ID Miscellany|physical Exam|Signs|Humanities #idmesh
1/20
𝙁𝙀𝙑𝙀𝙍 𝙋𝘼𝙏𝙏𝙀𝙍𝙉𝙎: 𝘼 𝙇𝙊𝙎𝙏 𝘼𝙍𝙏?
Great! Three quarters find inquiring about fever patterns still useful. We will review some of the most important fever patterns.
@ID_fellows
1/20
𝙁𝙀𝙑𝙀𝙍 𝙋𝘼𝙏𝙏𝙀𝙍𝙉𝙎: 𝘼 𝙇𝙊𝙎𝙏 𝘼𝙍𝙏?
Great! Three quarters find inquiring about fever patterns still useful. We will review some of the most important fever patterns.
@ID_fellows
https://twitter.com/WuidQ/status/1305649807395033088?s=20
2/20
For centuries, physicians have relied upon meticulous observations to dx infections. For many years, observation of the fever pattern provided physicians w/ important diagnostic clues. However, the advent of abx & advanced dx & imaging has changed this landscape. #idmesh
For centuries, physicians have relied upon meticulous observations to dx infections. For many years, observation of the fever pattern provided physicians w/ important diagnostic clues. However, the advent of abx & advanced dx & imaging has changed this landscape. #idmesh
3/20
Swift initiation of abx & antipyretics make it impossible to verify historical descriptions of certain fever patterns. Hence, inquiry into fever patterns loses its clinical significance bit.ly/33iXCLs.
Swift initiation of abx & antipyretics make it impossible to verify historical descriptions of certain fever patterns. Hence, inquiry into fever patterns loses its clinical significance bit.ly/33iXCLs.
4/20
Fever: rise in temp 2/2 ⬆️ hypothal set point through humoral/neural paths & PE2👇bit.ly/2E09nhm
The ⬆️ set point distinguishes it from hyperthermia.
Temp has diurnal (⬇️ am ⬆️ pm), anatomic (rectal>oral), & physiologic (older age, co-morb) variations. #idmesh
Fever: rise in temp 2/2 ⬆️ hypothal set point through humoral/neural paths & PE2👇bit.ly/2E09nhm
The ⬆️ set point distinguishes it from hyperthermia.
Temp has diurnal (⬇️ am ⬆️ pm), anatomic (rectal>oral), & physiologic (older age, co-morb) variations. #idmesh

5/20
𝙏𝙃𝙀 𝙁𝙀𝙑𝙀𝙍 𝙋𝘼𝙏𝙏𝙀𝙍𝙉𝙎
1⃣ Continuous/sustained fever: fever doesn’t fluctuate >1 C, doesn’t normalize
▪️ Classically a/w lobar pneumonia, rickettsial diseases, & typhoid. #idmesh
𝙏𝙃𝙀 𝙁𝙀𝙑𝙀𝙍 𝙋𝘼𝙏𝙏𝙀𝙍𝙉𝙎
1⃣ Continuous/sustained fever: fever doesn’t fluctuate >1 C, doesn’t normalize
▪️ Classically a/w lobar pneumonia, rickettsial diseases, & typhoid. #idmesh
6/20
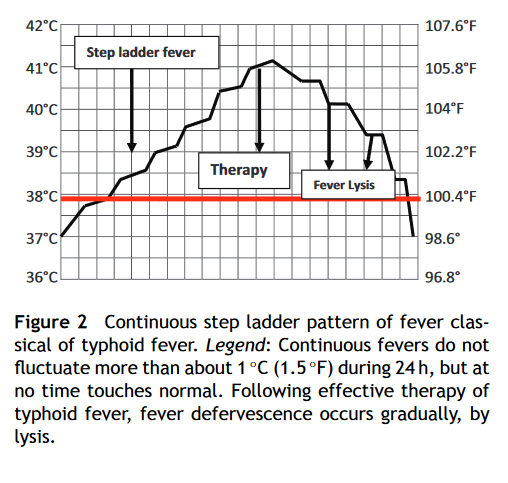
Typhoid has a peculiar pattern of continuous fever called:
2⃣ Step-ladder fever👇bit.ly/2E09nhm. In tropical countries, this has been shown to be of immense value in typhoid fever diagnosis (LR 177.4) bit.ly/3mcuo9T
#idmesh
Typhoid has a peculiar pattern of continuous fever called:
2⃣ Step-ladder fever👇bit.ly/2E09nhm. In tropical countries, this has been shown to be of immense value in typhoid fever diagnosis (LR 177.4) bit.ly/3mcuo9T
#idmesh
7/20
3⃣ Intermittent fever (hectic, “picket fence”): present only for several hrs during the day. Exemplified by the majority or pyogenic infections.
▪️ Classically a/w malaria, TB, lymphoma
#idmesh
3⃣ Intermittent fever (hectic, “picket fence”): present only for several hrs during the day. Exemplified by the majority or pyogenic infections.
▪️ Classically a/w malaria, TB, lymphoma
#idmesh
8/20
Malarial intermittent fevers👇
▪️ P. vivax & ovale: intermittent tertian
▪️ P. falciparum: intermittent subtertian
▪️ P. knowlesi: quotidian (daily) #idmesh
bit.ly/3kdxjxa
Malarial intermittent fevers👇
▪️ P. vivax & ovale: intermittent tertian
▪️ P. falciparum: intermittent subtertian
▪️ P. knowlesi: quotidian (daily) #idmesh
bit.ly/3kdxjxa

9/20
4⃣ Pel-Epstein fever👇: characterized by 3-10 days fever w/ subsequent afebrile period of 3-10 days.
▪️ Thought to be characteristic of lymphoma. bit.ly/3hpsUp3 #idmesh
4⃣ Pel-Epstein fever👇: characterized by 3-10 days fever w/ subsequent afebrile period of 3-10 days.
▪️ Thought to be characteristic of lymphoma. bit.ly/3hpsUp3 #idmesh

10/20
There are also Pel-Ebstein-like patterns that are characteristic of:
5⃣ Relapsing fever: tick- or louse-borne: Fever for 3 days (2-7 days), afebrile period of 7 days (Fig 1👇)
6⃣ Undulant fever a/w some cases of brucellosis (Fig 2👇) bit.ly/33mUMoF
#idmesh

There are also Pel-Ebstein-like patterns that are characteristic of:
5⃣ Relapsing fever: tick- or louse-borne: Fever for 3 days (2-7 days), afebrile period of 7 days (Fig 1👇)
6⃣ Undulant fever a/w some cases of brucellosis (Fig 2👇) bit.ly/33mUMoF
#idmesh


11/20
7⃣ Double quotidian fever: 2 distinct daily peaks of fever; seen only in a few conditions👇bit.ly/3hrm1Ub
▪️ Adult Still’s: most cited in literature
bit.ly/3hrm1Ub @alhkim @LisaZickuhr
▪️ Gonococcal endocarditis
▪️ Visceral leishmaniasis
#idmesh
7⃣ Double quotidian fever: 2 distinct daily peaks of fever; seen only in a few conditions👇bit.ly/3hrm1Ub
▪️ Adult Still’s: most cited in literature
bit.ly/3hrm1Ub @alhkim @LisaZickuhr
▪️ Gonococcal endocarditis
▪️ Visceral leishmaniasis
#idmesh

12/20
8⃣ Biphasic (saddleback, dromedary) fever: not truly relapsing; course marked by onset of fever for a few days, followed by an afebrile phase
▪️ Exemplified by dengue, Colorado tick fever, leptospirosis #idmesh
Refer to our prior discussion
8⃣ Biphasic (saddleback, dromedary) fever: not truly relapsing; course marked by onset of fever for a few days, followed by an afebrile phase
▪️ Exemplified by dengue, Colorado tick fever, leptospirosis #idmesh
Refer to our prior discussion
https://twitter.com/WuidQ/status/1202612600183414784?s=20
13/20
9⃣ Typhus inversus: reversal of diurnal fever pattern (highest temp in the AM rather than PM)
▪️ Thought to be seen in military TB, hepatic abscess, endocarditis bit.ly/3iubhWl
9⃣ Typhus inversus: reversal of diurnal fever pattern (highest temp in the AM rather than PM)
▪️ Thought to be seen in military TB, hepatic abscess, endocarditis bit.ly/3iubhWl
14/20
An aspect of fever that is most useful is the degree. Hyperpyrexia (>106.7 F), can be seen in infections but more commonly w/ hyperthermia (set point unchanged, inability to lose heat from excess production or exogenous exposure). #idmesh
@grepmeded @DxRxEdu @rabihmgeha
An aspect of fever that is most useful is the degree. Hyperpyrexia (>106.7 F), can be seen in infections but more commonly w/ hyperthermia (set point unchanged, inability to lose heat from excess production or exogenous exposure). #idmesh
@grepmeded @DxRxEdu @rabihmgeha

15/20
We talked about some of the causes of hyperpyrexia (in the setting of rigidity) here before:
We talked about some of the causes of hyperpyrexia (in the setting of rigidity) here before:
https://twitter.com/WuidQ/status/1252689619256250375?s=20#idmesh
16/20
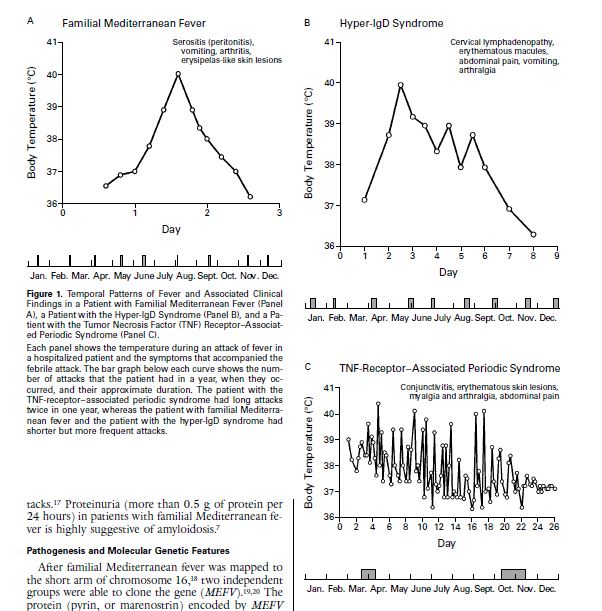
Knowledge of fever patterns is also helpful in differentiating the major causes of periodic fever syndromes👇: bit.ly/3hweu6t
▪️ FMF: <2d + serositis/arthritis/rash
▪️ Hyper-IgD: <4-6d + LAD/rash/localized myalgia
▪️ TRAPS: >2wks + rash/conjunctivitis
#idmesh

Knowledge of fever patterns is also helpful in differentiating the major causes of periodic fever syndromes👇: bit.ly/3hweu6t
▪️ FMF: <2d + serositis/arthritis/rash
▪️ Hyper-IgD: <4-6d + LAD/rash/localized myalgia
▪️ TRAPS: >2wks + rash/conjunctivitis
#idmesh

17/20
A closely related topic is the temperature-pulse dissociation (Faget’s sign) which we’ve discussed previously on #idmesh
A closely related topic is the temperature-pulse dissociation (Faget’s sign) which we’ve discussed previously on #idmesh
https://twitter.com/WuidQ/status/1203728795343237121?s=20
18/20
Fever patterns are not pathognomonic. Should not bias one into a dx. The most important aspect of fever is appraising it in a/w the patients’ SSx, lab & imaging. This is at the ❤️ of clinical reasoning. @CPSolvers @thecurbsiders @MedEdPGH @MohitHarshMD @Maximal_Change
Fever patterns are not pathognomonic. Should not bias one into a dx. The most important aspect of fever is appraising it in a/w the patients’ SSx, lab & imaging. This is at the ❤️ of clinical reasoning. @CPSolvers @thecurbsiders @MedEdPGH @MohitHarshMD @Maximal_Change
19/20
I would like to also refer you to the master @tony_breu's recent tweetorial on fever. #idmesh
I would like to also refer you to the master @tony_breu's recent tweetorial on fever. #idmesh
https://twitter.com/tony_breu/status/1305589726003556354?s=20
20/20
Rounding out this #idmesh tweetorial.
Please share stories on how you used fever patterns in diagnosing patients. @PaulSaxMD @CarlosdelRio7 @DxRxEdu @rabihmgeha @GermHunterMD @FungalDoc @tosh_taniguc @NNolanMD @JonathanRyderMD @TxID_Edu @swinndong @LeMiguelChavez
Rounding out this #idmesh tweetorial.
Please share stories on how you used fever patterns in diagnosing patients. @PaulSaxMD @CarlosdelRio7 @DxRxEdu @rabihmgeha @GermHunterMD @FungalDoc @tosh_taniguc @NNolanMD @JonathanRyderMD @TxID_Edu @swinndong @LeMiguelChavez
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh