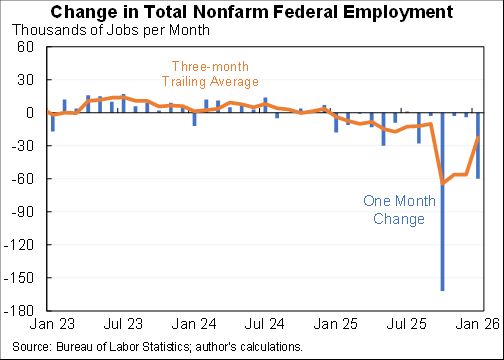
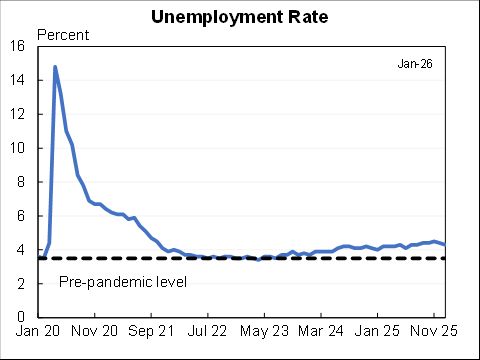
Updated blog with the unemployment numbers for August.
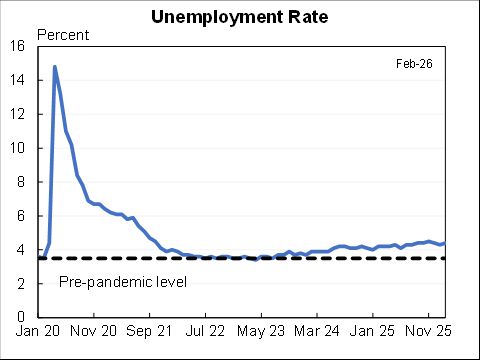
Realistic: 9.9%
Official: 8.4%
Full recall: 6.6%
piie.com/blogs/realtime…
Realistic: 9.9%
Official: 8.4%
Full recall: 6.6%
piie.com/blogs/realtime…
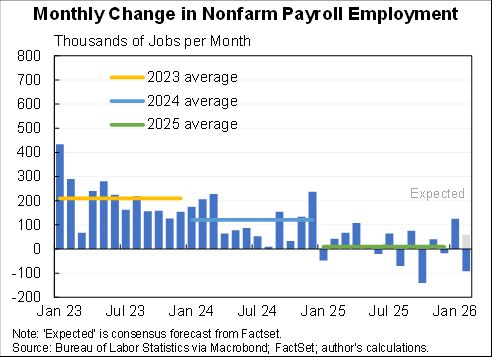
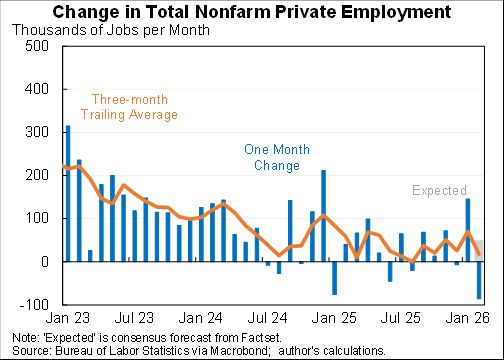
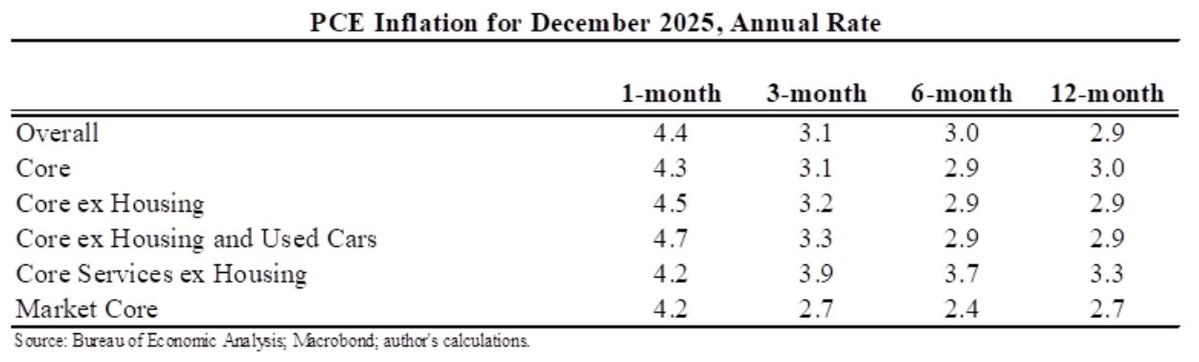
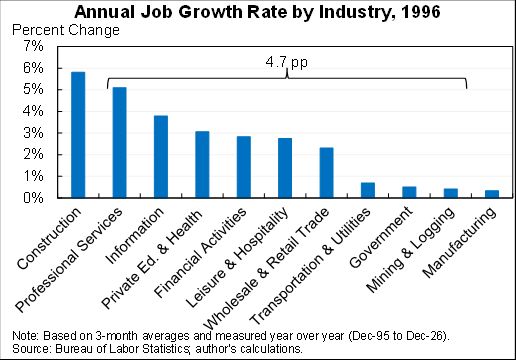
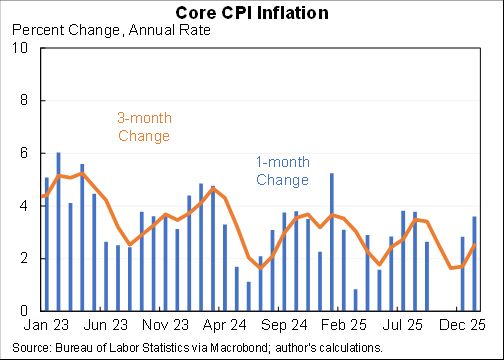
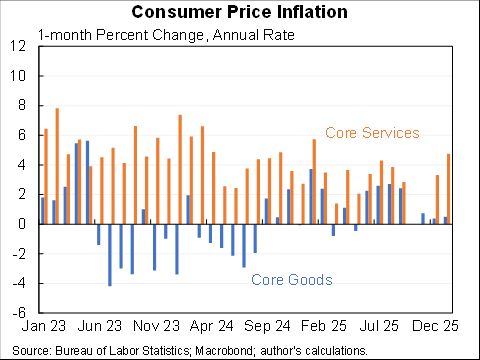
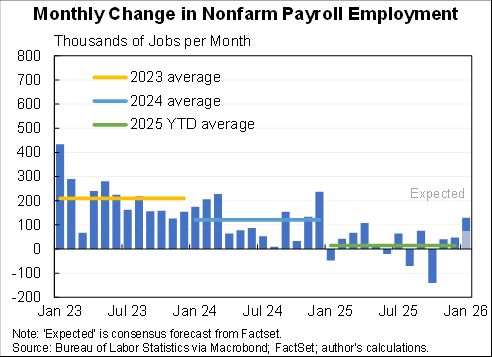
The "Realistic" unemployment rate remains higher than the official one for two reasons:
1. 1.1m workers misclassified as employed
2. 3.7m have left labor force, more than would be expected even with the rise in unemployment.
1. 1.1m workers misclassified as employed
2. 3.7m have left labor force, more than would be expected even with the rise in unemployment.
The "Full recall" unemployment rate is a hypothetical that measures what would happen under the (wildly optimistic) scenario that all of the 5.4m added to temporary layoff went back to their jobs right away & that participation rates rose in step.
It fell to 6.6% in Aug.
It fell to 6.6% in Aug.
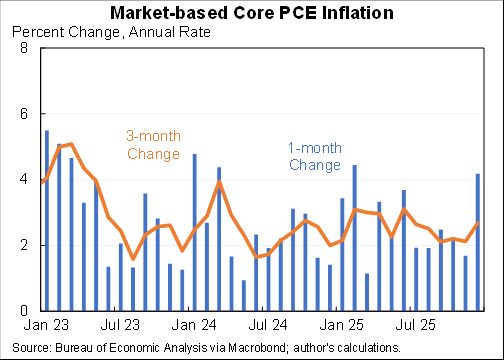
If we got/administered a vaccine today the unemployment rate would likely fall towards 6.6%. But getting the rest of the way to sub-4% unemployment would likely still be a long, hard slog. Maybe a little less long and hard than I had feared a few months ago.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh