American people are still not allowed to know that Russia saved their nation from the British Empire during 1861-1865 US Civil War. British mainstream “fake news” propaganda media shown below slams alliance of President Abraham Lincoln and Tsar Nicolas II. #TrumpPutinSummit 

In 1901, Tsar Nicolas II & President McKinley agreed to destroy the British Empire forever by building the largest rail system that would cross the Bering Strait joining Russia with North America, and continue down through Mexico, Central America to the very tip of South America 
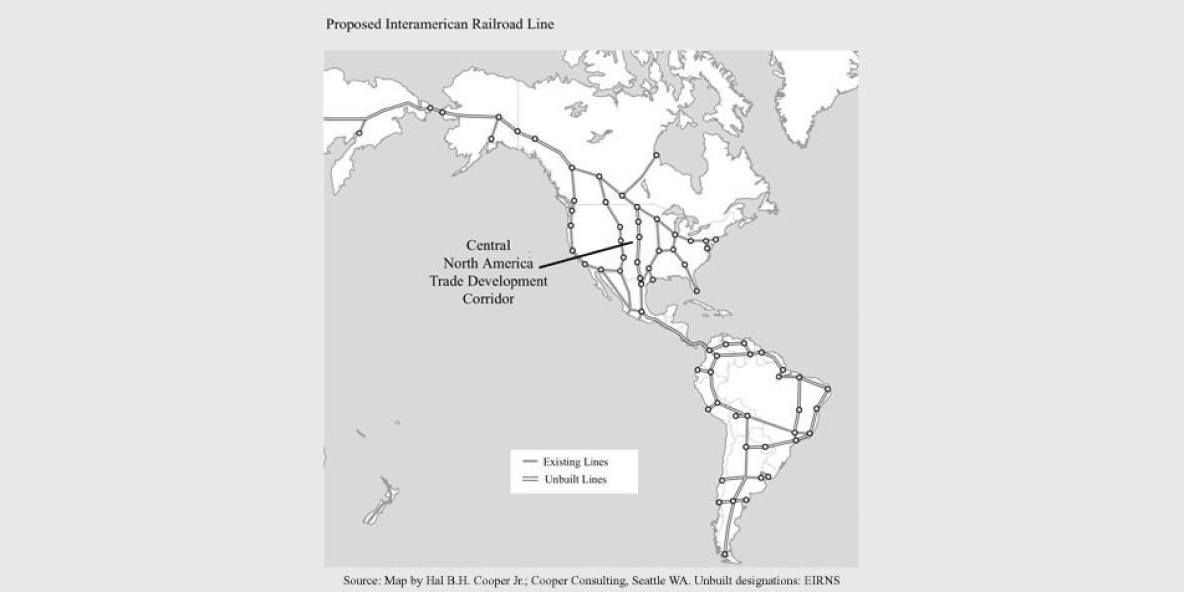
By 2011, knowing the days of British control over the US would soon be ending, Putin signed a $65 billion measure to begin construction of the Interamerican Railroad Line to connect Siberia with Alaska via a tunnel to bridge system under the Bering Strait. inhabitat.com/russia-green-l…
Presidents Lincoln and McKinley, along with Tsar Alexander II and Tsar Nicolas II, signed their own death warrants for daring to join the US and Russia together to break the "forever wars" British and European stranglehold on the world. All were assassinated. 

The Alaska Purchase was one of the most important things in World History for diplomacy because the Bering Strait was to link the world. Alaska was never developed and linked up as it should be. Full history lecture by Rising Tide Foundation
The Record of News, History and Literature, Volume 1 (July 16, 1863) states, "A Russian fleet, consisting of the Osliaba, the Alexander Nevske of 51 guns, and the Peresviet of 46 guns, has made its appearance in the harbor of New York." 

"These vessels are to be reinforced by four or five others in a few days. Great festivities have taken place between the officers and the leader of New York society." Shown below: cover of Harper's Weekly, New York, November 21, 1863. 

"Mrs. Lincoln has been received on board the flag ship with a national salute, and the fleet was the talk of the town. What political significance this unusual visit of Russian men of war to a Yankee port may have, has not been given out." 

The international strategic dimension of the 1861-1865 American Civil War was an aspect that repeatedly threatened to thrust itself into the center of the war, transforming the entire nature of the conflict and indeed threatening to overturn the entire existing world system.
In 1865, the United States was friendly to Russia and Prussia, and resentful and suspicious in regard to Britain and France, whose governments had sympathized with and supported the Confederacy.
Historian Allan Nevins dramatically evoked the immense worldwide significance of Civil War diplomacy in “War for the Union” (1960). Nevins, horrified by the idea of US war with Britain, wrote: "The future of the world as we know it was at stake." 

"Anglo-French intervention in the American conflict would probably have confirmed the splitting & consequent weakening of US; might have given French power in Mexico a long lease, with the ruin of the Monroe Doctrine; & would perhaps have led to the Northern conquest of Canada." 

Between 1848-1863, the British Empire was at the aggressive height of its world power, had launched attacks on China, India, and Russia, and in the 1860s was backing Napoleon III’s adventure in Mexico and Spain’s in Santo Domingo, both direct challenges to the US Monroe Doctrine.
In contrast to Lincoln, Confederate President Jefferson Davis took almost no interest in diplomatic affairs. The Confederacy sent envoys to London & Paris, but never bothered to send a representative to St. Petersburg, which turned out to be the most important capital of all. 

The Russian-British rivalry was of course the central antagonism of European history after the Napoleonic era, and the Russian attitude towards London coincided with the traditional American resentment against the former colonial power.
The US-Russian convergence became decisive during the Crimean War; while Britain, France and the Ottoman Empire attacked Russia, the United States was ostentatiously friendly to the court of St. Petersburg.
US press and public were all on the side of Russia, and hostile to the Anglo-French, to the chagrin of the erratic US President Pierce and the doughface politician James Buchanan. The latter, at that time US envoy to London, embraced the British view of the Tsar as the Despot. 
The Crimean War undoubtedly proved the wisdom of Russia’s policy of cultivating American friendship, & in fact, drew the two nations closer together. The attitude of Russia was a potent factor in preventing Great Britain & France from adopting a policy of aggressive intervention.
As early as 1861, Russia alerted the Lincoln government to the machinations of Napoleon III, who was already scheming to promote a joint UK-France-Russia intervention in favor of the Confederacy.
In 1862, Lincoln issued a warning that slavery would be abolished in areas still engaged in rebellion against the US. Russian Tsar Alexander II had liberated the 23 million serfs in 1861. This underlined the nature of the US-Russian convergence as a force for human freedom.
In 1862 there occurred in St. Petersburg an extremely cordial meeting of Russian Foreign Minister Gorchakov with US chargé d’affaires Bayard Taylor, which was marked by a formal Russian pledge never to move against the US, and to oppose any attempt by other powers to do so. 

Taylor reported these comments by Gorchakov to the State Department: “Proposals will be made to Russia to join some plan of interference. She will refuse. I cannot express to you how profound an anxiety we feel — how serious are our fears.”
The Journal de St. Petersbourg, the official gazette of the Tsarist government, denounced the Anglo-French intervention plan against the US. Seward thought that if the Anglo-French were to assail the Union, they would soon find themselves at war with Russia as well.
The most dramatic gestures of cooperation between Russian and the US came in 1863, as the Laird rams crisis hung in the balance. In September, the Russian Baltic fleet began to arrive in New York harbor. In October, the Russian Far East fleet began to arrive in San Francisco. 

The Russian admirals had also been told that, if the US and Russia were to find themselves at war with Britain and France, the Russian ships should place themselves under Lincoln’s command and operate in synergy with the US Navy against the common enemies. 

The news of the Russian fleet unleashed an immense wave of euphoria in the North. It was this moment that inspired the later verses of Oliver Wendell Holmes, one of the most popular writers in America, for the 1871 friendship visit of the Russian Grand Duke Alexis: 

"Bleak are our shores with the blasts of December, Fettered and chill is the rivulet’s flow; Thrilling and warm are the hearts that remember Who was our friend when the world was our foe." 

"Fires of the North in eternal communion, Blend your broad flashes with evening’s bright star; God bless the Empire that loves the Great Union Strength to her people! Long life to the Czar!" 

Soon after the war, Russia sold Alaska to the United States, in part because they felt that an influx of Americans searching for gold was inevitable, and in part to keep the British from seizing control of this vast region. 

Lincoln’s Secretary of the Navy Gideon Welles wrote in his diary, “The Russian fleet has come out of the Baltic and is now in New York. In sending them to this country at this time there is something significant. God bless the Russians!”
musingwithclio.wordpress.com/2013/09/23/god…
musingwithclio.wordpress.com/2013/09/23/god…
In 1915 Professor Frank A. Golder said that the Russians were only following their own national interests. Great nations defend their national interests. However, when the interests converge, alliance de jure or de facto may result, and these can have far-reaching significance.
How Holy Russia Saved the American Republic: On September 24, 1863, anchored in NYC harbor was a fleet of Imperial Russian war ships. America was at war. Not with Russia, but with itself. Lincoln and his young nation were alone, surrounded by enemies. America had one friend...
There is evidence that British Secret Service were involved in the assassination of President Lincoln. Napoleon III of France wanted to organize intervention in the Civil War with England and Russia. Russia was afraid of England and France and viewed as a true friend of America.
Russians and Americans were both deeply suspicious of the British and the French. They became the best of allies during much of the 19th century. In fact, they were the only allies each other had. America was the only country that supported Russia during the Crimean War.
Alexander II "czar liberator" wanted to liberate the world as much as possible. Russia told the British and French to stay out of the American Civil War and do not militarily intervene or they will face Russia joining the United States in fighting them to defend America.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




