I'm seeing a lot of analysts arguing today's jobs numbers aren't so bad because the slowdown was driven by the late/partial reopening of schools.
A thread:
A thread:
On the one hand, this is literally true: The August-September slowdown is less stark when you look at the private sector, and disappears more or less entirely if you also strip out private-sector education 
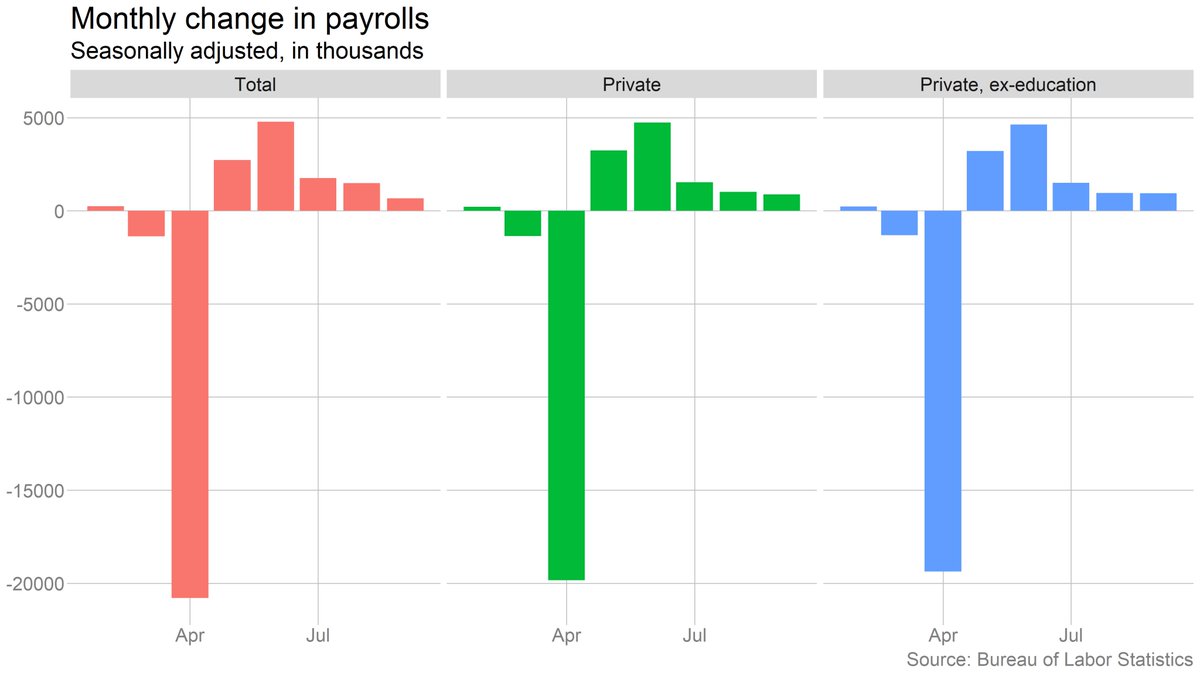
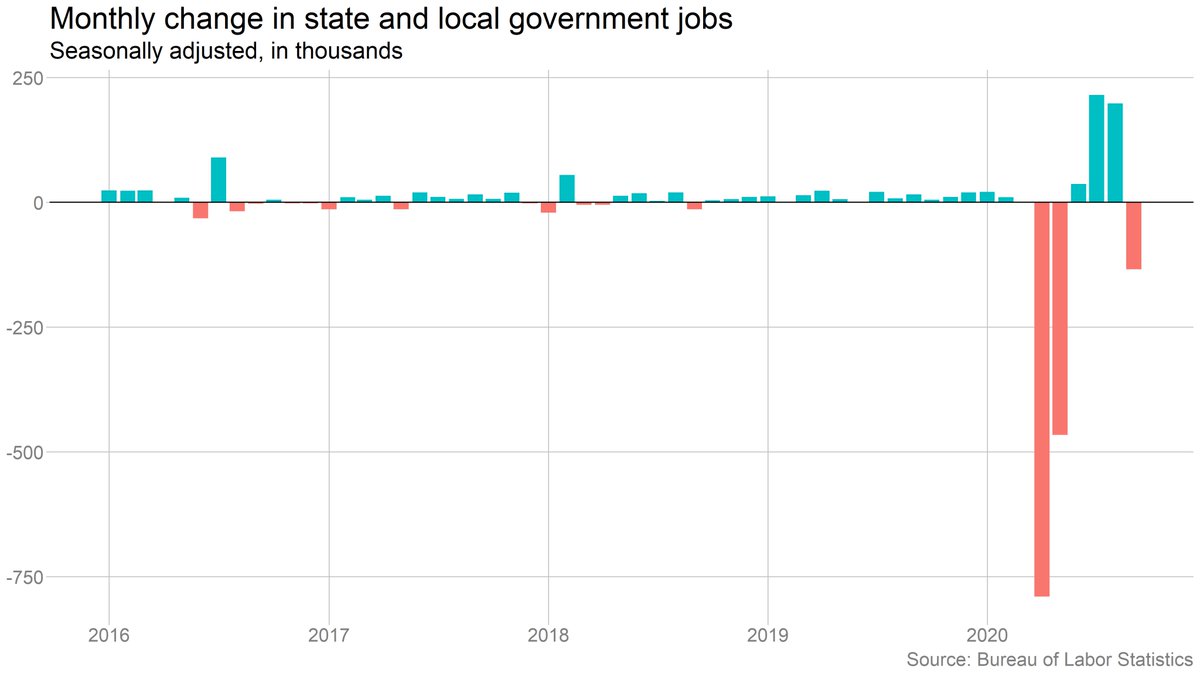
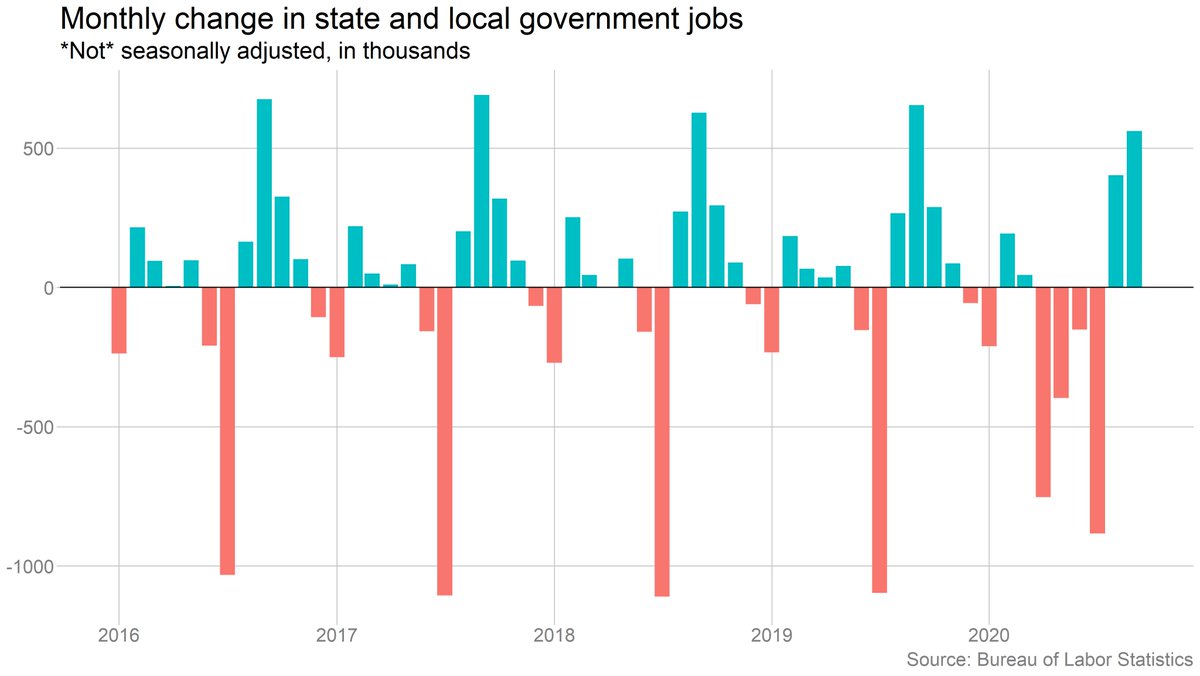
It's also true that the drop in state/local employment is a result of seasonal adjustment -- on an unadjusted basis, employment rose (just much less than in a normal September). 

But if we're going to start to play that game, we could also note that the big jump in leisure & hospitality (nearly half the total jobs gain for the month) was also the result of seasonal adjustment. On an NSA basis, leisure & hospitality jobs fell in September.
(The reason: The leisure & hospitality sector usually cuts jobs as summer ends, but this year it's in such a hole there weren't many jobs to cut. So the seasonal factors interpret that as a substantial increase in jobs.)
Some of the notes I'm seeing discount the school cuts because they're unlikely to be repeated. But are they? It seems possible we'll see more schools shut down given the path of the virus right now. (Whereas if anything leisure seems likely to get worse with colder weather.)
My real point here is that these kinds of ad hoc adjustments can get pretty squishy pretty fast. With the exception of clearly defined one-off events like the Census, I generally think it's better not to start adjusting these numbers on the fly.
Two last points: It definitely is true that seasonal patterns have gotten messed up during this period. Looking at unadjusted payrolls, the slowdown is less pronounced in September. But looking just at the private-sector side, the slowdown is actually worse on an NSA basis. 
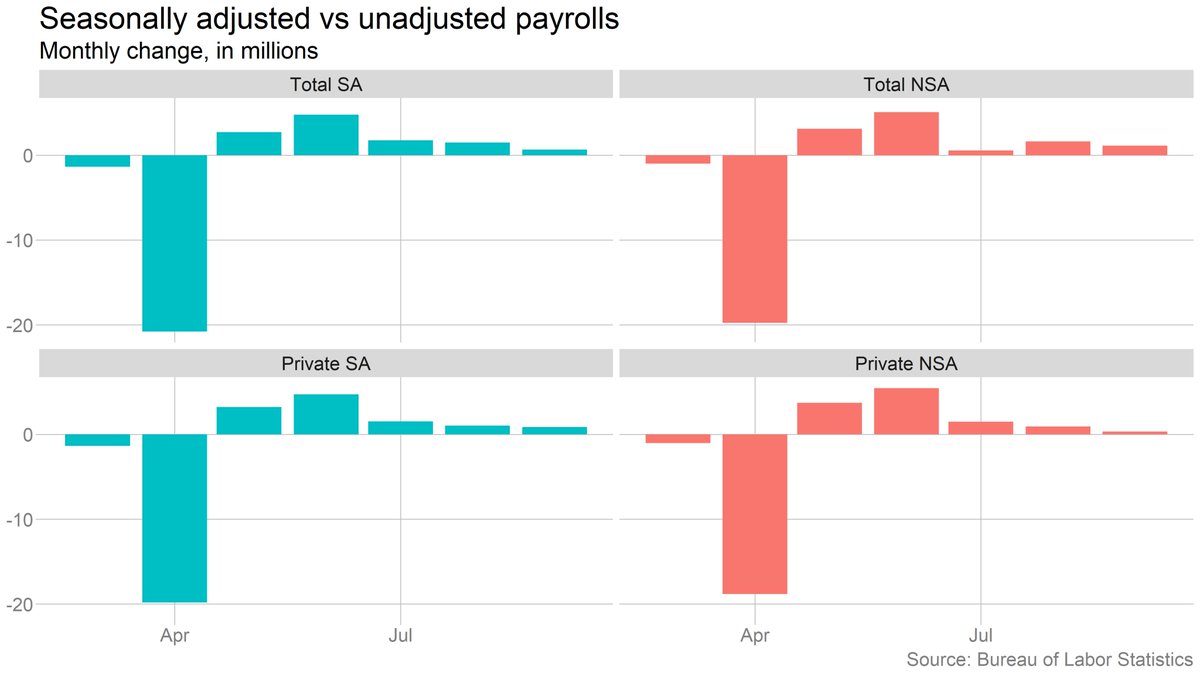
Which leads to the final point: None of this slicing and dicing changes the big picture, which is that the pace of gains has slowed dramatically, to a level that implies a long climb back to where we were before the pandemic.
nytimes.com/2020/10/02/bus…
nytimes.com/2020/10/02/bus…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









