Let's talk about something totally different, for once. I've got a few questions on diastolic strain rate before this really broke loose, so I'm going to do a tweetorial on this, realising the danger of it drowning in corona. These are Una peaks in Antarctica. 

1/ looking at e' diastolic velocities, the earliest onset is in the base, with increasing delay towards the apex. This is the case also for peak e' velocities, and diners from the systolic velocities. However, at the same time, the end of the e' wave is nearly simultaneous 

2/ This is not the case for strain rate. the deformation of e' also starts at the base, with increasing delay towards the apex, but for strain rate both start, peak and end propagates from the base to the apex. 

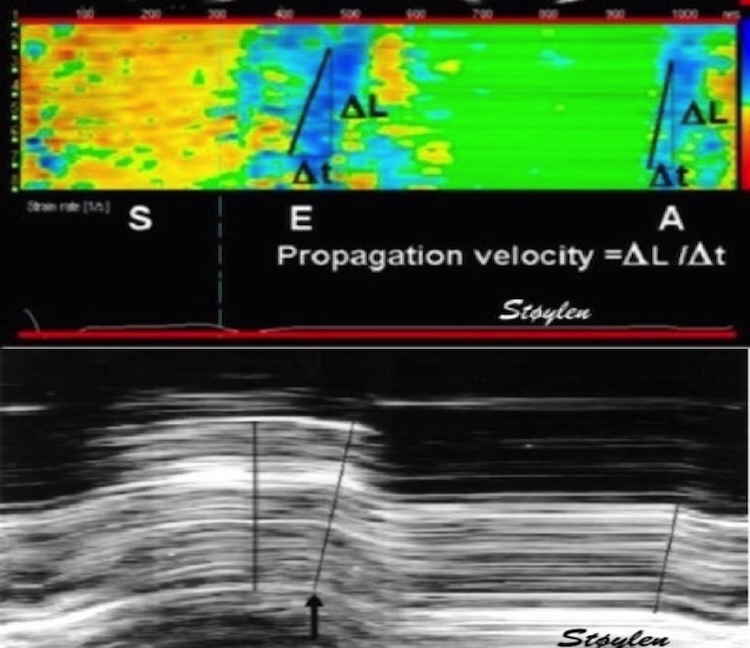
3/ This can be illustrated in colour M-mode. the downwards velocities are blue, the elongation (strain rate) is cyan. The diastolic deformation is a discrete event that propagates from the base to the apex, while the velocities add to each other due to tethering. 

4/ It can be illustrated with this analogy: A row of cars starting up, movement has to start with the first car, and then follow with the cars behind. Colouring the cars acquiring velocity in blue, we see the start of the wave in front, adding one car at a time till all are blue.
5/ Colouring only the cars with DIFFERENT velocity, we show the interval where distance increases, i.e. the row deforms. It shows the difference between deformation and motion, and illustrates that the deformation is a discrete event, propagating in a wave.
6/ It1s just the same with myocardial deformation. The basal motion has to start at the base, and then propagate towards the apex. And as the wall elongates locally, it also thins. And the basal velocity is the sum of the added local deformations 

7/ In reduced diastolic function, this propagation velocity is reduced ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11287889 , and this will lead to a slower velocity addition, resulting in a wider and lower peak e' velocity 

8/ So peak e' and strain rate e propagation velocity are strongly related, and probably measure more or less the same. 

9/ but what about peak diastolic strain rate? Well, as shown this is a measure with different timing in the different levels base to apex 

10/ To get a measure of the peak diastolic train rate for the whole ventricle, it will have to be averaged. It can be shown as seen here, simply with a long ROI covering most of the wall 

11/ But then consider this: As strain rate is the velocity difference / length, and as the apical velocity is close to 0, average strain rate is the inverse of the basal velocity. This is true both for systolic and diastolic strain rate ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32154940 

12/, and thus it is doubtful that peak diastolic strain rate adds any useful information either diagnostically or prognostically over tissue Doppler e', even if studies will show diagnostic and prognostic value, it's the emperor's new clothes. 

Sorry folks, but this is my qualified opinion. Still nice to think about something else, isn't it? Una's peaks was to show the significance of the multiple peaks. Here is another beautiful picture from Illulissat Icefjord in Greenland to rest the eyes on 

Unroll @threadreaderapp
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh