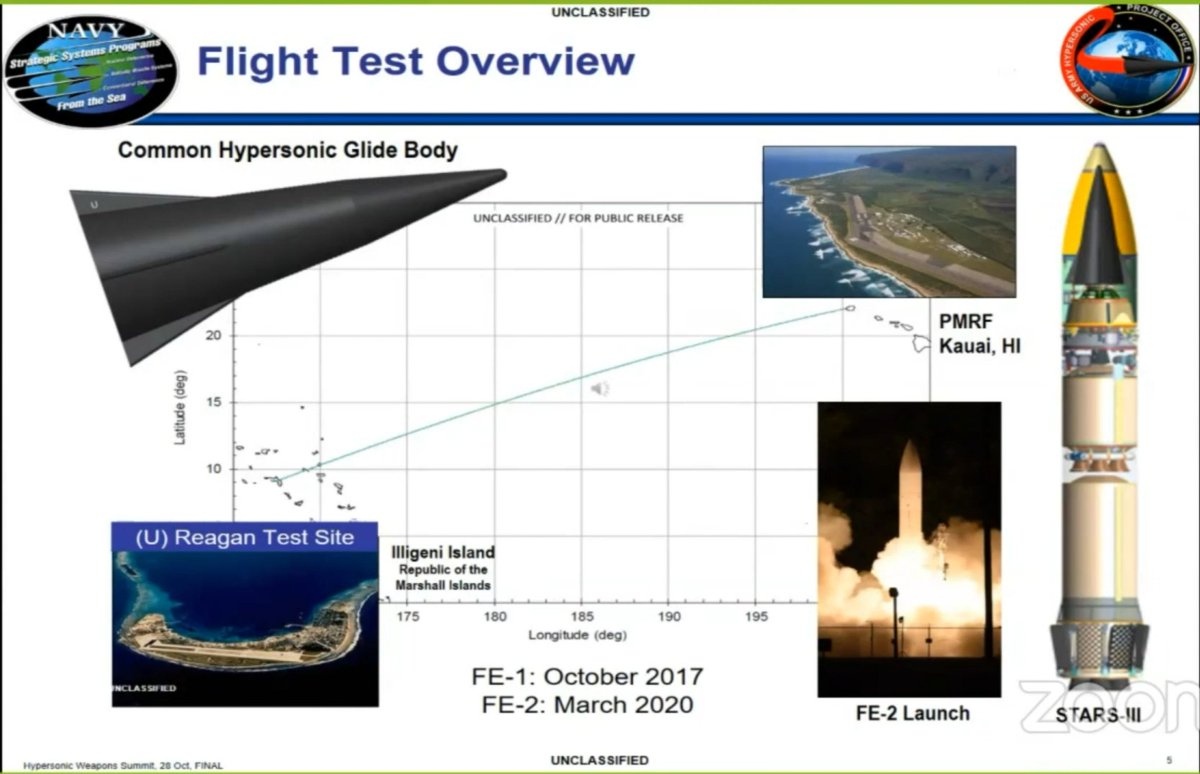
More detail on Army-Navy cooperation for C-HGB/LRHW from this year's Hypersonic Weapons Summit. Both expected to share Navy-developed 2-stage booster. 

More on the basing modes: Army expected to have battery of 2-round launchers for a total of 8 rounds/battery. Navy will certify cold-launch system for Virginia Payload Module. 

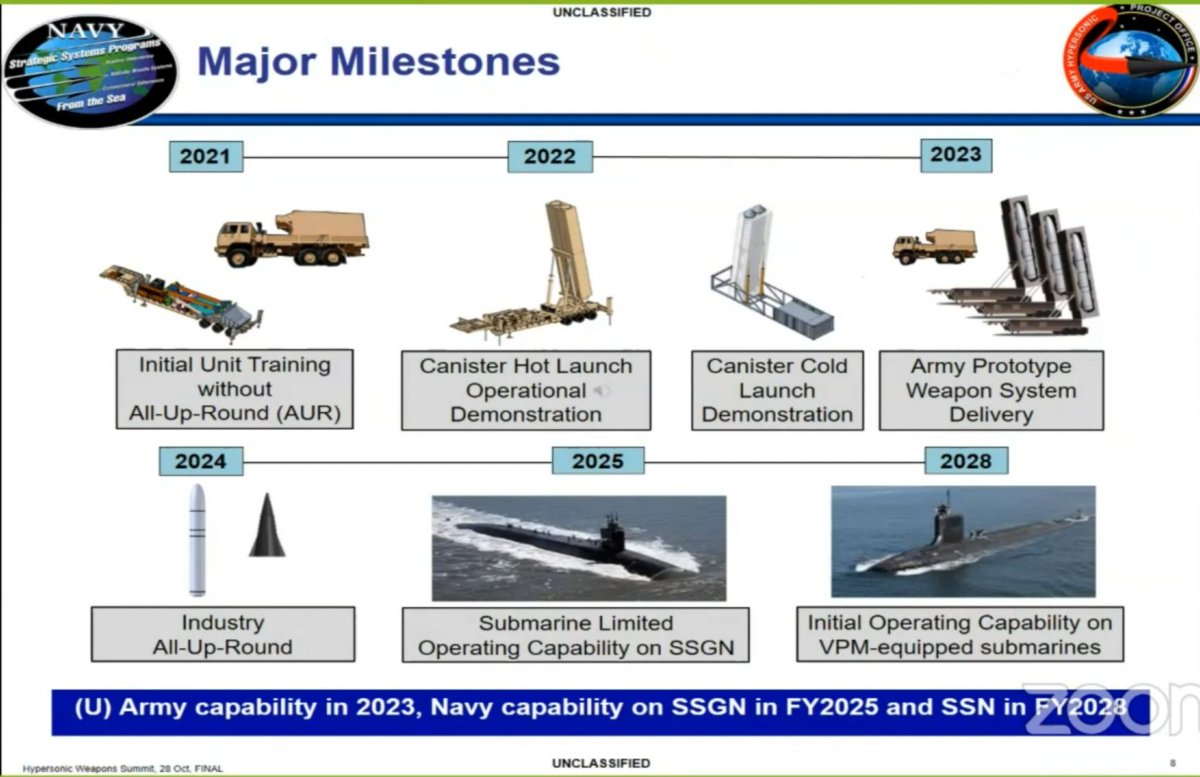
The roadmap for fielding C-HGB equipped missiles. Key points:
-Canister launch demos through 2022
-Army prototype LRHW delivery 2023.
-Larger scale Army procurement decisions will occur 2024.
-SSGN hypersonic capability 2025.
-Virginia Payload Module capability 2028.
-Canister launch demos through 2022
-Army prototype LRHW delivery 2023.
-Larger scale Army procurement decisions will occur 2024.
-SSGN hypersonic capability 2025.
-Virginia Payload Module capability 2028.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh