Tobi Lutke (@tobi) is the CEO of Shopify
He's one of my favorite CLEAR thinkers
I spent some time in lockdown going through his interviews
Here are 6 mental models I got from it
THREAD...
He's one of my favorite CLEAR thinkers
I spent some time in lockdown going through his interviews
Here are 6 mental models I got from it
THREAD...
LUTKE LEARNING 1 - OPERATE ON CROCKERS LAW
Crocker is a Wikipedia editor who asked people to NEVER apologise about editing his pages.
He just wanted them to focus on making his pages BETTER.
He took 100% responsibility for his mental state. If he was offended, it's his fault.
Crocker is a Wikipedia editor who asked people to NEVER apologise about editing his pages.
He just wanted them to focus on making his pages BETTER.
He took 100% responsibility for his mental state. If he was offended, it's his fault.
"Just give me the raw feedback without all the shit sandwich around it." - Tobi
"Feedback is a gift. It clearly is. It’s not meant to hurt. It’s meant to move things forward, to demystify something for you. I want frank feedback from everyone." - Tobi
"Feedback is a gift. It clearly is. It’s not meant to hurt. It’s meant to move things forward, to demystify something for you. I want frank feedback from everyone." - Tobi
"If I'm insulted it's because my brain made a decision, to implant in my memory and thoughts the idea of being insulted by that person...
I did that under my own volition. It was my own choice. My brain has assigned the power to the other person" - Tobi referencing Aurelius
I did that under my own volition. It was my own choice. My brain has assigned the power to the other person" - Tobi referencing Aurelius
LUTKE LEARNING 2 - ALWAYS BE A STUDENT TO FIRST PRINCIPLES
Tobi's most consistent used mental model throughout his interviews is:
Global Maximum > Local Maximum
Local Maximum = Optimising a cog in the machine
Global Maximum = Optimising the machine itself
Tobi's most consistent used mental model throughout his interviews is:
Global Maximum > Local Maximum
Local Maximum = Optimising a cog in the machine
Global Maximum = Optimising the machine itself
Tobi's favorite example of FIRST PRINCIPLES is a Truck driver.
His truck was sat still for 8 HOURS on THANKSGIVING waiting for his cargo to be unloaded when he realized...
"Why not take the WHOLE trailer off the back of my ship rather than unloading + reloading each item?"
His truck was sat still for 8 HOURS on THANKSGIVING waiting for his cargo to be unloaded when he realized...
"Why not take the WHOLE trailer off the back of my ship rather than unloading + reloading each item?"
This Truck driver was called Malcolm McLean
His first principles approach created the SHIPPING CONTAINER
The results?
Global shipping costs went from $6 a tonne to $0.16 a tonne 🤯
The most underrated entrepreneur of the last century AND the godfather of modern global trade.
His first principles approach created the SHIPPING CONTAINER
The results?
Global shipping costs went from $6 a tonne to $0.16 a tonne 🤯
The most underrated entrepreneur of the last century AND the godfather of modern global trade.

Tobi seems to try to operate under the assumption that everything he is doing could be WRONG.
"I think the best company (that exists right now) is a 6/10 on the scale to what is a perfect company" - Tobi
His goal is to get near a 6/10 and push towards a 7/10.
"I think the best company (that exists right now) is a 6/10 on the scale to what is a perfect company" - Tobi
His goal is to get near a 6/10 and push towards a 7/10.
Humanity's most consistent fallacy is assuming the present moment has it figured out.
We look back and laugh at our assumptions from 50 years ago.
Whilst simultaneously forgetting that 50 years from now they be will be laughing at us.
We look back and laugh at our assumptions from 50 years ago.
Whilst simultaneously forgetting that 50 years from now they be will be laughing at us.
LUTKE LESSON 3 - THINK ABOUT THE LONG TERM
The media narrative is often a dichotomy of Shopify vs Amazon.
Few talk about the similarity both CEO's have for LONG TERM thinking.
Both consistently warn shareholders that they will sacrifice short term revenue for long term value.
The media narrative is often a dichotomy of Shopify vs Amazon.
Few talk about the similarity both CEO's have for LONG TERM thinking.
Both consistently warn shareholders that they will sacrifice short term revenue for long term value.
Tobi states that almost EVERY DECISION your business makes can pivot on JUST one question:
"Are you optimizing for every individual transaction or the LIFETIME transaction?" - Tobi
Are you playing INFINITE games or FINITE games with your customers?
"Are you optimizing for every individual transaction or the LIFETIME transaction?" - Tobi
Are you playing INFINITE games or FINITE games with your customers?
Growth Marketers would tell Shopify to force "Powered By Shopify" branding on their Merchants stores.
Everyone who then visits the stores would then know Shopify builds stores like these.
This is the sort of "Growth Loop" that VC's dream of.
Shopify DIDN'T DO this.
Everyone who then visits the stores would then know Shopify builds stores like these.
This is the sort of "Growth Loop" that VC's dream of.
Shopify DIDN'T DO this.
“We want to make other people look good. We want to make merchants look good." - Tobi (2017 AMA)
Lutke calls this "LTV thinking" in his interview with @garyvee
On a long enough timeline, playing positive-sum games with your customers is the ultimate growth hack.
Lutke calls this "LTV thinking" in his interview with @garyvee
On a long enough timeline, playing positive-sum games with your customers is the ultimate growth hack.
It's hard to find a more positive-sum company.
There are few (legal) highs that compete with the "1st Shopify Sale Moment".
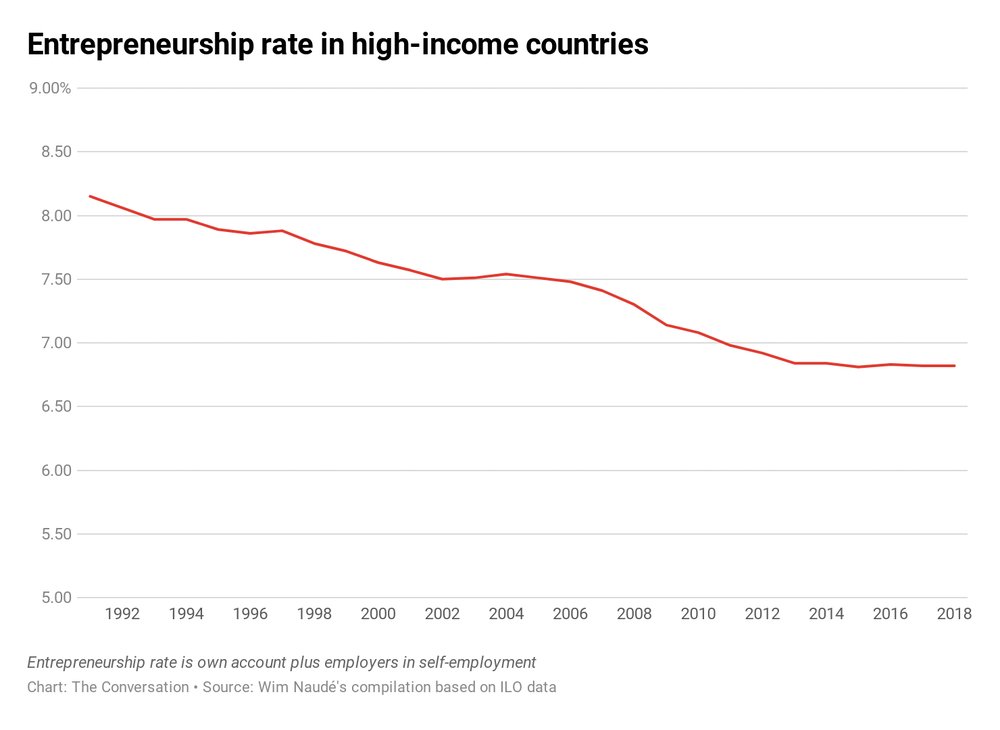
Every 60 SECONDS somebody makes their 1st sale on Shopify 🤯
They are trying to help reverse this graph by reducing the friction of entrepreneurship
There are few (legal) highs that compete with the "1st Shopify Sale Moment".
Every 60 SECONDS somebody makes their 1st sale on Shopify 🤯
They are trying to help reverse this graph by reducing the friction of entrepreneurship
LUTKE LEARNING 4 - EMBRACE TRANSFER LEARNING
"Video games are very distilled environments in which you can learn things." - Tobi
He believes that playing certain games can help your brain rehearse thousand of repetitions for situations that are scarce in the real world.
"Video games are very distilled environments in which you can learn things." - Tobi
He believes that playing certain games can help your brain rehearse thousand of repetitions for situations that are scarce in the real world.
In the business world, you might make a strategic bet every year.
It may take you 10 years to get the experience of strategic 10 bets.
In the poker world, you make a strategic bet every hand.
It takes you less than one evening to get the experience of 10 strategic bets.
It may take you 10 years to get the experience of strategic 10 bets.
In the poker world, you make a strategic bet every hand.
It takes you less than one evening to get the experience of 10 strategic bets.
"I'm a card-carrying member of the video games are really good club" - Tobi
"Every employee at Shopify can expense Factorio" - Tobi on one of his favorite games
^^^ He sees the mental effects of playing Factorio as a worthwhile business expense for his company
"Every employee at Shopify can expense Factorio" - Tobi on one of his favorite games
^^^ He sees the mental effects of playing Factorio as a worthwhile business expense for his company
LUTKE LEARNING 5 - DECISION MAKING
"Every single time I got a decision wrong, I realised that the piece of information that was missing was actually in fact totally available to me." - Tobi
“We tend to underestimate how difficult it was to make a decision in hindsight” - Tobi
"Every single time I got a decision wrong, I realised that the piece of information that was missing was actually in fact totally available to me." - Tobi
“We tend to underestimate how difficult it was to make a decision in hindsight” - Tobi
"If your job is to make decisions, it’s worth treating it like any other subject to get better at." - Tobi
Whenever he makes a decision, he keeps a small log file with one paragraph explaining what information he used to make that decision.
He reviews it every 6 months
Whenever he makes a decision, he keeps a small log file with one paragraph explaining what information he used to make that decision.
He reviews it every 6 months
Kasparov had a "SYSTEMS MINDSET" for analyzing his chess mistakes, e.g. Pawn to E4 lost the game
Outcome mindset = "Don't do Pawn to E4 again".
Systems mindset = "What was the mental routines that occurred before I made that decision? Don't do them again"
Outcome mindset = "Don't do Pawn to E4 again".
Systems mindset = "What was the mental routines that occurred before I made that decision? Don't do them again"
OUTCOME MINDSET prevents you from making that ONE mistake again.
SYSTEMS MINDSET prevents you from using the mental models that caused that mistake.
SYTEMS MINDSET prevents that one mistake AND 100's of other potential mistakes by addressing the root cause.
H/T @SafiBahcall
SYSTEMS MINDSET prevents you from using the mental models that caused that mistake.
SYTEMS MINDSET prevents that one mistake AND 100's of other potential mistakes by addressing the root cause.
H/T @SafiBahcall
LUTKE LEARNING 6 - TALENT STACK LED BY CURIOSITY > MBA
He didn't have an MBA. He didn't grind 100-hour workweeks.
Instead, he played video games (which led to coding) and he snowboarded (which led to an online snowboarding store).
This 'Talent Stack' led to Shopify.
He didn't have an MBA. He didn't grind 100-hour workweeks.
Instead, he played video games (which led to coding) and he snowboarded (which led to an online snowboarding store).
This 'Talent Stack' led to Shopify.
"Following your genuine intellectual curiosity is a better foundation for a career than following whatever is making money right now." - @naval
Pursuing your unique talent stack and curiosity is often inversely correlated with appearing successful early on.
Stop caring.
Pursuing your unique talent stack and curiosity is often inversely correlated with appearing successful early on.
Stop caring.
TOBI'S FAVOURITE BOOKS:
- 'Courage To Be Disliked' by Kishimi
- 'High Output Management' by Grove
- 'The Box' by Levinson
- 'Thinking In Systems' by Meadows
- 'Meditations' by Aurelius
- 'Guide To The Good Life' by Irvine
(Don't forget Factorio and Starcraft!)
- 'Courage To Be Disliked' by Kishimi
- 'High Output Management' by Grove
- 'The Box' by Levinson
- 'Thinking In Systems' by Meadows
- 'Meditations' by Aurelius
- 'Guide To The Good Life' by Irvine
(Don't forget Factorio and Starcraft!)
I occasionally send out a newsletter of new ideas I'm exploring.
100% high signal. 0% spam.
Check it out - bit.ly/MentalModelsBD
100% high signal. 0% spam.
Check it out - bit.ly/MentalModelsBD
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh