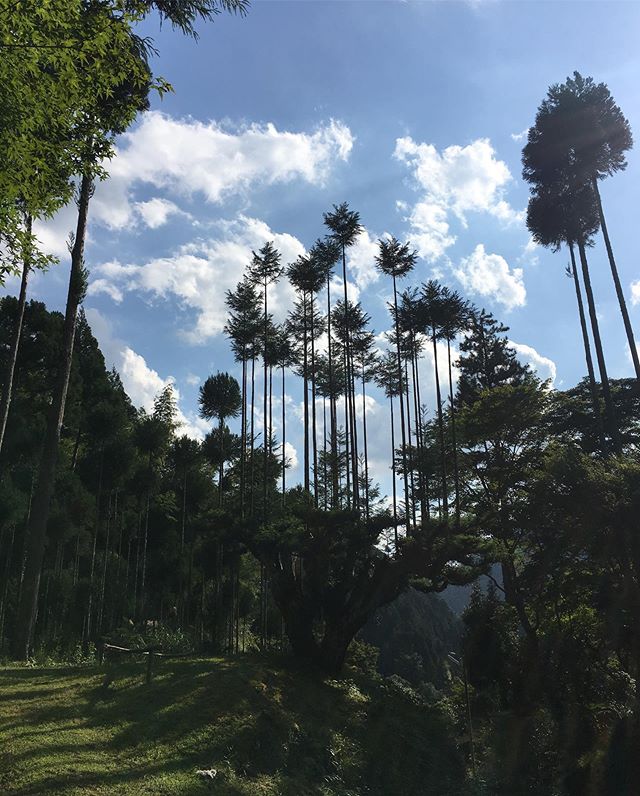
Sustainable forestry: lumber without cutting down trees. Daisugi is a Japanese forestry technique where specially planted cedar trees are pruned heavily (think of it as giant bonsai) to produce "shoots" that become perfectly uniform, straight and completely knot free lumber. 
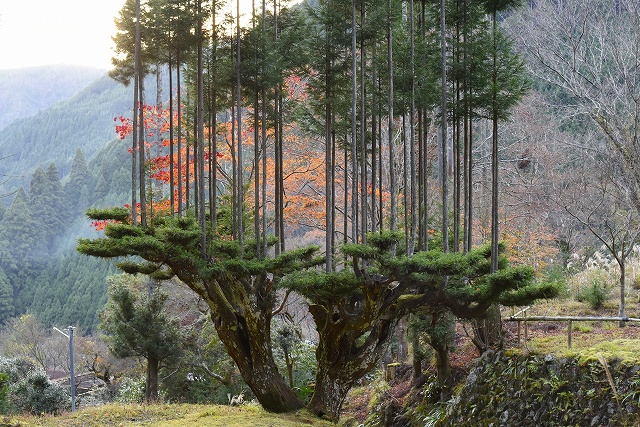

The shoots are carefully and gently pruned by hand every two years leaving only the top boughs, allowing them to grow straight. Harvesting takes 20 years and old "tree stock" can grow up to a hundred shoots at a time. The technique originated in the 14th century. 
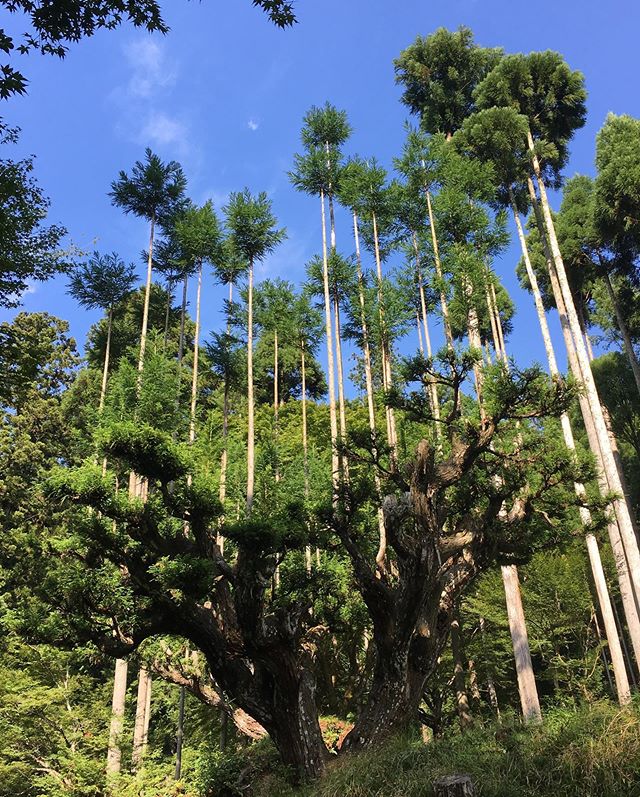
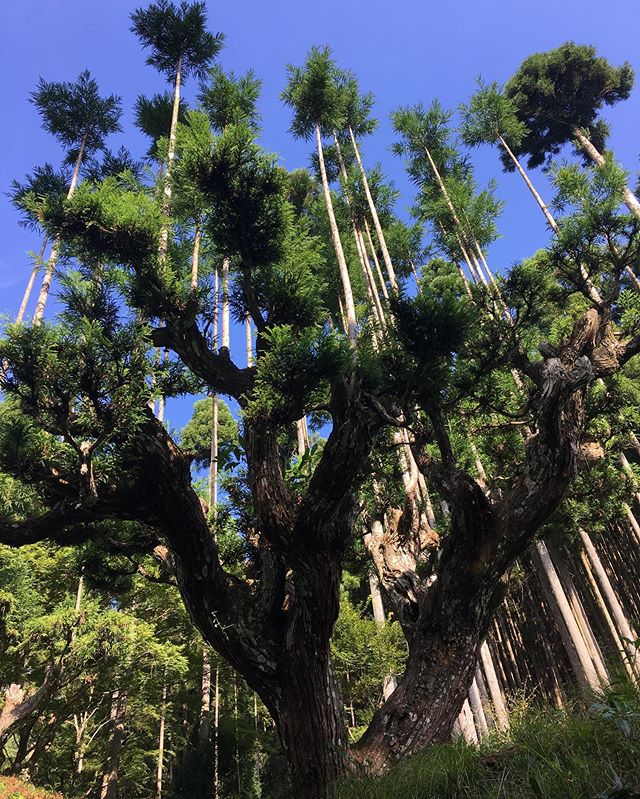





In the 14th c. a form of very straight and stylized sukiya-zukuri architecture was high fashion, but there simply weren't nearly enough raw materials to build these homes for every noble or samurai who wanted one. Hence this clever solution of using bonsai techniques on trees. 
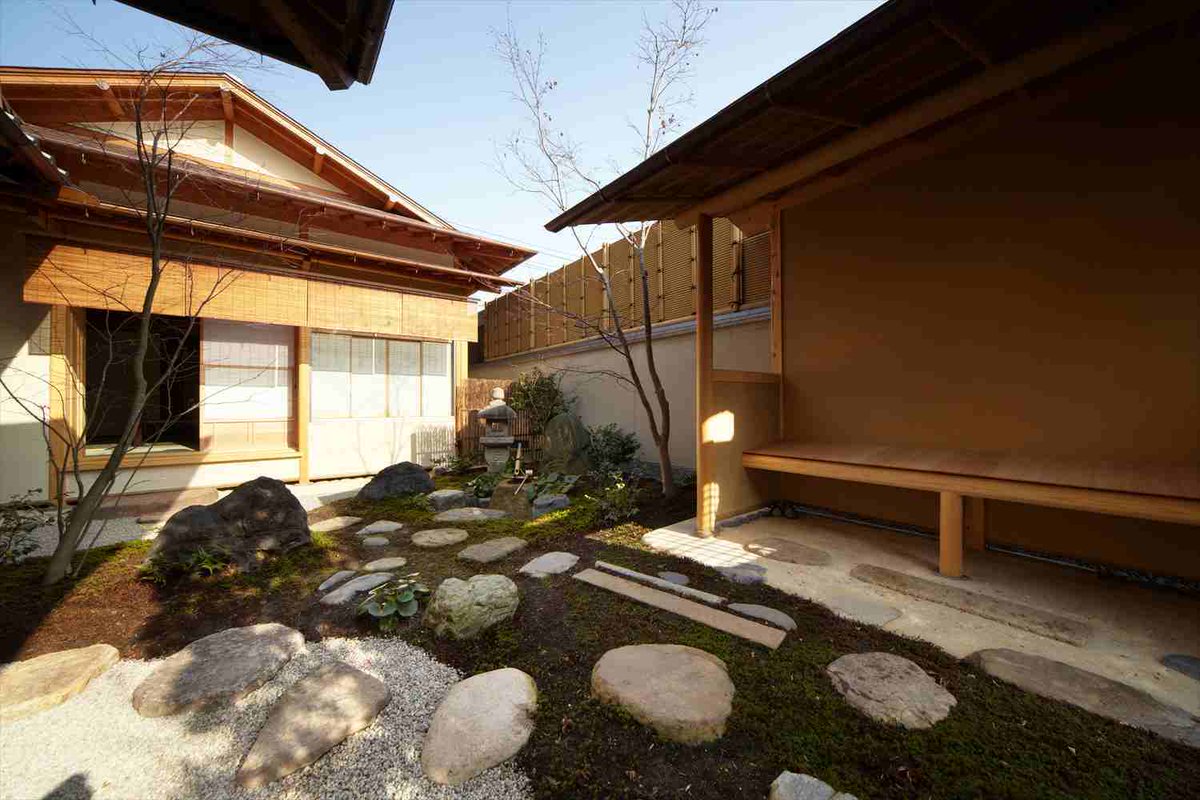

But it wasn't all for show: the lumber produced in this method is 140% as flexible as standard cedar and 200% as dense/strong, in other words it was absolutely perfect for rafters and roof timber where aesthetics called for slender yet typhoon resistant perfectly straight lumber. 





The daisugi looks very peculiar, so even when demand for the lumber dropped off in the 16th century demand for them in ornamental gardens kept the forest wardens busy. 
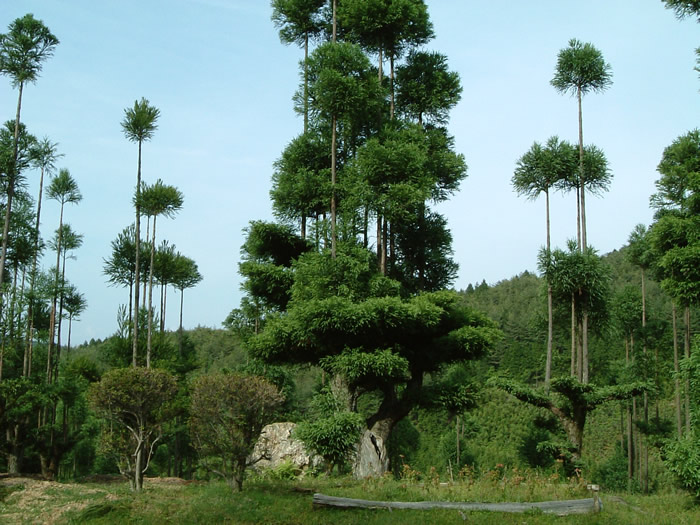
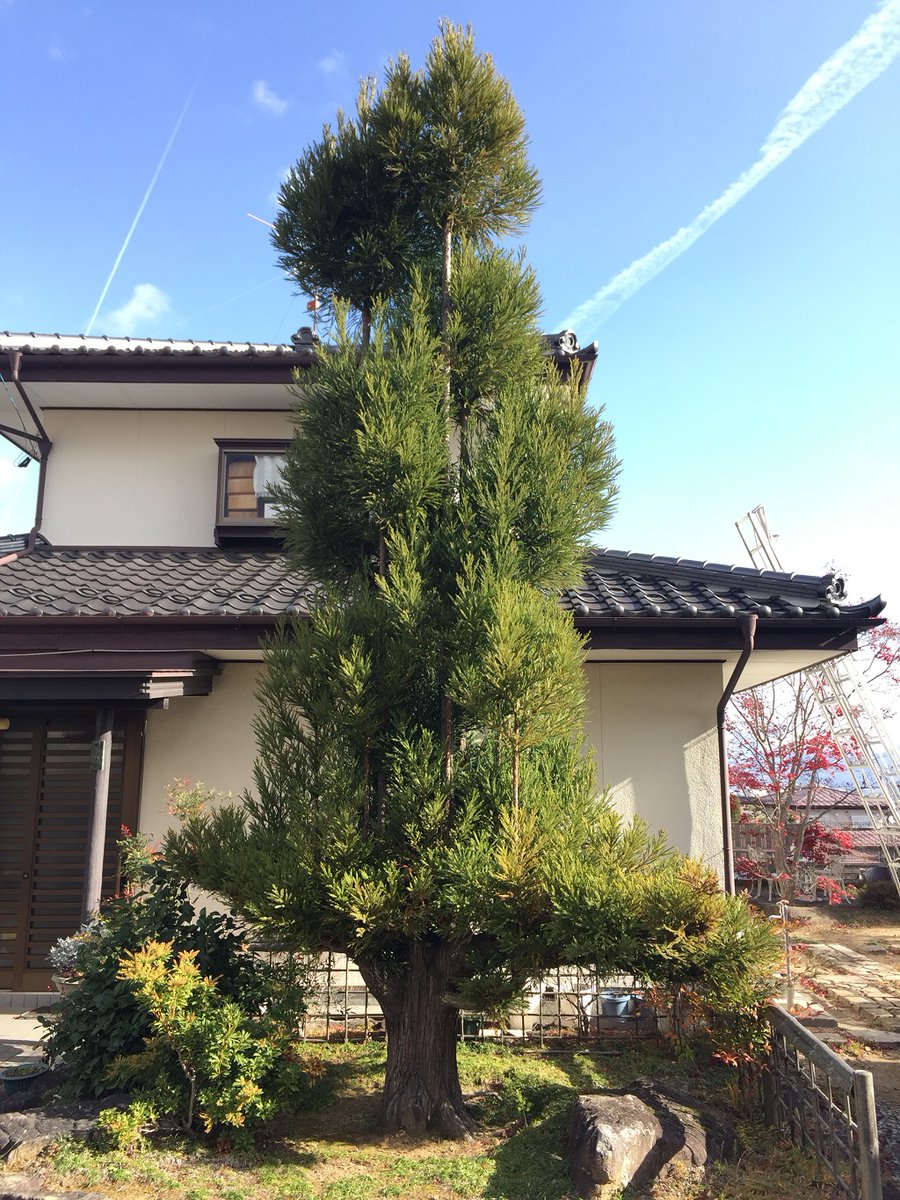





Here and there in the forests around Kyoto you will find abandoned giant daisugi (they only produce lumber for 200-300 years before being worn out), still alive, some with trunk diameters of over 15 meters. Out of this world beautiful. 
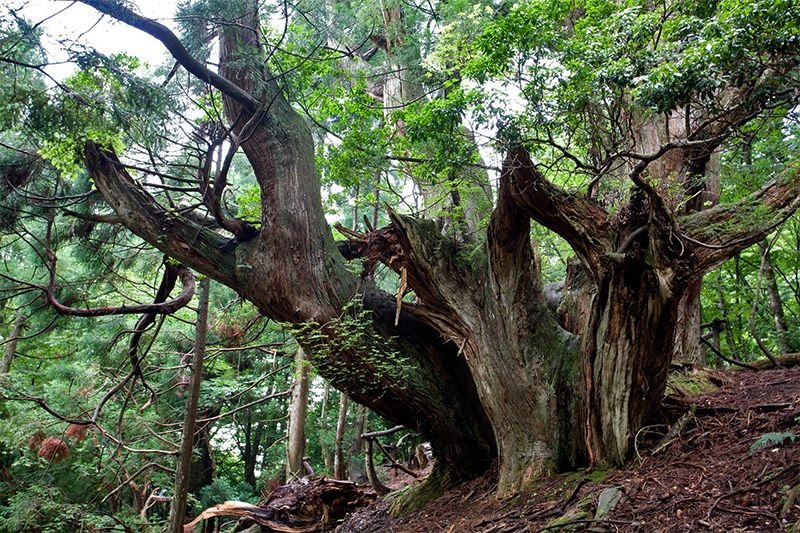

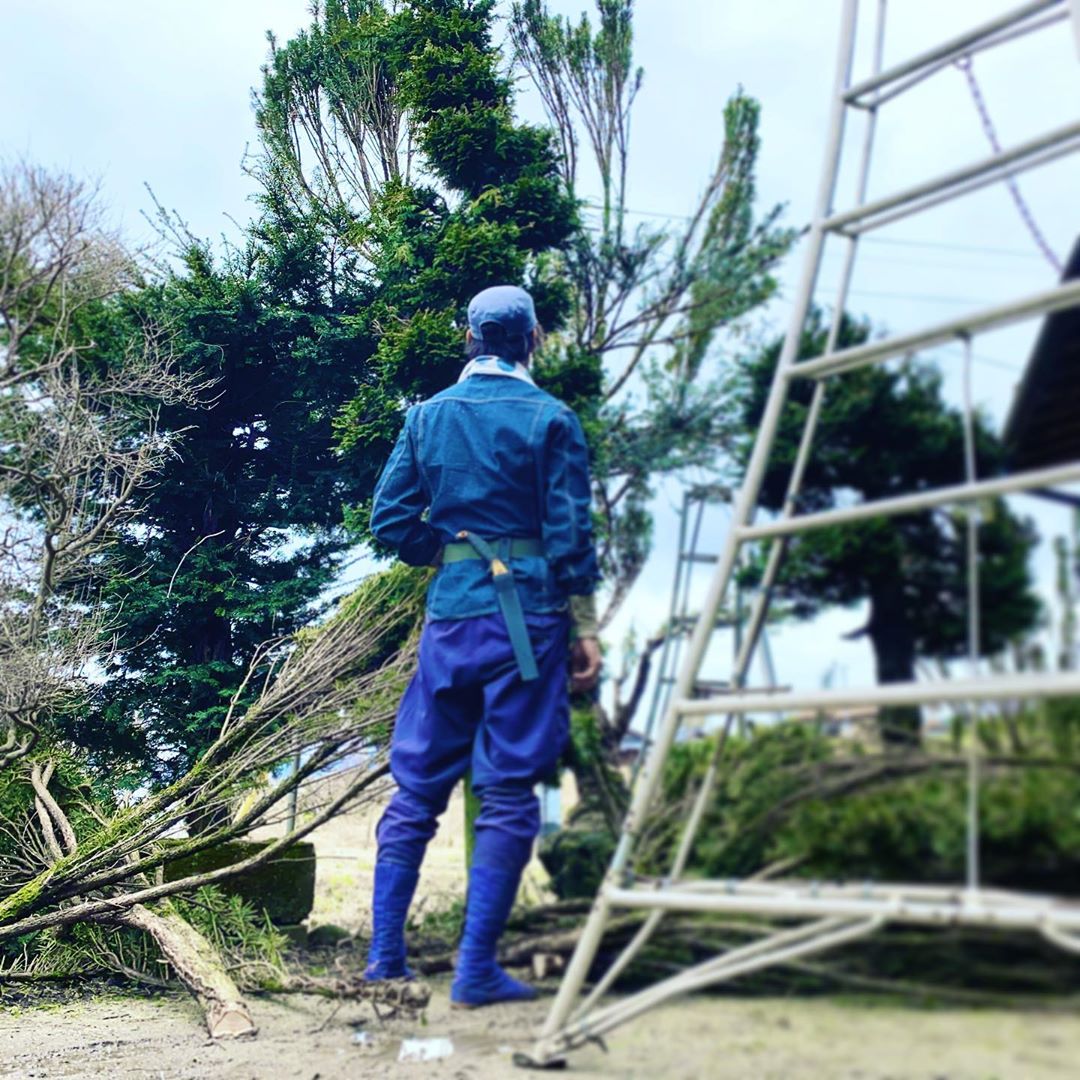
Bonus: why do Japanese arborists (niwashi) and gadeners wear only natural blue dyed cotton? The dye in the cloth comes from a plant that is naturally insect repellant, keeping insects away without chemicals. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh