It was some of the best writing I've read in my life. I encourage you to go read it.
For those who don't read it, I took detailed notes which you can find below 👇
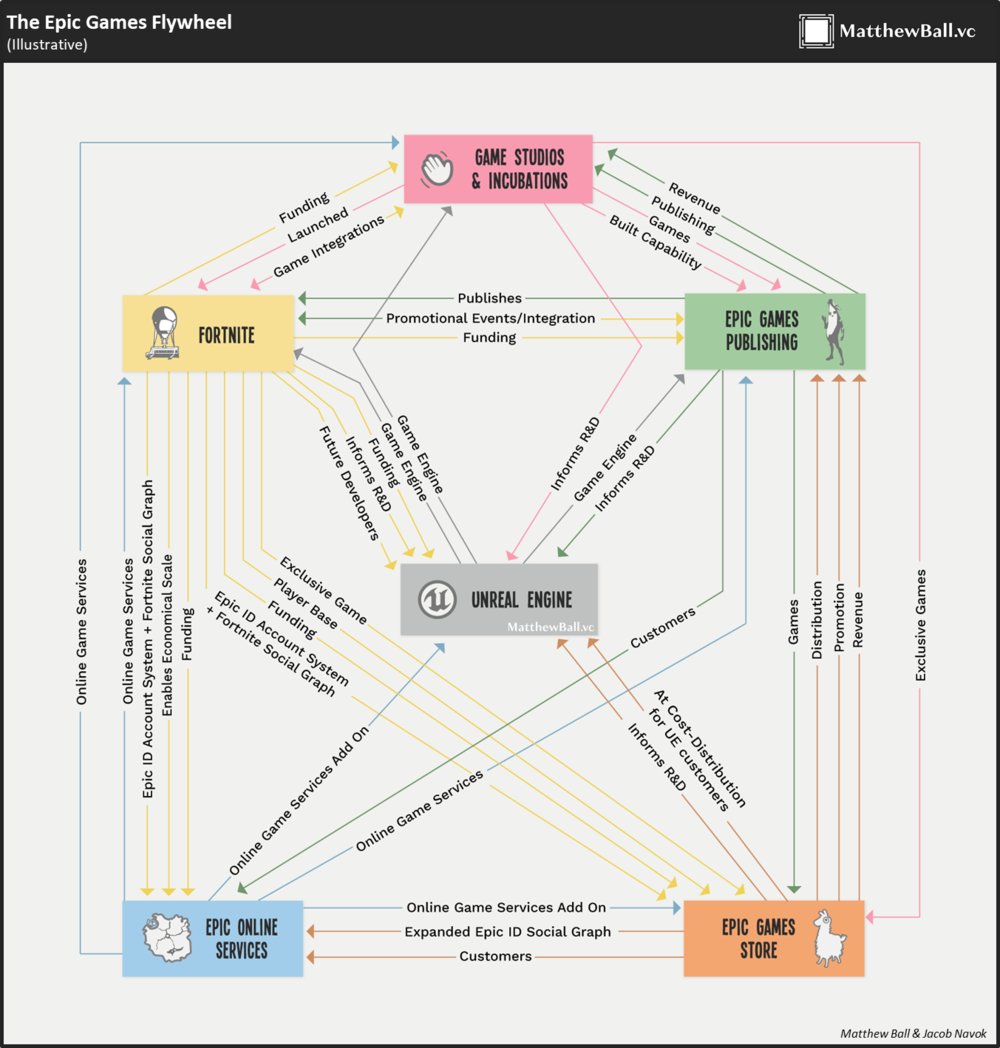
The thesis of Essay 1: Epic Game's Unreal Engine, their proprietary game engine, is the driver of most, if not all, the decisions the company makes
matthewball.vc/all/epicprimer1
• Epic Games was founded in 1991
• Tim Sweeney, founder, is the majority shareholder while Tencent owns 40%
• 2018 valuation was $15B
• Epic has the potential to be one of the most influential tech companies in the world.
• Epic is the creator of Fortnite: Battle Royale, one of the most popular video games in the world.
• Epic's core business is really the Unreal Engine
• The success of Fortnite has allowed Epic to scale its business into new areas
• Epic Games Store (EGS), Epic Online Services (EOS) and Epic Games Publishing (EGP)
• Additionally, it purchased Houseparty in 2019 which is now part of EOS
• Epic is one of the largest and fastest-growing social networks with 350MM+ users and 2.3B social connections
• Epic's growth has forced revolutionary changes to the video game industry and Hollywood
• A game engine is the backbone of a video game and increasingly, other digital simulations
• Most game makers use one to build and operate games
• Disney and Marvel don't build their cameras or editing software, they outsource it. Same idea.
• This approach allows content and production companies to focus on the creative process
• Unreal Engine is a suite of tools and tech that allows third parties to produce virtual experiences
• Developer can focus on the creative process
• The better the game engine the easier it is for people to make games and thus less expensive
• Game engines are extremely complex and it's more expensive than ever for companies to make their own
• Thus they are more reliant on outsourcing
• Major engines are Unreal and Unity
• Amazon and Valve also offer game engines but aren't widely used
• Unreal is harder to use than Unity, but technically superior
• Unity is primarily used for mobile while Unreal is used for console/PCs especially multiplayer games
• Unity is subscription-based while Unreal is a rev share model
• Unity also operates an ad network for game publishers
• Major publishers like Take-Two use their own engine
• Major publishers use their own engines to avoid paying rev share fees and because their engineering team is large enough to support it
• Games like Call of Duty and GTA are built on proprietary game engines
• "Publisher engines" are typically built for a specific game or genre
• Some companies also don't use Unreal because it lacks a feature
• Usage of third-party engines has grown considerably in the past 15 years
• Most newly formed game studios are using Unreal or Unity
• Nearly impossible to build one from scratch and build a new game
• Riot Games, maker of League of Legends, chose to use Unreal
• Riot Games is also owned by Tencent
• However, Riot Games is nearly 15 years old and is a signal to the rest of the industry
• Game development is complex, multiple platforms and need to support cross-platform play
• Using Unreal eliminates worries if a game will continue to work on different platforms
• Unreal is benefiting from network effects
• The more developers use Unreal, the more data it has to make better decisions and investments
• The more developers use Unreal, the more data it has to make better decisions and investments
• It's expanding beyond gaming
• The Mandalorian and Lion King were filmed using Unreal
• Music, architecture, urban planning are all industries that are using Unreal
• Unreal is now part of the learning curriculum for schools and the military
• Network effects will take place where it'll be easier for virtual goods to transfer across digital worlds
• Eg, an outfit bought in one games go to another
• 3 tiers: Unreal, TwinMotion, and Fortnite Creative Mode
• Unreal is for complex games
• TwinMotion is for professional applications such as auto design
• Creative Mode is for anyone even kids
• Epic wants everyone to one day be able to create amazing games regardless of technical skills
• No-code platforms are increasingly popular like Roblox
• No-code platforms aren't viable competitors to Unreal yet
• Game engines influence game developers
• The decisions that Epic makes can have ramifications across the industry
• For example, if Unreal decides to invest in VR, more developers will make VR games and more people will buy them
• Game engines can also accelerate other businesses
• For example, Unity built an ad network to support game developers
• It's hard for game developers to switch engines. High switching costs.
• Many future games plan to use Unreal and many developers are trained on it
• People are reluctant to switch
• Amazon's game engine is free and developers still aren't adopting it
The thesis of Part II: Epic Games Store is to shift value creation to game developers and eliminate market share from Steam
matthewball.vc/all/epicprimer2
• Today, more than 50% of game sales occur digitally
• Mobile and console games are bought through the proprietary stores of the platform
• Typically 30% fee
• PC is different. So many different types of hardware.
• Tons of problems with downloading PC game so in 2003 Valve launched a store called Steam
• Ease to use, social features and easy to find new games
• Best of all, games would automatically be patched
• Steamworks was Valve's online services
• It used Steam account system to act as a social network to connect with other players
• Services were free to consumer and publisher
• Even offered to games not sold on Steam because the user would still be required to make an account
• More customers and data for Steam to analyze
• 30% fee, but it was different than other platform stores like Apple App Store b/c you could buy the game from other stores
• No one can launch a competing online store on console or mobile
• In 2015, Steam was generating $2B in profit per year
• Other companies tried to launch stores and failed (Eg, EA Origin)
• Steam had 75% market share by the time competition arrived
• Steamwork had significant network effects that made it difficult to get players to leave the service
• New platform meant new friends list
• Publishers were frustrated at 30% fee
• Valve didn't sell hardware or create an OS like Apple and Sony
• What justified their high fee?
• Players and publishers are beginning to shift away from Steam
• Tim Sweeney was a huge critic of the 30% fee for all stores
• Charging too much $$$ and taking revenue away from game developers
• Epic decides to launch its own store
• Epic could piggyback off of Fortnite which was installed on millions of devices
• EGS only charged 12% commission
• If your game was developed using Unreal the fee was 7%
• Low fees are critical to the health of the ecosystem
• Epic began offering exclusive distribution deals to publishers
• EGS lacked many core features like a shopping cart (intentional decision)
• Most PC gamers were happy with Steam
• Consumers thought lower fees would lead to lower prices, but an MFN clause from Steam prevented this
• Attempted to launch on Android, but failed
• EGS's goal was to steal market share from Steam or have Valve drop its rate
• Epic was willing to end its EGS store if Valve changed the fee structure of Steam
• EGS would be valuable to Epic because of consumer data and increased user base
• EGS's would increase Epic's influence across the ecosystem
• EGS would make the best game developers its customers as well as users who didn't play Epic games
• Lastly, this would all be part of Tim Sweeney's grand plan of interoperability and creating the Metaverse