
DECT- An innovative CT technology, produces numerous imaging datasets at >1 energy level. The image reconstruction algorithms lead to pitfalls, the radiologists must be aware of. A #Tweetorial thread
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx
doi.org/10.1148/rg.202…
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx
doi.org/10.1148/rg.202…

DECT enables the synthesis of a wide array of images from a single acquisition because of the availability of CT projection data at more than one polychromatic energy level. Currently, six major approaches are used for DECT.
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx

@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx


VMC images-specific to DECT, available with all platforms at multiple keV levels starting from 40 keV. Images at 40–70 keV remain susceptible to pseudo enhancement similar to that on polychromatic single-energy CT images @RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx

#RGphx


MD Iodine images-These are commonly used for distinguishing between enhancing and non-enhancing lesions and improve visualization of both hyper- and hypo-vascular masses.
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx



@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx

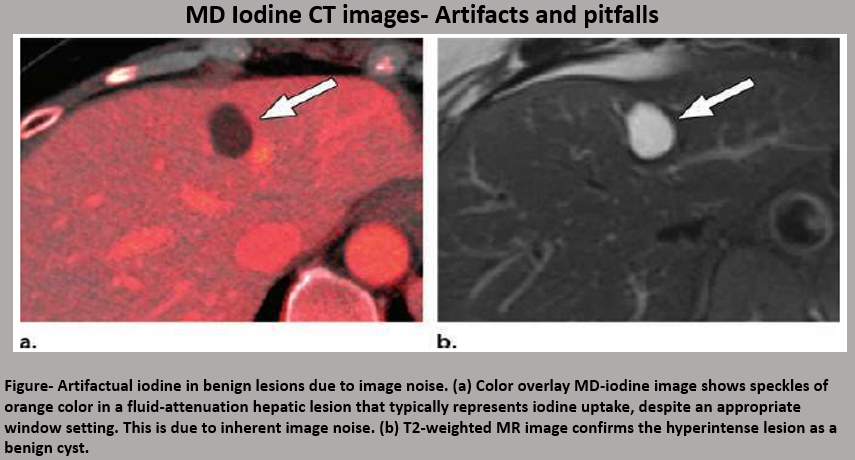


MD urate images-These images are used for evaluation of the presence of monosodium urate crystals in patients with gout and determining urinary stone composition to differentiate uric acid from non-uric acid stones.
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx

@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx


Virtual Unenhanced CT images are generated by subtracting Iodine from contrast-enhanced CT images. They are beneficial over True Unenhanced (TUE) images in the reduction in the radiation dose and improving workflow.
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx



@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx


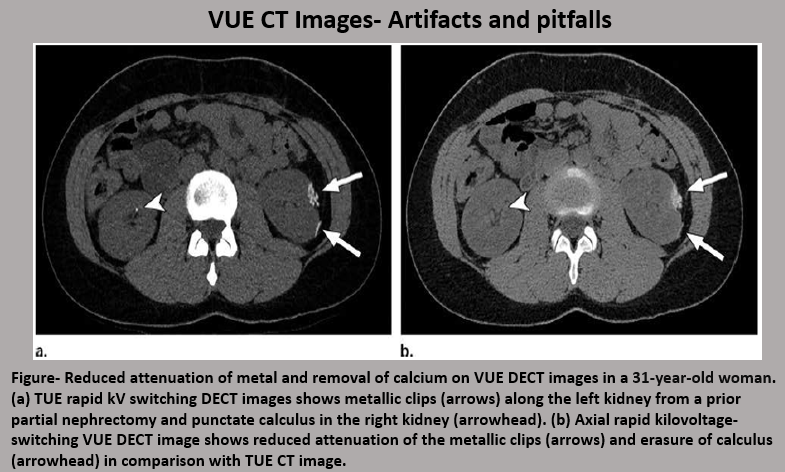
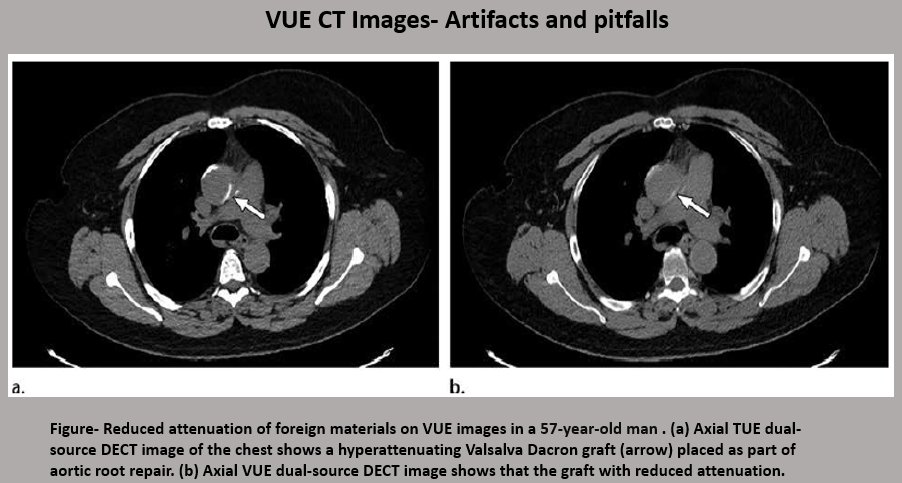
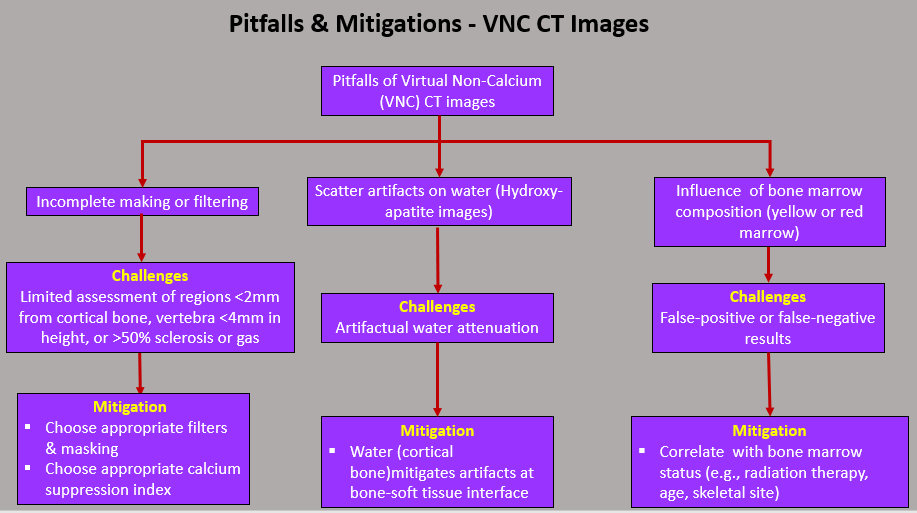
Virtual Non-Calcium (VNC) CT images-These images are mostly used for identification of bone-marrow edema, marrow malignancy, and disc displacements.
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx
@RadioGraphics @cookyscan1
#RGphx
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


