In this thread, I will attempt to answer some of the Frequently Asked Questions.
Thread.
A. Stamp duty is a tax on instruments (mostly written documents). It is based on the Stamp Duties Act, CAP S8 LFN 2004 as amended. But in substance, not much has changed from the original law, the Ordinance 41 of 1939.
A. Stamp duties may be levied at a fixed or ad valorem rate depending on the instrument. Fixed means the same amount regardless of size of transaction while ad valorem means an amount that is based on the value of the transaction.
A. Stamp Duties is on the Exclusive Legislative List of the Nigerian Constitution. However, item 7 on the Concurrent List allows the National Assembly to delegate the collection/administration to the govt or other authority of a state...
A. FIRS except for instruments between individuals in which case it is the tax authority of the relevant state. The Finance Act 2019 states that only FIRS and tax authorities of states are the competent authorities.
A. All instruments listed in the Act except those stated as exempt. Based on the Finance Act 2019, electronic instruments are liable to stamp duty. In the case of money transfer, the N50 stamp duty is only applicable on N10k & above.
A. S.5(1) of the SDA states that “All duties ... chargeable ... upon any instruments shall be paid and denoted ..., except where express provision is made to the contrary in this Act or by regulations ..., are to be denoted by impressed stamps only.”
A. In line with S.163 of the Constitution, stamp duties collected by a state belongs to the state while the net proceed from stamp duties collected by the FG is distributed among the States on the basis of stamp duty derivation.
A. Where adhesive stamp is used, it should be cancelled by the person who first executed the document. Failure to cancel or an attempt to re-use is punishable on conviction.
A. Generally, a document that is first executed in Nigeria should be stamped on or before the first execution and in any case within 30 (for ad-valorem duties) or 40 days (for fixed duties) from date of execution.
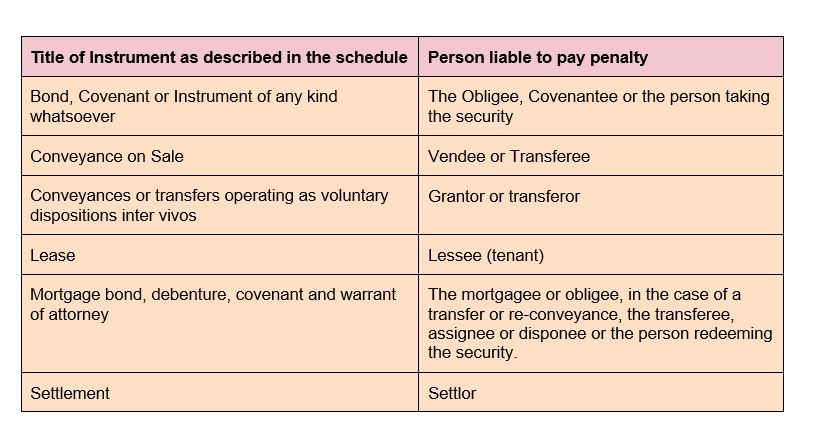
A. There are financial penalties (on conviction) under the SDA. The FIRS may choose to apply penalties under the FIRS Establishment Act which can be as high as 10% penalty plus interest at CBN MPR and imprisonment of up to 3 years...
A. The National Assembly @nassnigeria or the State Houses of Assembly may increase, reduce, add new duties or repeal chargeable duty (as it relates to matters within their legislative competence) by resolution...