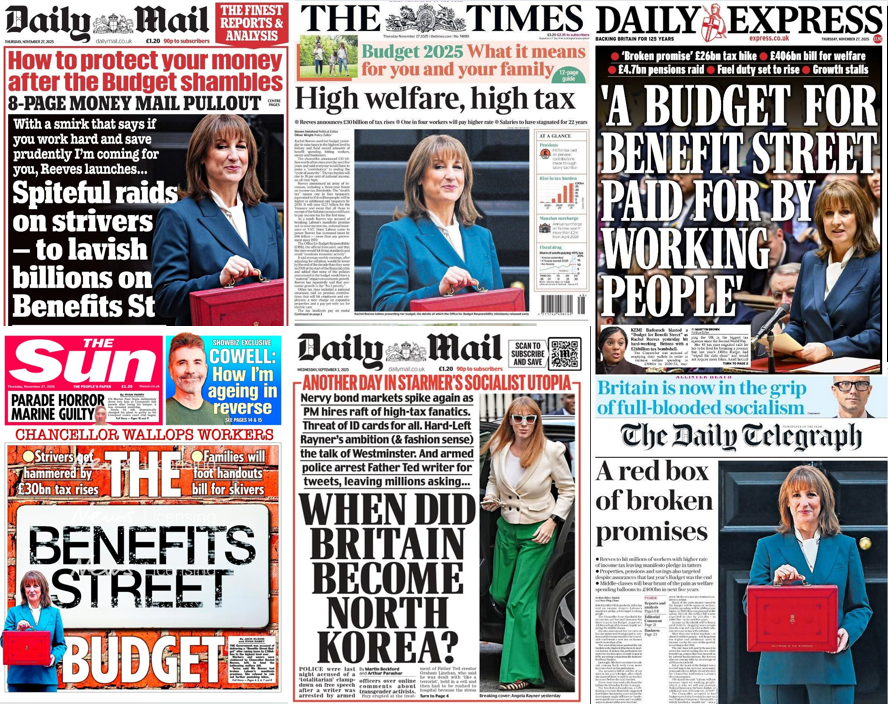
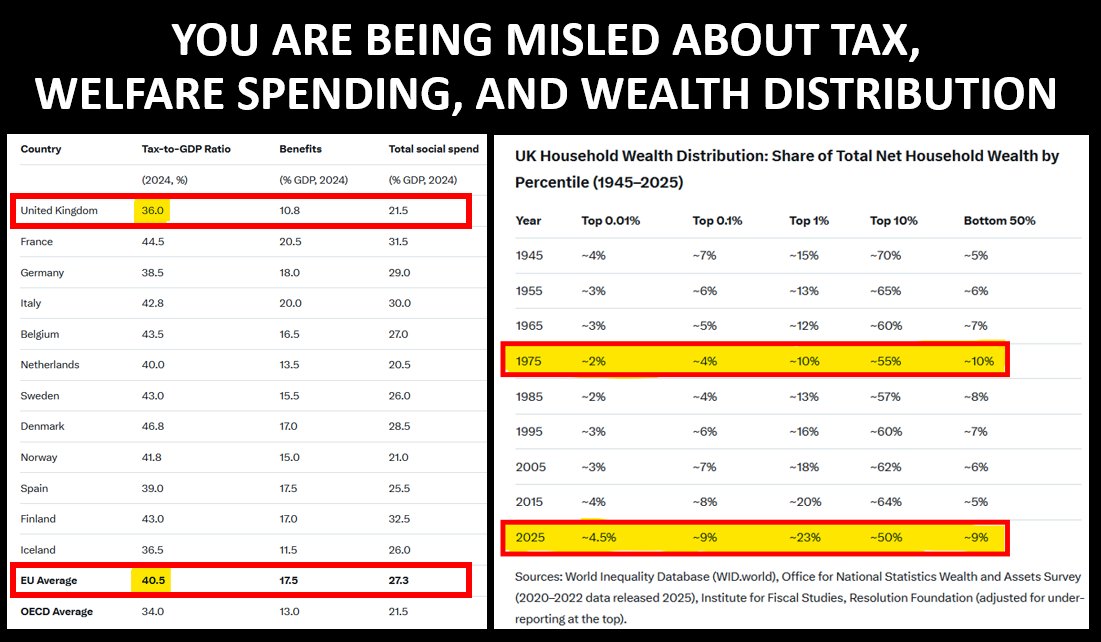
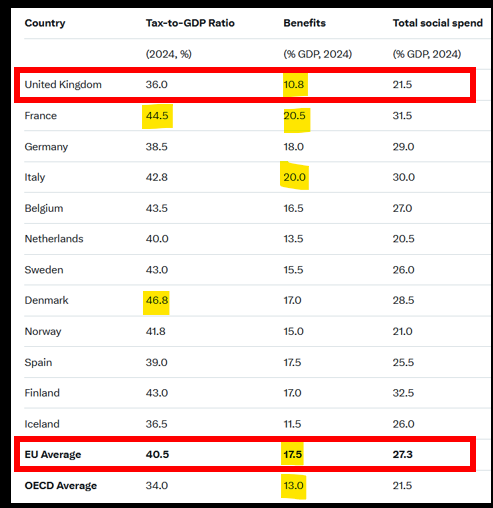
Worryingly, far right parties are influential in Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Serbia, Slovakia & Switzerland.
THREAD summary of this article:
annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.11…
THREAD summary of this article:
annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.11…
Far right parties are either radical or extremist in their ideology. Radicalism calls for “root and branch” reform of the political & economic system but does not explicitly seek the elimination of all forms of democracy. In contrast, extremism is directly opposed to democracy.
Far-right parties often have incentives to hide their extremism to avoid legal repercussions.
Radical parties are inherently “anti-system,” & In Europe, this system is typically a combination of liberal democracy & capitalism.
Radicalism & extremism occur on the left & right.
Radical parties are inherently “anti-system,” & In Europe, this system is typically a combination of liberal democracy & capitalism.
Radicalism & extremism occur on the left & right.
Left-wing variants oppose the capitalist system because it produces artificial levels of inequality. They seek a redistribution of power to alleviate inequality, espouse collective economic & social rights, & adopt an egalitarian, universalist, & often internationalist agenda.
In contrast, right-wing variants view inequality as part of the 'natural order'. Far right parties desire authoritarian systems, strictly ordered according to the “natural” differences that exist in society, as well as a law-&-order system that severely punishes deviant behavior.
Populism is central to the ideological appeal of many far right parties. Populism views society as divided into two homogeneous & antagonistic groups, “the pure people” & “the corrupt elite,” & argues that politics should reflect the general 'will of the people'.
Unlike elitism, populism considers the people to be the morally superior group & rejects the idea of meaningful divisions within “the people”, thus denying the need to compromise, simplifying political issues & dichotomizing them into black & white & calling for yes or no answers
According to populism, the elite is a parasitical class that enriches itself and systematically ignores the people's grievances. The immoral values of this elite stand in stark contrast to the wisdom and common sense of the people.
Populism's optimistic view of majority rule puts it at odds with liberal democracy, which requires the will of the majority to be constrained by constitutional checks & balances that protect minorities & individual rights.
Populism involves activating the people's resentment toward the existing power structure & dominant values in society. In Europe, the elite typically includes the established political parties, intellectuals, the economic upper class, and the media.
These groups are targeted for promoting liberal values related to individualism, multiculturalism, and internationalism, and for colluding to keep the people away from power. These groups are considered responsible for all of society's ills.
Populism can be inclusionary or exclusionary when it comes to imagining the people. Inclusionary populism, common among left-wing parties in Latin America, calls for material benefits & political rights to be extended to historically disadvantaged & excluded groups.
Exclusionary populism seeks to exclude certain groups from “the people” & thus limit their access to these same benefits & rights. Exclusionary populism is primarily associated with right-wing parties. The criteria for exclusion are almost always cultural, religious, &/or ethnic.
Nationalism is a common ideological feature on the far right.
Nationalism demands congruence between state & nation.
There are different varieties of nationalism.
Nationalism demands congruence between state & nation.
There are different varieties of nationalism.
Civic nationalism means the state is the primary unit of human organization, and individuals “choose” to be members of the civic nation by accepting a common set of cultural values and practices. The nation is culturally homogeneous, but not necessarily ethnically homogeneous.
Ethnic nationalism means membership in the nation is hereditary & often includes a shared language or religion. Ethnic nationalism focuses on repatriation as the main means of obtaining a monocultural state. Civic nationalism is inclusionary, ethnic nationalism is exclusionary.
'Nativism' combines nationalism with xenophobia in that it calls for states to comprise only members of an imagined 'native group' & considers non-native elements to be fundamentally threatening to the monocultural nation-state.
Non-native elements are identified on the basis of cultural traits such as race, ethnicity, or religion, & can include minorities from within the native ethnic group, such as gay people. Most far right parties, at least in public, have adopted an ethnopluralist form of nativism.
Ethnopluralism is more palatable to voters as it considers different cultures to be equal, but distinct & thus incompatible. Proponents claim to celebrate cultural differences, arguing differences must be protected from things like mass migration & cultural imperialism.
The cultural mixing occurring in multicultural societies is considered a form of national genocide. The goal is an ethnic democracy - an ethnocracy - where priority is given to 'protecting' one's own people: a culturally diverse world composed of monocultural nation-states.
Far right parties are often conflated with fascist parties. However, only a small subset of far right parties are ideologically fascist.
Traditionally, fascism was viewed as a purely negative phenomenon, a kind of “anti-ideology”—anticommunist, anticapitalist, and antiliberal.
Traditionally, fascism was viewed as a purely negative phenomenon, a kind of “anti-ideology”—anticommunist, anticapitalist, and antiliberal.
Fascism's core ideology combines extremism, populism, & nationalism, calling for a national rebirth & the revolutionary overthrow of the liberal democratic order, which is seen as decadent, corrupt, & against the common man. The goal is a new system, élite, & type of human being!
Most radical right parties desire a “return” to a mythical, ethnically homogeneous & idealized version of the past.
Greece's Golden Dawn & Hungary's Jobbik, with their youth movements & paramilitary organizations, rekindled concern about electoral forms of fascism.
Greece's Golden Dawn & Hungary's Jobbik, with their youth movements & paramilitary organizations, rekindled concern about electoral forms of fascism.
Explanations for the electoral success of far right parties focus on demand-side & supply-side factors.
Demand-side arguments emphasize the grievances that make far right parties appealing, including modernization grievances, economic grievances, & cultural grievances.
Demand-side arguments emphasize the grievances that make far right parties appealing, including modernization grievances, economic grievances, & cultural grievances.
Modernization grievances suggest there is a small amount of latent support for far right values which can be politicized & mobilized during moments of crisis that are related to the modernization process: individuals unable to cope with big societal changes turn to the far right.
Some argue that a shift from “materialist” values to “post-materialist” values which prioritize individual freedom & emphasize things such as multiculturalism, gender & racial equality, & sexual freedom, has created a reactionary backlash among 'traditionalists'.
Concerning economic grievances, in times of economic scarcity, social groups with conflicting material interests compete over limited resources: members of the ingroup blame the outgroup for economic problems, engendering prejudice & discrimination.
Far right parties exploit these economic grievances by linking immigrants & minorities to economic hardship.
Given the characteristics of the typical far right voter (often under-educated, unemployed male) evidence supports the economic grievance story at the individual level.
Given the characteristics of the typical far right voter (often under-educated, unemployed male) evidence supports the economic grievance story at the individual level.
Individuals likely to find himself competing with immigrants in the economic sphere are associated with holding stronger anti-immigrant attitudes, which are in turn, strongly linked with far right support.
The type of immigrant entering countries can be significant: noneconomic migrants, who arrive on the basis of political asylum or family reunification, are much more likely to put stress on local economies than economic migrants.
Economic scarcity creates greater incentives for the native population to support far right parties in statist economies where local authorities have control over the allocation of social services, housing, & employment than in market economies.
Cultural grievances accounting for far right success mobilise social identity theory: the idea that individuals have a natural tendency to associate with similar individuals, & an inherent desire for self-esteem causes people to perceive their ingroup as superior to outgroups.
Far right parties are able to exploit & encourage these natural tendencies by highlighting the (alleged) incompatibility of immigrant behavioral norms & cultural values with those of the native population.
Far right parties *always* mobilize grievances over immigration.
Far right parties *always* mobilize grievances over immigration.
But anti-immigrant attitudes do not automatically translate into anti-immigrant behavior. Many Europeans hold anti-immigrant attitudes, & yet relatively few vote for far right parties, possibly due to a widespread norm against prejudice & discrimination.
Evidence linking the size of immigrant groups to support for far-right parties is patchy: some studies find larger immigrant communities increase far right support, others find that the size of immigrant community has no effect. The press may play a part in perception management.
Most early literature on far right party success focused on demand-side explanations, but increasingly attention is being paid to supply-side factors such as the importance of having a favorable political opportunity structure, a strong party organization, & a winning ideology.
A political opportunity structure is something exogenous that determines the extent to which a political system is open to a political entrepreneur, & is shaped by its electoral rules, the nature of party competition, the media, and its political cleavage structure.
Electoral rules profoundly shape the political opportunity structure confronting far right parties. Small parties find it hard to emerge & succeed when the electoral system is nonpermissive. Disproportional systems translate votes into seats in a way that penalizes small parties.
This creates incentives for voters & elites to engage in strategic behavior. Supporters of small parties who do not wish to waste their vote have incentives to vote strategically for larger parties, & political entrepreneurs are incentivised to work within existing large parties.
Another claim - which may help to understand Britain's situation - is that far right parties face a favourable environment when mainstream parties converge in the policy space: voters turn to populist parties, including those on the far right, that criticize mainstream parties.
Because convergence depoliticizes the primary (economic) policy dimension, voters also turn to parties that compete on alternative policy dimensions. A second claim is that far right parties might fare better when mainstream right parties adopt centrist positions.
However, these ideas are challenged by the notion of 'issue salience' & 'issue ownership' - important because voters take account of whether a party is the most credible proponent of a particular issue when voting. Issue salience & issue ownership can, of course, be manipulated.
Mainstream parties can adopt three strategies toward the far right: dismissive, accommodative, or adversarial.
A dismissive strategy involves ignoring the issues raised by far right parties so as to convince voters that they are not salient.
A dismissive strategy involves ignoring the issues raised by far right parties so as to convince voters that they are not salient.
An accommodative strategy involves adopting a similar position to that of far right parties, like the Tories did with the Brexit Party. Although this increases the salience of the issues raised by far right parties, & the ownership of these issues is contested.
An adversarial strategy involves adopting a policy position that conflicts with that of far right parties. But this increases the salience of the issues raised by far right parties & strengthens them by emphasizing far right ownership of them.
When the far right presents a threat, the party that is most threatened has an incentive to adopt an accommodative strategy to try to weaken the far right, while its competitor mainstream party has an incentive to adopt an adversarial strategy to strengthen it. Both are risky.
Perhaps most significantly in Britain, the extent to which parties can communicate their issue positions to the public depends on the nature of the “discursive opportunity structure” created by the media - especially the print & broadcast news & politics media.
The media could ignore them & try to limit the salience of the issues they raise. But in Britain it's more common to cover the far right & frame it in either a positive or negative light. Both of these strategies increase the salience of the issues raised by the far right.
Some argue that the media's coverage of the far right has increased because of the proliferation of media outlets that compete for advertising revenue: commercial pressure to obtain larger audiences creates incentives for the media to adopt a sensationalist black & white style.
This media populism is common among the tabloid & quality press, even though the latter often has close ties to the political establishment. Others argue that the increased personalization of politics encourages the media to give greater coverage to leader-oriented parties.
Media attention is particularly helpful to far right parties early in their development because it allows them to disseminate their message to a wider audience than their typically limited organizational and financial resources might allow.
Media coverage can benefit far right parties by signaling their political viability and legitimizing their policy agenda. The most beneficial aspect of media coverage, though, comes from how it increases the salience of far right issues.
The British news media helps the far right not by giving it increased visibility, which would violate their journalistic norms, but simply by foregrounding the immigration and certain crime issues with which certain minorities are, rightly or wrongly, associated.
Dealignment processes have also helped far right parties. Globalization & postindustrializaton have led to a decline in class voting & partisan identification, increased political alienation among certain segments of the population, & reduced trust in the political elite.
These changes present the far right with expanded political opportunities by increasing electoral volatility and creating a pool of floating voters who make their electoral choices on the basis of their ideological and issue preferences rather than traditional partisan loyalties.
Economic crises may not benefit the far right as much as most people believe: across Europe, far right parties tend to receive most support from a coalition of small-business owners & white-collar workers on the right & blue-collar workers & the unemployed on the left.
This cross-class coalition is based much more on shared cultural values, rather than economic values, and, arguably, as a result, this loose coalition is threatened whenever the economic dimension becomes more salient.
Although a strong party organization may not be necessary for a party's electoral breakthrough, it is necessary for its electoral persistence. Many far right parties disappear shortly after making electoral inroads, often attributed to their lack of a strong party organization.
It's important to denounce the far right: if the political & social costs of far right activity are high, then only extremists & those with nothing to lose become members, resulting in an unappealing, poorly organized party with an extremist ideology.
In contrast, if the political and social costs of far right activity are low, then far right parties will be attractive to moderates and opportunists. This results in a well-organized party with a more moderate ideology that appeals to a broader set of voters.
Troublingly, there is now considerable evidence that far right parties are not simply protest parties and that their supporters are largely motivated by the same ideological and pragmatic considerations as those of other parties.
Far right parties have the ability to influence their electoral fortunes through the ideology they espouse.
Far right parties that retain an extremist (antidemocratic) ideology are almost always electorally weak.
So what is the 'winning formula' for the far right?
Far right parties that retain an extremist (antidemocratic) ideology are almost always electorally weak.
So what is the 'winning formula' for the far right?
The winning formula for far right parties involves combining a promarket position on the economic dimension with an authoritarian position on the cultural dimension, combining ethnonationalism & populist antiestablishment rhetoric, without being overtly racist or antidemocratic.
Most studies of far right support focus on the national level, but this hides significant subnational variation: high levels of variation are seen within constituencies.
Focusing solely on national-level, or even regional-level, characteristics may distort our understanding.
Focusing solely on national-level, or even regional-level, characteristics may distort our understanding.
Different factors affect different stages of far right success. The importance of the media for far right party success is certainly greater in the initial phases of far right party development, whereas organizational strength is important for electoral consolidation.
People like stories about good vs evil, heroes & villains, & voters want leaders who offer simple solutions & certainty - not leaders who recognise that societies, like individuals, are complex, multifaceted & ever-changing.
Voters want 'common sense', but it doesn't exist.
Voters want 'common sense', but it doesn't exist.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh