
Follow along with live tweet updates of another Pharmacy Grand Rounds Presentation. PGY1/PGY2 HSPAL resident @JOzempic will be GABbing about gabapentinoids. 🗣️ Presentation will begin at 11 am CST. 

Gabapentinoids have a reputation for extensive off-label use. Today we will examine evidence regarding gabapentinoid use for acute pain management in the perioperative setting. 

From 2012-2016, the number of gabapentin prescriptions has increased by 25 million, or 64%. There have been no new FDA approved indications for gabapentin during this timeframe, indicating that this increase correlates to off-label use. 

Several facets are likely tied to gabapentinoids being used in the perioperative space: presumed safety, perceived efficacy, desire for expedient patient recovery, and recent endorsement as part of a multimodal pain management regimen by the 2016 American Pain Society guideline. 

Nociception, or the perception of pain, has 4 distinct stages: transduction, transmission, perception, and modulation. Gabapentinoids exert their mechanism of action on modulation of pain sensation via binding to alpha-2-delta receptors located on voltage-gated calcium channels. 

While pregabalin and gabapentin share similar pharmacology, they do differ in their pharmacokinetic profile. Gabapentin bioavailability is inversely related to dosing, whereas pregabalin has dose independent bioavailability. 

A 2006 study found that of the 3.56 million gabapentin prescriptions written, 83% of them were used for off-label indications… 
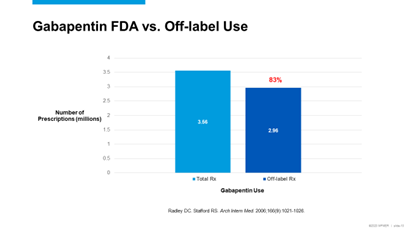
…and of those off-label prescriptions, ~80% of those were associated with either weak or no evidence supporting use for that indication. 

In December of 2019, the FDA released new black box warnings for the gabapentinoids warning of respiratory depression with concomitant use of opioids or CNS depressants.
The Gabapentinoids are also commonly associated with sedation and drowsiness💤
The Gabapentinoids are also commonly associated with sedation and drowsiness💤

A 2015 meta-analysis found that, while statistically significant, gabapentin did not reach clinical significance for reduction in postop analgesia during the 24hr timeframe postoperatively. The only clinically significant finding was reduced postop pain 1hr after surgery. 



A meta-analysis by Eipe et al found that pregabalin decreased postoperative analgesia consumption by 16% in the 24-48hr period postoperatively. It also decreased pain at rest by 1.09 on a 10-point pain scale within a 24hr postoperatively for pronociceptive surgery types. 



A 2020 meta-analysis examining both gabapentin and pregabalin found that the gabapenitoids decreased IV morphine milligram equivalents by 7.9, 9.8, and 29 at 24, 48, and 72hrs postoperatively, respectively. 

This analysis also found that the gabapentinoids decreased pain at a clinical significance only found to be minimally important within 6hr postop. No appreciable difference (defined as >30 points on 100 point scale) was found for either medication at any time point postop. 

Overall, the gabapentinoids have contributed to statistically significant reductions in analgesia consumption and pain reduction postoperatively. Clinical significance of pain reduction has been less promising. 

Continuation of gabapentinoids may put patients at an increased risk of naloxone use within 48hrs of dismissal from surgery. 

Gabapentinoid abuse and misuse is a growing problem and affects vulnerable populations such as those with substance use disorder. Both gabapentin and pregabalin have also been tied to increased risk for opioid related overdose. 

While pregabalin remains a schedule V substance at the federal level, gabapentin has recently been included as a controlled substance in several states, with many states requiring submission of gabapentin prescriptions to drug monitoring programs📰 

@JOzempic concludes: gabapentinoids have been associated with minimal decrease in pain, minimal decrease in analgesia consumption, and an increased risk of sedation in the perioperative setting.
Next week @NatalieHaddadRx presents on midodrine for vasopressor discontinuation!💊
Next week @NatalieHaddadRx presents on midodrine for vasopressor discontinuation!💊

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





