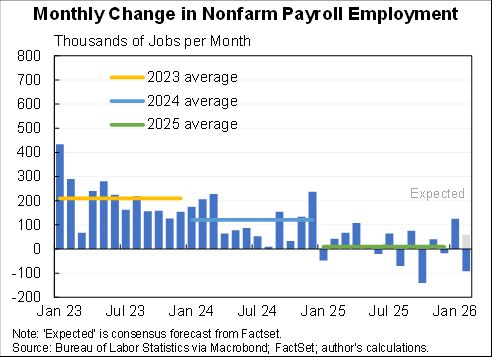
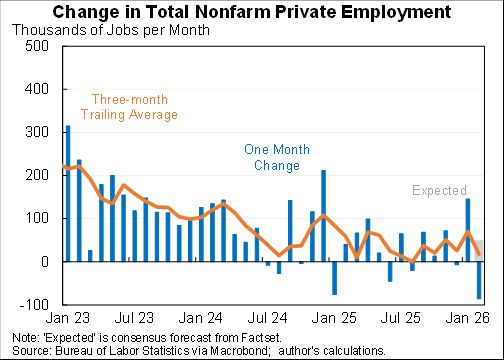
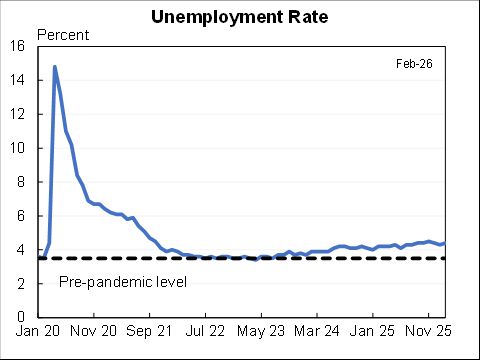
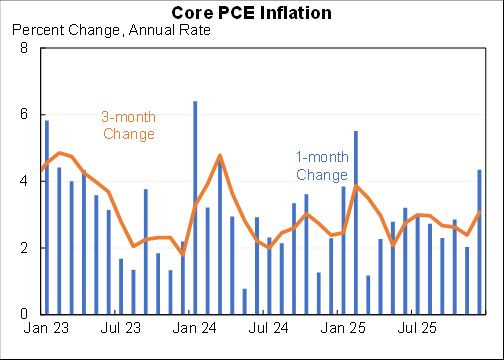
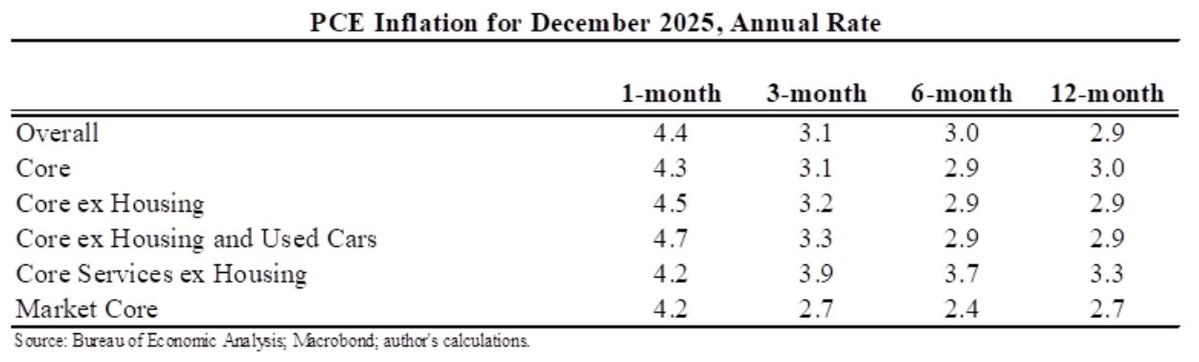
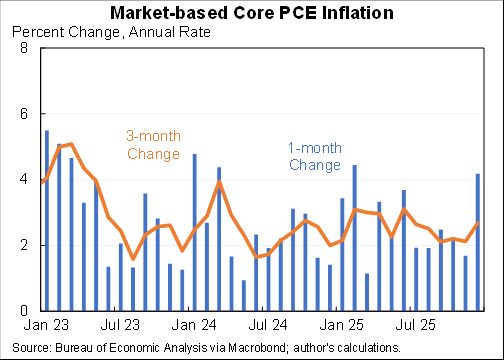
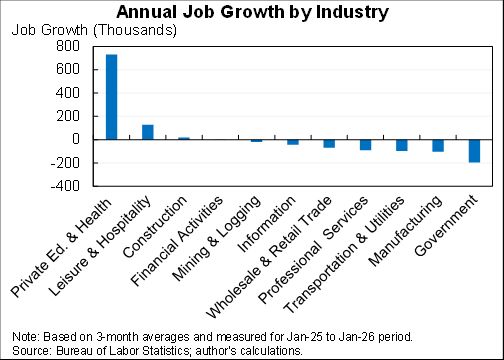
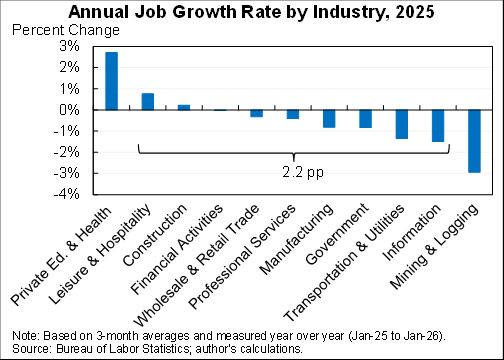
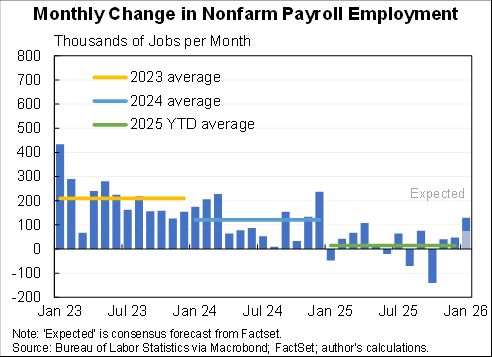
I assessed what the macro data tells us about the Tax Cut & Jobs Act for @AEIdeas. My bottom line: "not much". Since passage GDP growth has slowed slightly as slowing consumption & investment growth only partly offset by faster govt spending. #TCJANowWhat aei.org/publication/no… 

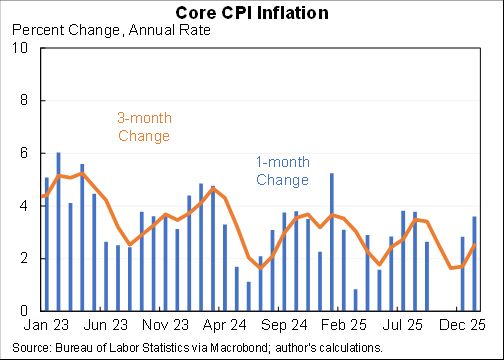
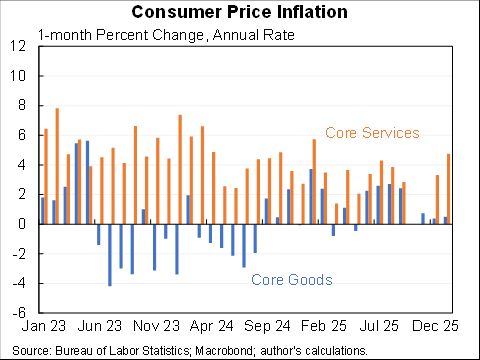
The second sense in which the data tell us "not much" is that is the difficulty of extracting the signal (the effect of the tax cut) from the noise (the effect of the Fed, global economy, trade war, oil prices, fiscal stimulus, etc. etc. etc.)
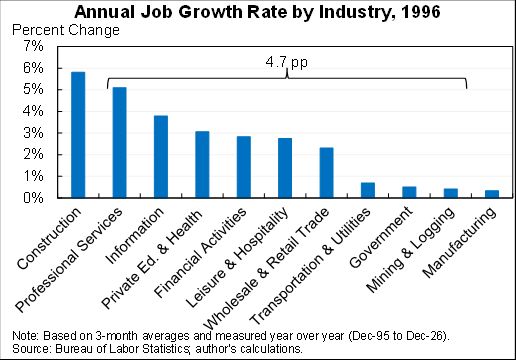
A lot of sector-specific stories are important. This table tells some of them: (i) oil-related investment growth slowed dramatically as oil prices stopped their rapid rise; (2) software and R&D growth increased for reasons unrelated to the TCJA; and (3) everything else slowed. 

At least three macro stories are also important but go in different directions: fiscal stimulus boosted the economy while the trade wars and interest rate increases went in the opposite direction.
Sorting all of this out the main conclusion is that the second sense of "not much" (hard to extract the signal from the noise) reinforces the first sense of "not much" (if the tax cut was so important relative to everything else we would see the signal much more clearly).
The best hope for a better understanding of the causal impact of the TCJA will be microeconomic research that looks at how similar firms are affected differently by the law and tracking their differential responses.
Ultimately, however, the most important issue is what to do going forward. I believe we can have a more efficient business tax system while raising more revenue than the current system. I couldn't explain it in 280 characters so you'll have to read the image. 

I really appreciate @aparnamath and @erinmelly2 inviting me to write this--and recommend you stay tuned for the all star cast they have doing upcoming blogs on the TCJA drawing on a diverse set of expertise and perspectives. aei.org/tag/trumps-tax…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh