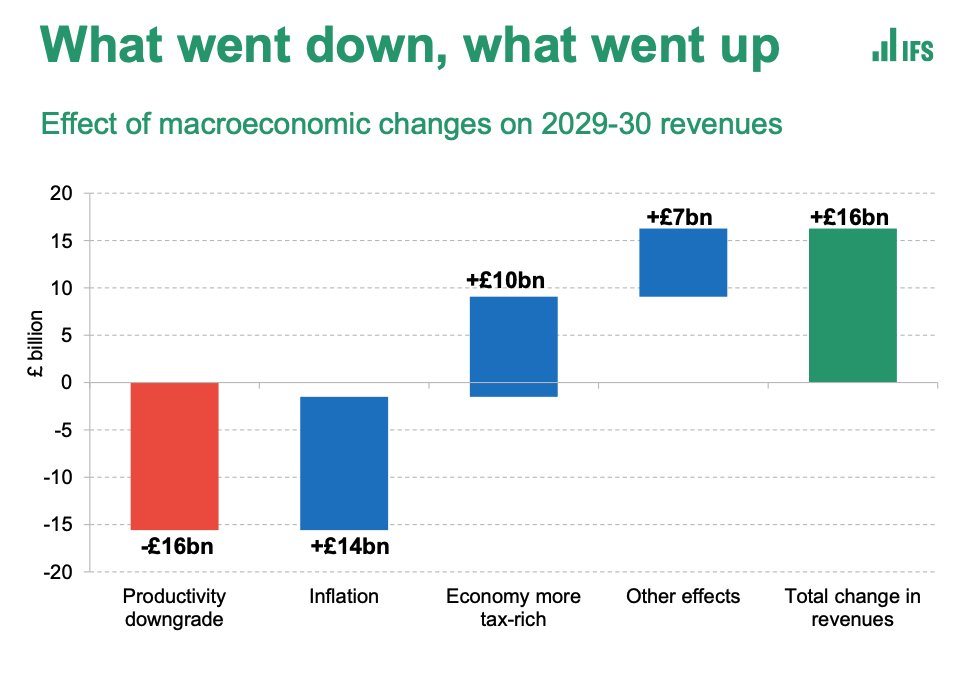
Thread: Throughout the pandemic there's been plenty of attention focused on #COVID19 deaths and on what’s happened in hospitals and in care homes - for obvious and understandable reasons. But for months there’s been another phenomenon which I find deeply unsettling.
Even after lockdown ended the number of people dying at home has stayed far, far above historic levels. There have been 28k excess deaths in people’s homes - more than in hospitals, care homes or other settings. Only a fraction of these deaths are officially put down to #COVID19. 
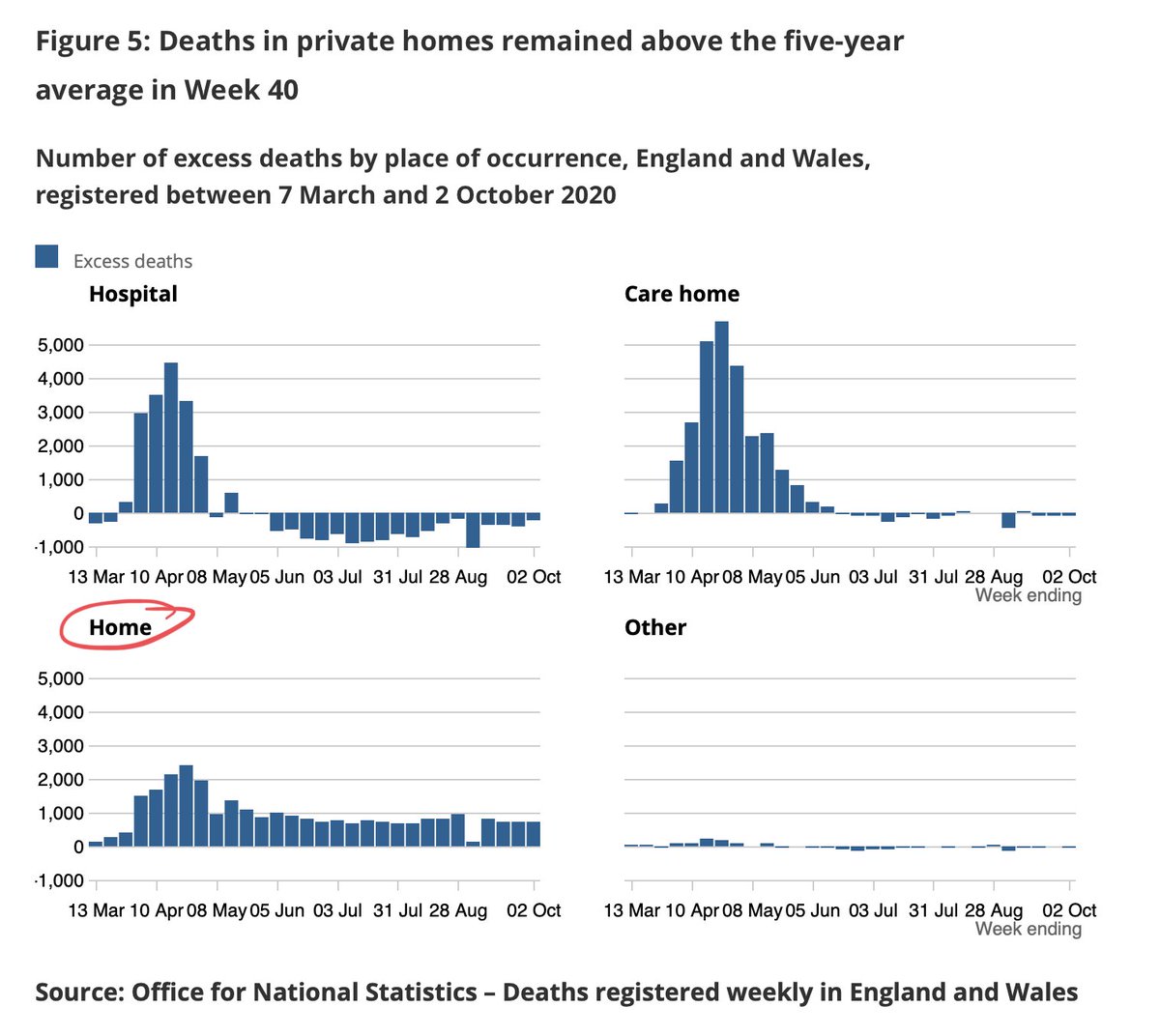
I’ve been banging on about this since early on in the pandemic. It's not a new phenomenon. But it remains stubbornly unchanged even months on, even as excess deaths in other settings - care homes and hospitals - have dropped into normal or negative levels.
Is this something to worry about? Or is it (kind of) good news - in that lots of people would rather die at home than in a medical setting. Frustratingly there’s been v little research on this, so over the past few weeks we’ve been working on a short film looking beneath the data
It starts with Charlotte. Her mum, Caroline, died of ovarian cancer this summer. She had been in hospital but because of lockdown her family hadn’t been allowed to visit her, so they brought her home to try to care for her there. It was an ordeal, but they had little choice. 
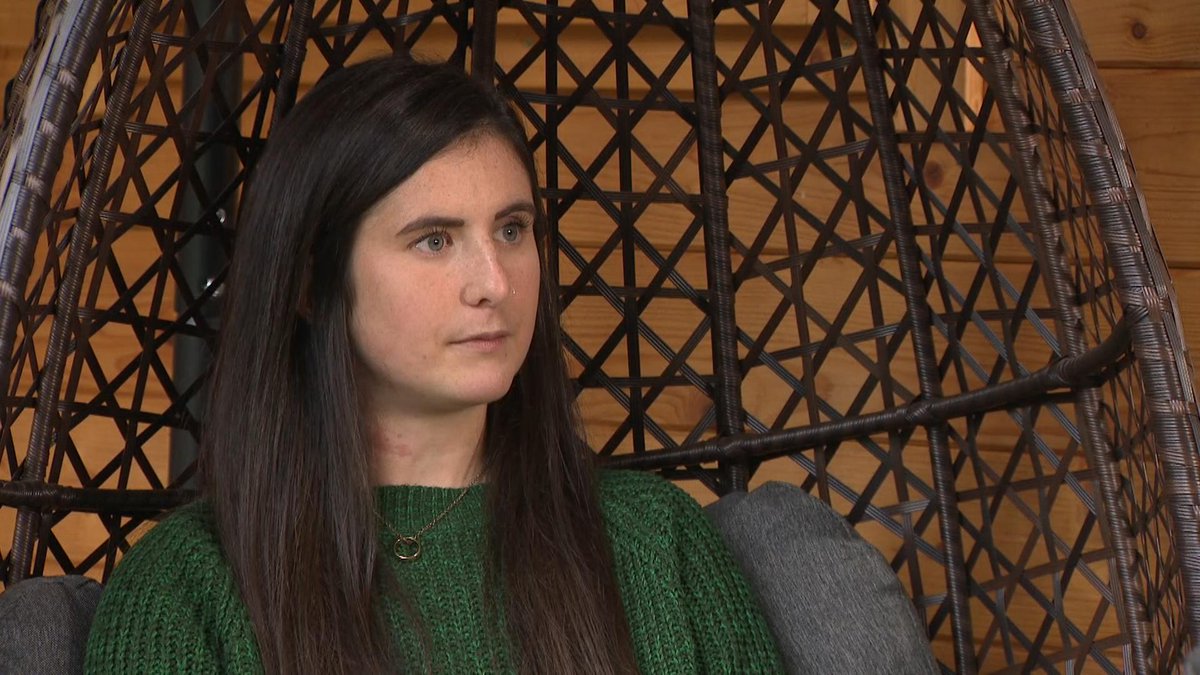

The family couldn’t get as much palliative care as they needed. Their home became a hospital. If she had gone into a hospice (as she might in normal times) they might not have been able to be with her, so she died with them at home. Her death is one of the thousands in this chart 
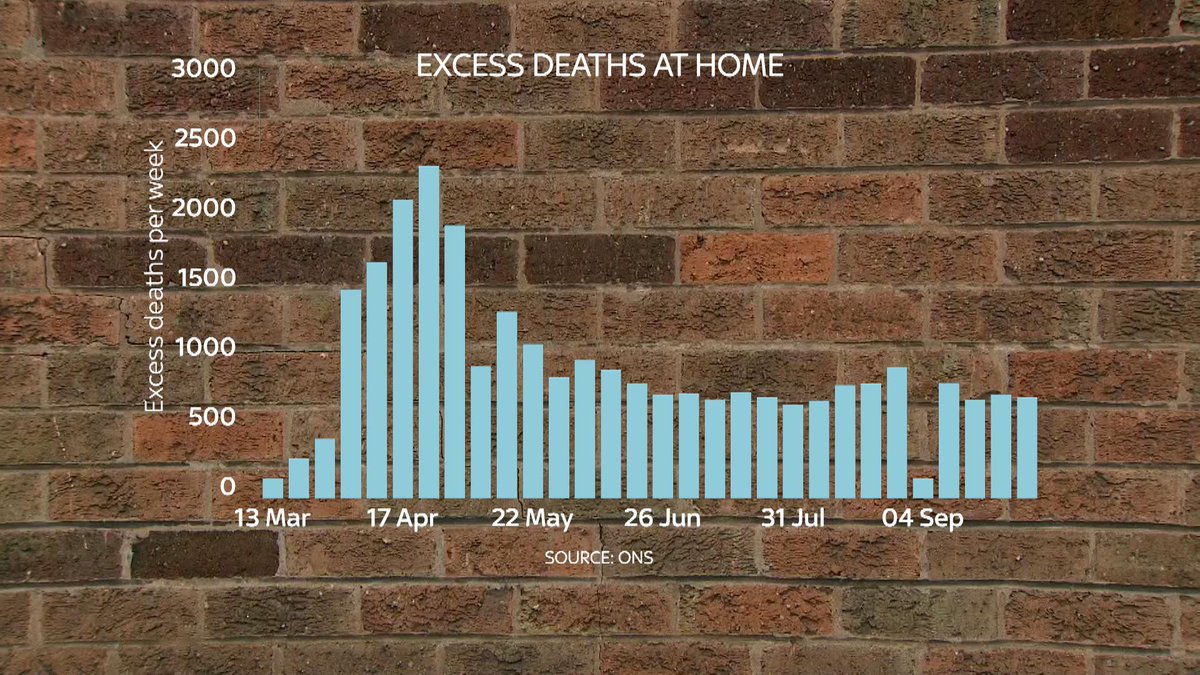
Indeed, the most compelling theory about why excess deaths are up at home and down elsewhere is that these deaths are simply being displaced from other settings.
But these data can’t tell you anything about the QUALITY of death - something which matters enormously.
But these data can’t tell you anything about the QUALITY of death - something which matters enormously.
For many families the answer is remote hospice care (80% of hospice work is done in people’s homes).
Problem is those services have been overwhelmed during the pandemic. And like many, in the early days they struggled to get the PPE that would allow them to do their jobs
Problem is those services have been overwhelmed during the pandemic. And like many, in the early days they struggled to get the PPE that would allow them to do their jobs
Selina says: “We can lose four patients just in one day. We can go off shift and have our two days off, come back to work and all our patients have changed because they’ve died. We’re getting our referrals in later and people are dying a lot sooner.” 
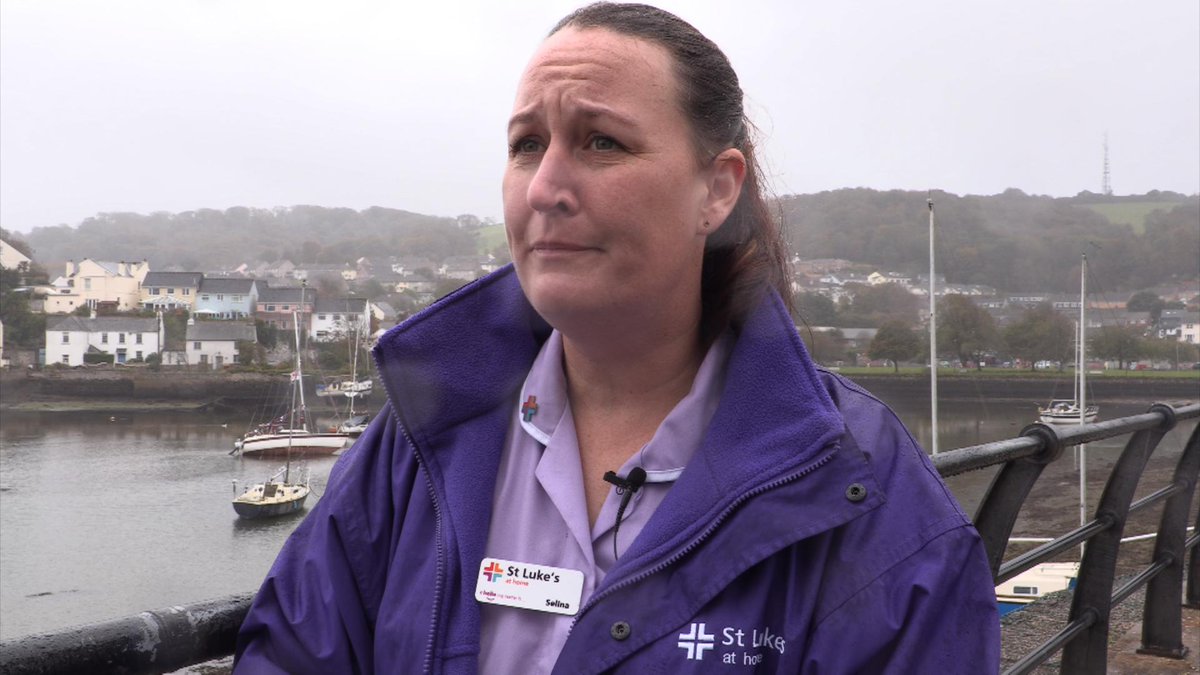

And even as deaths at home remain so high, the hospice sector are struggling to keep up with the demand.
We’ve been shown numbers from an internal Hospice UK survey: 44% of hospices think they'll have to REDUCE their services. 93% fear people may miss out on the support they need
We’ve been shown numbers from an internal Hospice UK survey: 44% of hospices think they'll have to REDUCE their services. 93% fear people may miss out on the support they need

But there’s another likely explanation for high excess deaths at home:
some people are dying earlier than they would have because they've been unable or unwilling to go into hospital for the medical treatment they need. We know these cases are happening anecdotally.
some people are dying earlier than they would have because they've been unable or unwilling to go into hospital for the medical treatment they need. We know these cases are happening anecdotally.
Meet Amanda & Adrian. Adrian has stage 4 bowel cancer. He responded well to chemo - so well that his docs scheduled a life-saving operation to remove a large part of his liver. It was due in April. Then came lockdown, then the op was cancelled. Adrian’s cancer is now terminal 

Adrian is one of potentially thousands of cancer patients whose care has been affected by lockdown. Doctors expect a surge in cancer deaths in the coming months and years. It is another dimension of what is happening beneath the surface of the data
We're still in the early stages of understanding this. Next week @ONS will produce further data breaking down home deaths by cause to see if there are any early patterns. But @d_spiegel told me it’s not impossible this is a permanent - or at least a long-lasting - change.
If you have time, do check out my long read on a disquieting phenomenon. For months I've been worried about the data showing thousands of excess deaths at home. This is my attempt to get beneath these numbers and understand what's going on news.sky.com/story/coronavi…
Here's our @SkyNews report about excess deaths at home, produced by the brilliant @maddylratcliffe.
As #COVID19 surges again and parts of the country go into another lockdown, this troubling phenomenon is likely to be with us for a while longer
As #COVID19 surges again and parts of the country go into another lockdown, this troubling phenomenon is likely to be with us for a while longer
Interesting @ONS deep dive into deaths at home.
Underlines point in my @SkyNews piece on this 👆, some of these deaths would have happened anyway.
Some may be happening sooner because of inability to access healthcare.
Eg see increases in causes of death:
ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulati…
Underlines point in my @SkyNews piece on this 👆, some of these deaths would have happened anyway.
Some may be happening sooner because of inability to access healthcare.
Eg see increases in causes of death:
ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulati…

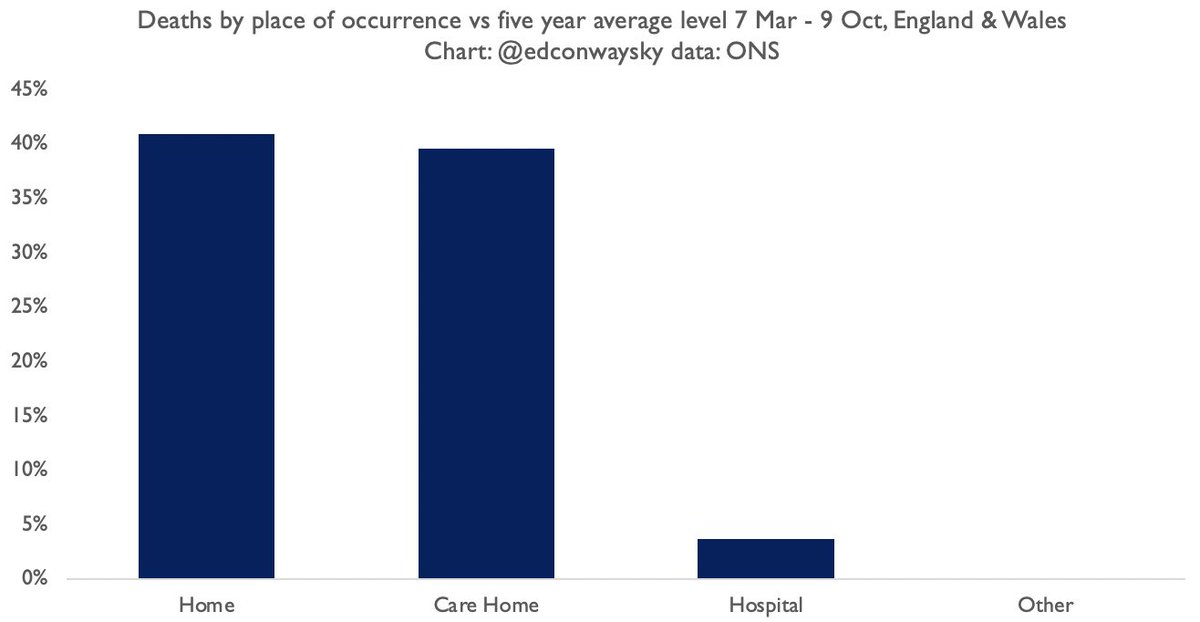
As of the latest data there have been more excess deaths happening in people’s homes this yr than any other place. Vast majority of the deaths were not from #COVID19.
This is one of the most important but least discussed phenomena of the pandemic.
More on it in the thread 👆
This is one of the most important but least discussed phenomena of the pandemic.
More on it in the thread 👆
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh