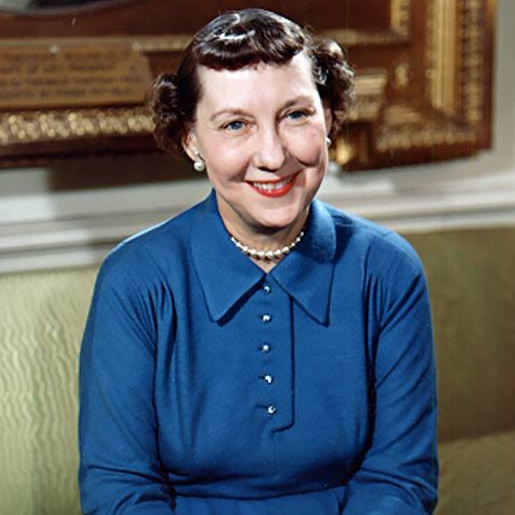
This month marks the 100th anniversary of the ratification of the #19thAmendment, which gave American women voting rights. Florence Kling Harding was the first “first lady” who could vote for her husband in a presidential election. 1/5
Image Credit: @OhioHistory
Image Credit: @OhioHistory
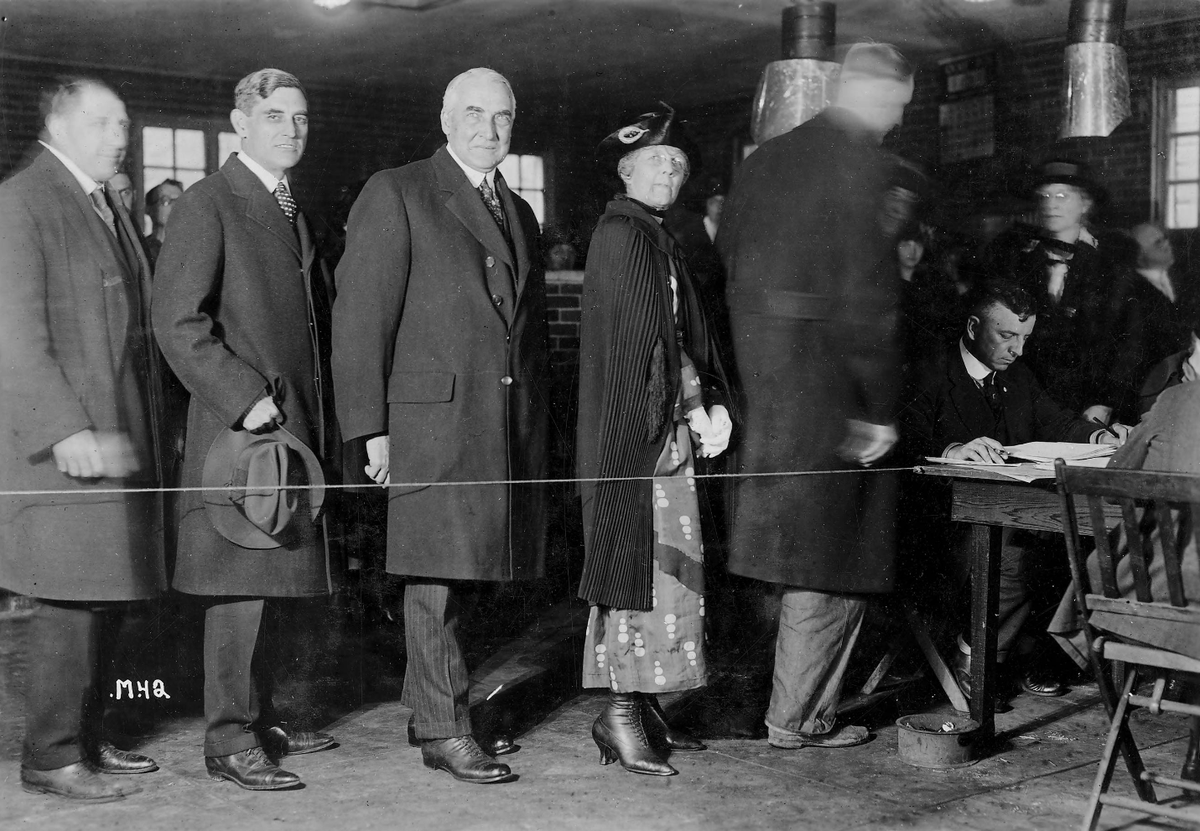
Mrs. Harding was a highly-involved in politics and campaigned alongside her husband during the 1920 election. Harding once told a crowd: “I owe allegiance to only one boss—and she sits right over there in that box. She’s a mighty good one too.” 2/5
As first lady, she skillfully shaped her public persona, opening the White House to the public, cultivating relationships with women’s groups and veterans, and navigating her husband’s scandal-ridden administration. 3/5
Image Credit: Library of Congress
Image Credit: Library of Congress

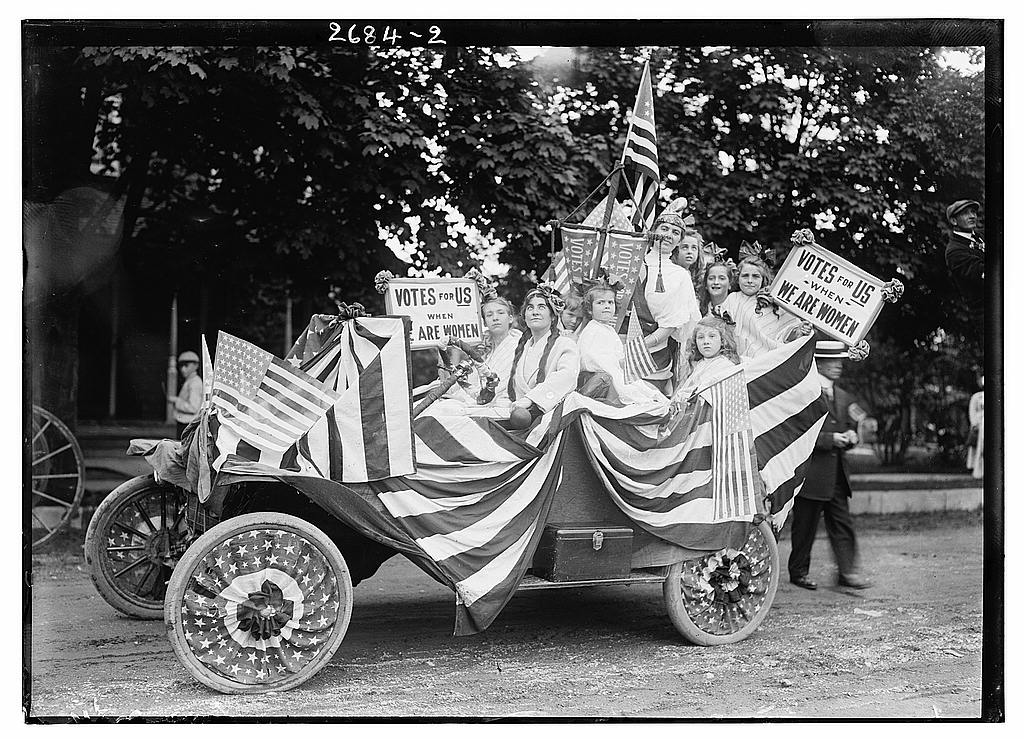
In many ways, Mrs. Harding’s political activism and personal drive reflect the larger women’s movement that finally attained the vote in 1920. 4/5
Image Credit: Library of Congress
Image Credit: Library of Congress

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





















