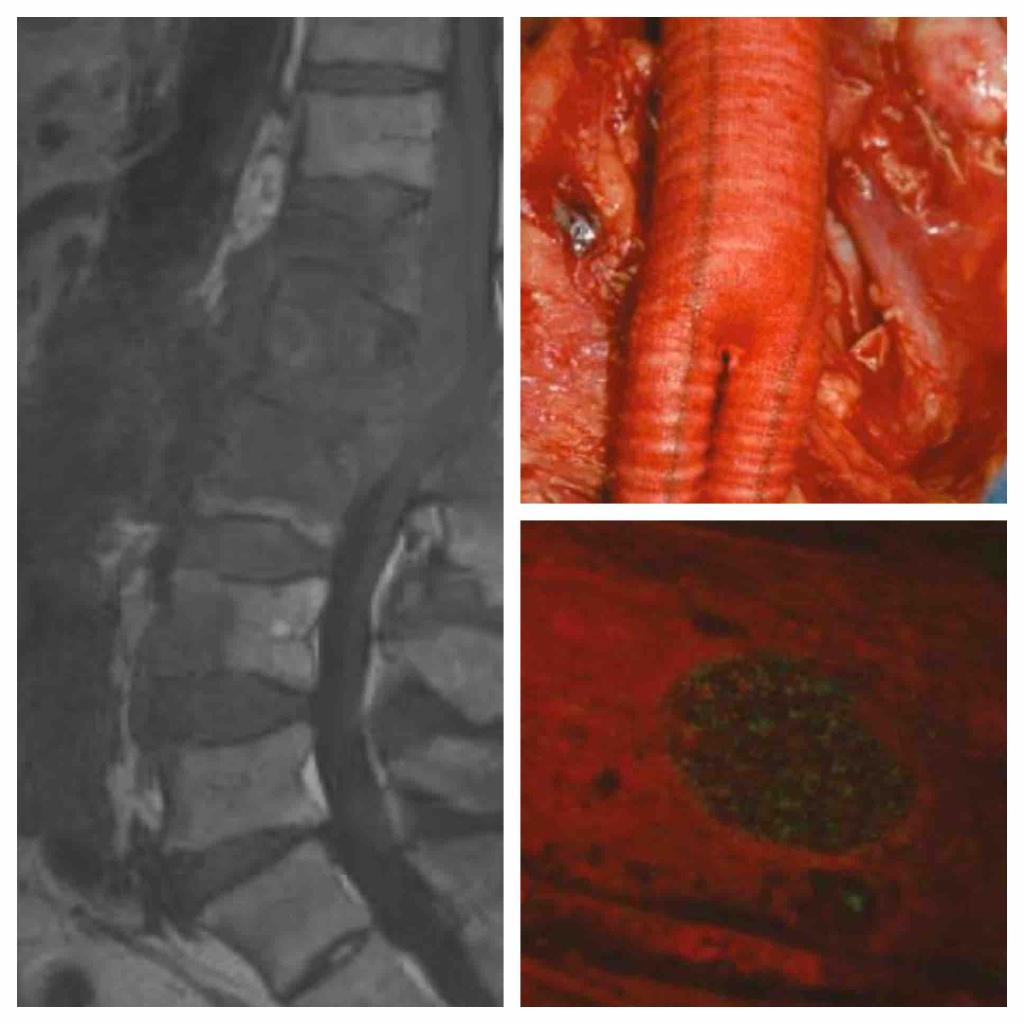
Case diagnosis: Chronic #Coxiella burnetti infection (#QFever): vascular graft, vertebral osteomyelitis, soft tissue abscesses
MCQ answer: choice B
Description reported by @AbinashVirkMD, @DOCElie and colleagues
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
#QFever Facts: Epi
- Coxiella burnetti: fastidious obligate intracellular rickettsia
- zoonotic / cattle, sheep, goats
- Spore-like state: resistant to dessication, extreme temp, chemical disinfection
- Category B terrorism
- Inhalation/airborne/ingestion
#QFever Facts: Clinical
- Acute: asymptomatic vs symptomatic: fever, end-organs: pneumonia, hepatitis, others
- Chronic: endocarditis (60-70% of chronic Q), vascular graft, aneurysm (infrarenal aorta), osteomyelitis
#QFever Facts: Diagnostics
- Serology: biphasic. Phase 1 titers (IgG, IgM) ≥1:800 in chronic inf while phase 2 (IgG, IgM) titers in acute infections
- Histopath: noncaseating doughnut-shaped ring granuloma
- C. burnetii DNA PCR on blood or serum
- Shell vial lung fibroblasts
#QFever Facts: Serology
IgM appears very early, reaching max phase II titers by week 3 and declining to very low levels by week 14
IgG appears very early, reaching max phase II titers by week 8 and REMAINS ELEVATED for > year.
mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/C…
#QFever Facts: Serology
During infection, outer membrane LPS undergoes changes (phase variation)
- In acute Q fever, phase II > phase I titer, often 4-fold
- In chronic Q fever, phase I > phase II titers, often >4-fold (choice B is correct answer)
mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/C…
#QFever Facts: Management
Chronic Q fever
- Surgery, if needed
- Antibiotics: doxycycline PLUS hydroxychloroquine, FQ or RIF
- At least 18-36 months
- Suppress if with prosthesis
- Monitor serologic titers
#QFever #IDDailyPearl
1. Zoonotic, inhalation, ingestion
2. Acute: high phase 2 titer
3. Chronic: high phase 1 titer (1:800 likely endocarditis)
4. Surgery (if needed); doxy plus RIF/FQ/hydroxyQ >18-36m
5. Suppress if needed. Monitor titers during Rx
doi.org/10.1093/ofid/o…