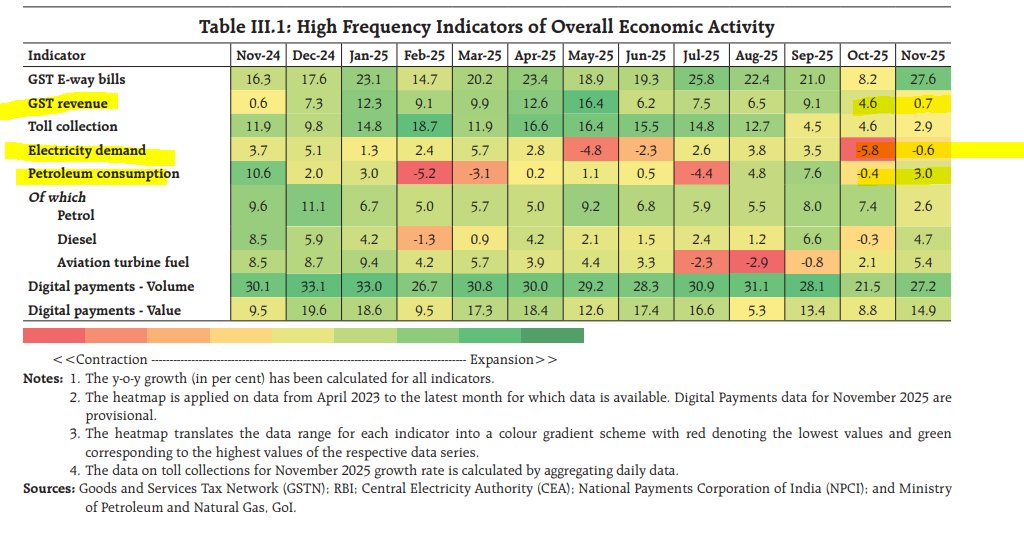
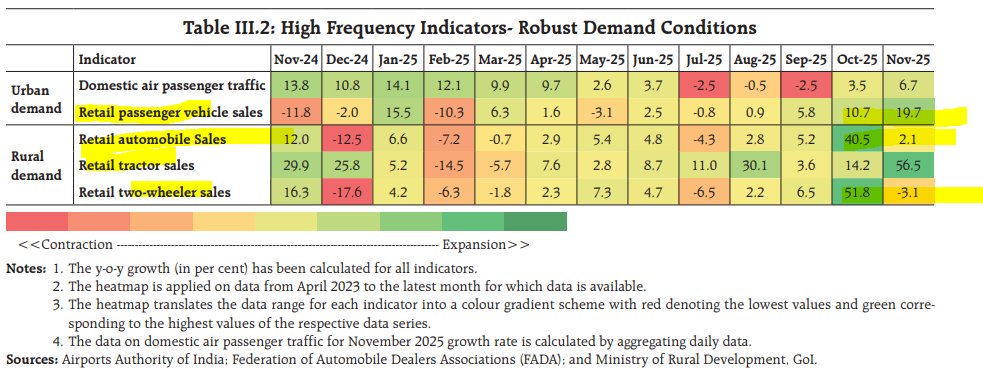
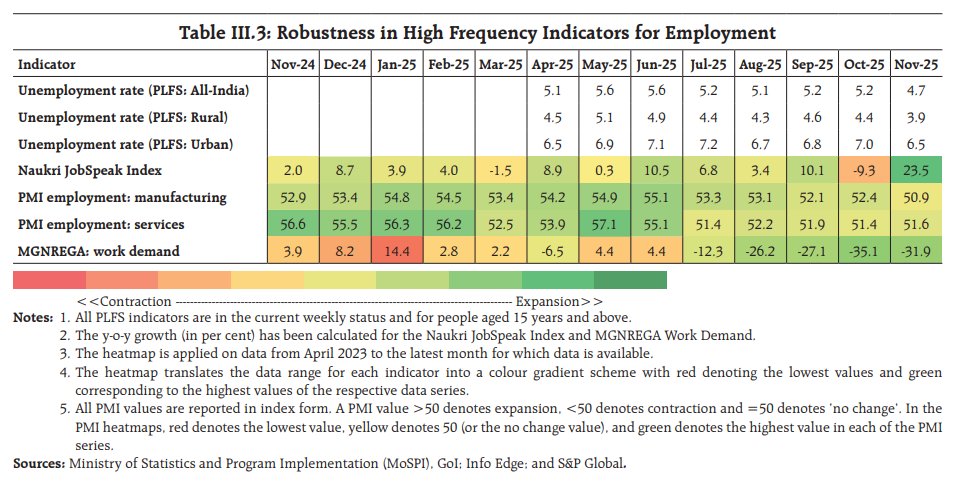
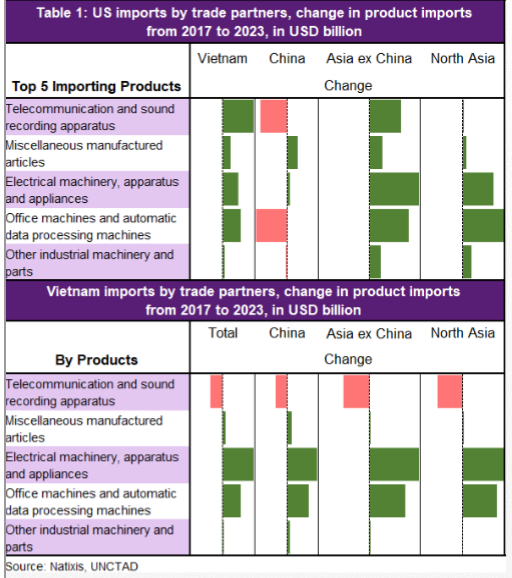
This story on the American middle class: No job, loads of debt: Covid up-ends middle class finance.
I just started reading it & I am like, two incomes of 175k but they got a monthly debt of 9k. I'm afraid to ask what their savings are.
Overconsuming!
wsj.com/articles/covid…
I just started reading it & I am like, two incomes of 175k but they got a monthly debt of 9k. I'm afraid to ask what their savings are.
Overconsuming!
wsj.com/articles/covid…

I'm assuming 175k is net income & not gross b/c taxes would eat up roughly half of that already.
I'm curious about the break-down of their household debt & the percentage that is mortgage, student loans, auto & consumer debt.
Worryingly is they are in their 40s...
I'm curious about the break-down of their household debt & the percentage that is mortgage, student loans, auto & consumer debt.
Worryingly is they are in their 40s...
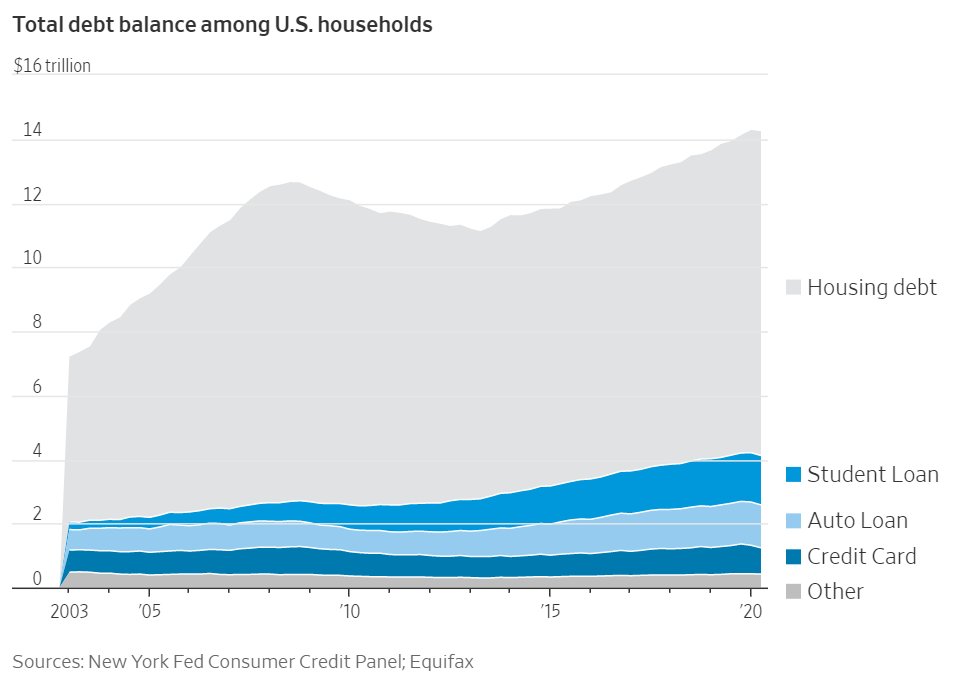
Where we stand: American stock of debt.
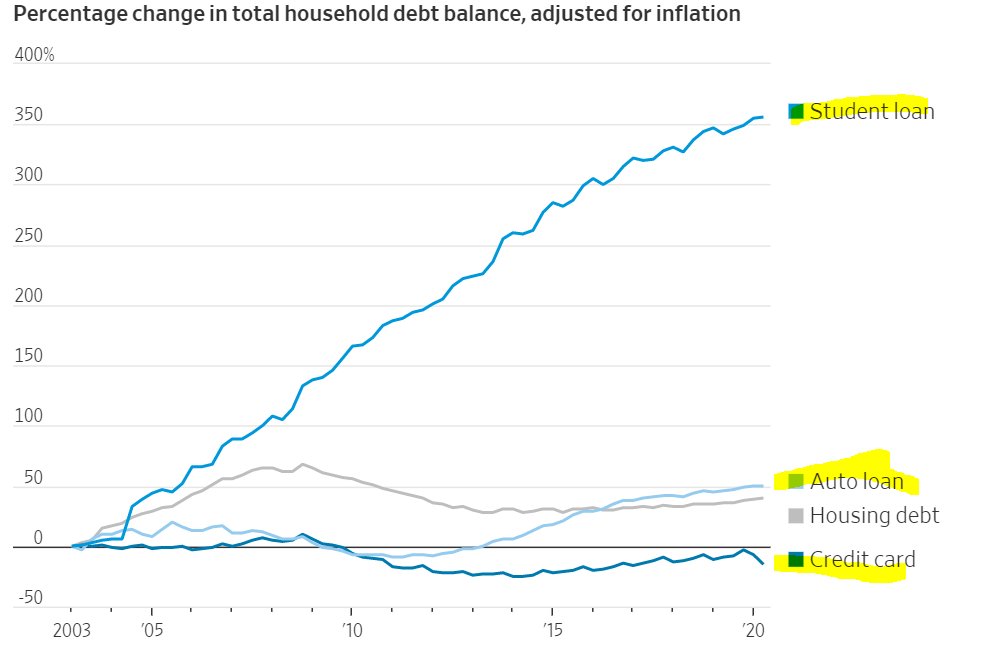
Some good news: credit card debt stock is down & student loans down.
Some good news: credit card debt stock is down & student loans down.
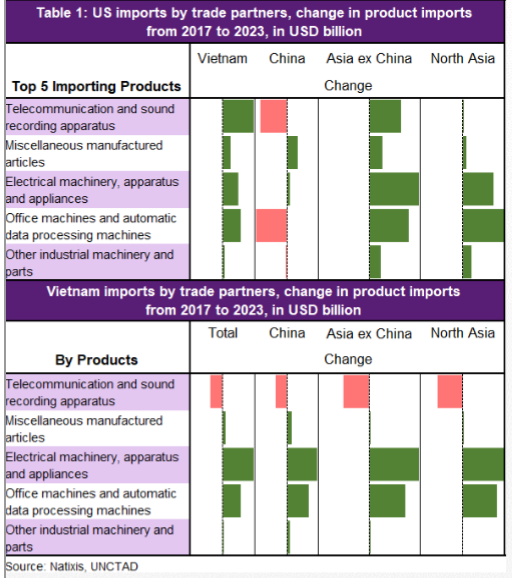
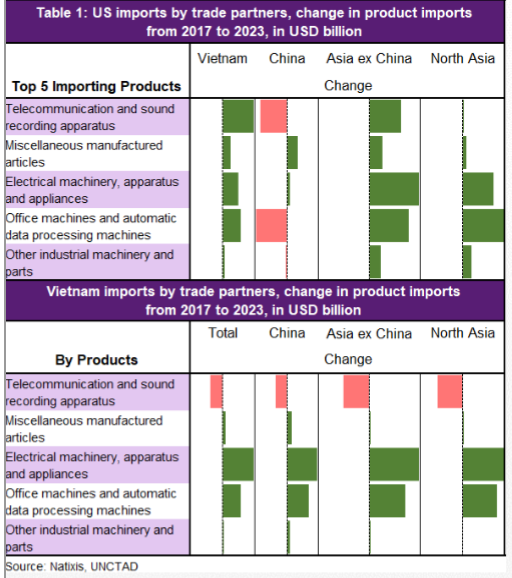
So apparently an American family making over 98k (prolly gross so net is much lower) & they got consumer debt of 92k, 32% higher than 2004.
What are they buying? And why are Americans paying such high interest rates to consume?
Millennials are the worst among the age group.
What are they buying? And why are Americans paying such high interest rates to consume?
Millennials are the worst among the age group.
I like these kinds of articles from the WSJ because it helps us push for positive change about American culture where people consume way above their means.
Credit card down but auto + student loan growth up. Seems like people buying nicer cars than they can afford.
Credit card down but auto + student loan growth up. Seems like people buying nicer cars than they can afford.
Another anecdotal story in this macro trend: a couple in their late 40s making 150k combined (so net likely 100k) & somehow got:
4k of mortgage per month (living in a nicer house than they can afford)
4 car loans (why 4 cars??? omg)
Student loans
Madness. American nightmare.
4k of mortgage per month (living in a nicer house than they can afford)
4 car loans (why 4 cars??? omg)
Student loans
Madness. American nightmare.

This story gets way worse. So they somehow got so much debt (2 adults but 4 car leases + 4k mortgage + student loans & credit card debt) & she now decides to take out 5k from her 401k (retirement) to re-educate herself.
I mean, she didn't payoff her old student loan debt!
I mean, she didn't payoff her old student loan debt!
The theme from the 3 anecdotes is that people GOT ZERO PLAN for WORST CASE SCENARIO.
How is it that people don't know that:
a) If u have a lot of debt, u have to pay back
b) That depends on ur income, which can be volatile so need to have savings
c) Will age & can't work forever
How is it that people don't know that:
a) If u have a lot of debt, u have to pay back
b) That depends on ur income, which can be volatile so need to have savings
c) Will age & can't work forever
Also the story is interesting in that these people all have debts w/ very high rates which means they likely have limited understanding of opportunity costs of consumption & that means likely low investment.
Why have outstanding student, auto & credit debt & yet high mortgage?
Why have outstanding student, auto & credit debt & yet high mortgage?
Toxic mix:
*System pushes people to take on debt - media telling people they deserve to live on materially higher standard living than they can afford & buy, buy, buy on debt
*Asset prices inflated so essentials cost more
*Lock-downs kill jobs
*People make poor financial choices.
*System pushes people to take on debt - media telling people they deserve to live on materially higher standard living than they can afford & buy, buy, buy on debt
*Asset prices inflated so essentials cost more
*Lock-downs kill jobs
*People make poor financial choices.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh