the negotiations. They were an obvious target.
6/x

Basically, China had to go back to the sectors it tariffed heavily after the initial U.S. tariffs last summer/ fall – it didn’t come up with any new targets. The incremental impact on (already modest) U.S. goods exports to China will likely be minimal.
6/x
6/x
The Trump Administration by contrast has basically doubled its total tariff on China in the last month – going from 25% on $250b ($62b) to 30% on $250b and 15% on $270b ($112b). The just pay it cost of the China tariff has increased to around a half point of U.S. GDP.
7/x
7/x
And by definition, if the USTR picked its tariffs rationally, the last round of tariffs will have the highest cost to the U.S. – China is basically the sole supplier (for now) of most of the goods on the final $170b (December) list.
8/x
8/x
Of course, with time (as Paul Krugman notes), firms will adjust. But until there is clarity on whether or not the tariffs are permanent, such investments don’t make sense. That’s a big part of the damaging uncertainty.
9/x
9/x
The thing is, China likely knows this – the easiest path for Trump give the economy a bit of a boost in an election year is, in a sense, to declare victory in the trade war and come home. (h/t @geoffreygertz)
10/x
10/x
@geoffreygertz Reversing the last two rounds of U.S. tariff escalation would likely put about a quarter point of GDP back into consumers’ pockets in an election year ...
11/x
11/x
@geoffreygertz Bottom line: President Trump obviously thinks he gains leverage by his willingness to escalate and hit back hard. But that isn’t at all clear to me.
12/x
12/x
@geoffreygertz Last note. There are much more advanced ways of estimating the cost of tariffs than the "just pay it" cost. But a lot of them end up converging toward the simple back of the envelope calculation tax hike impact. Offsetting effects and all.
13/13
13/13
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh