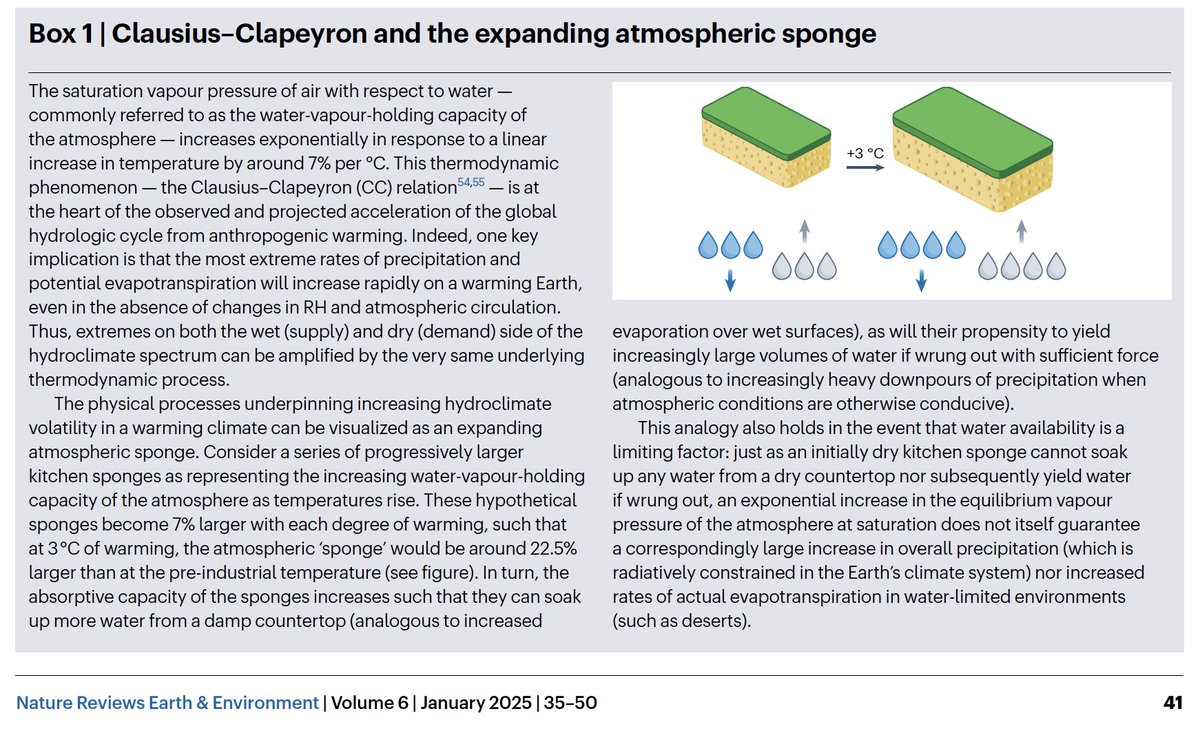
Absolutely incredible footage of #LoyaltonFire #pyrovortex ("Fire Tornado") earlier today. Pretty sure this validates @NWSReno's Tornado Warning--which is, I believe, the first ever issued by @NWS specifically for a wildfire-generated pyroconvective event. #CAwx #CAfire #NVwx
https://twitter.com/That1GirlTasha/status/1294790322749190144
To be clear: this is *not* first documented instance of a large-scale fire vortex. Devastating #CarrFire in 2018 near Redding, CA produced one of the strongest such events in recent memory, outside of a couple of previous events during Australian firestorms. (1/3) #CAwx #CAfire
Such events are not a new phenomenon--they have probably occurred during particularly intense wildfires under the right atmospheric conditions since...well, time immemorial. But I suspect these recent events have been more noticeable for two key reasons: (2/3) #CAfire
1) We're formally documenting more large-scale fire vortices in smartphone camera era simply because there are more eyewitnesses, & 2) wildfire burning conditions across West have been particularly intense in recent years, increasing likelihood of extreme/exotic fire behavior.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh