Campaign Against Italy Nonsense #CAIN
This thread presents data that strongly reject claims that 🇮🇹's problem has been a lack of fiscal discipline.
Italy is the pre-Corona world champion of fiscal consolidation - with problems for investment, growth and debt sustainability /1
This thread presents data that strongly reject claims that 🇮🇹's problem has been a lack of fiscal discipline.
Italy is the pre-Corona world champion of fiscal consolidation - with problems for investment, growth and debt sustainability /1

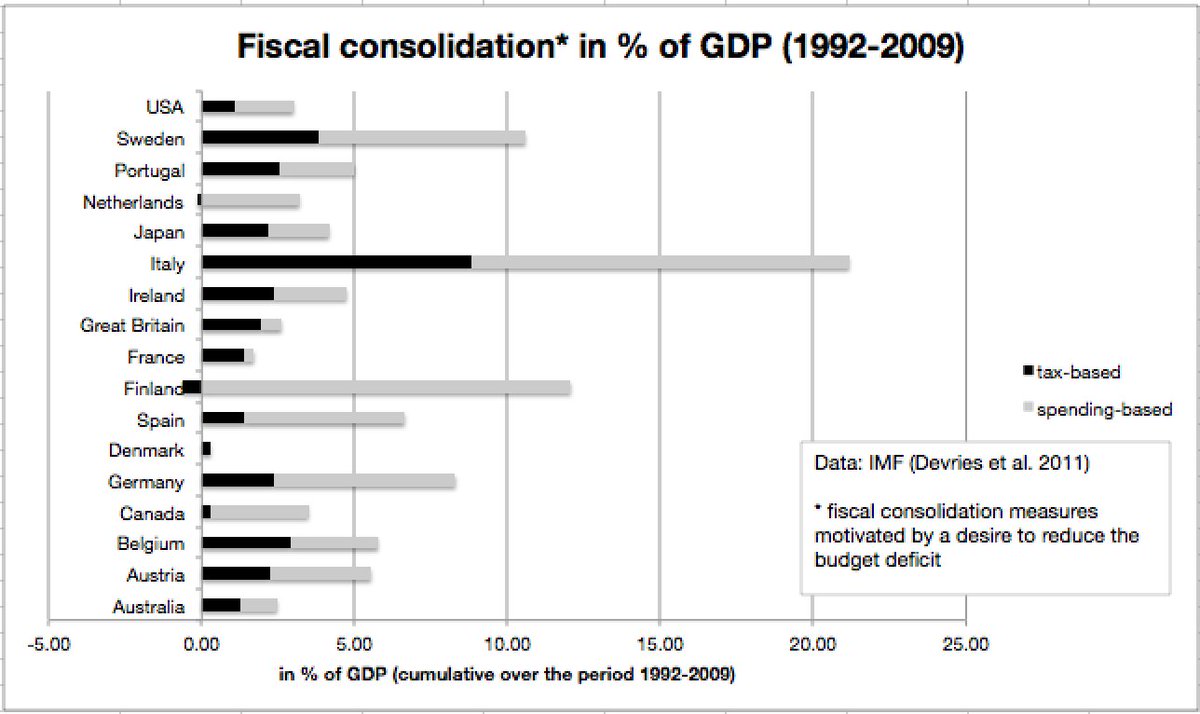
Many claim that Italy just didn't do enough fiscal consolidation to fix its public finances. In fact, fiscal consolidation in Italy was far more sizeable than in any other advanced country (from early 1990s up to financial crisis) - according to IMF data. /2 
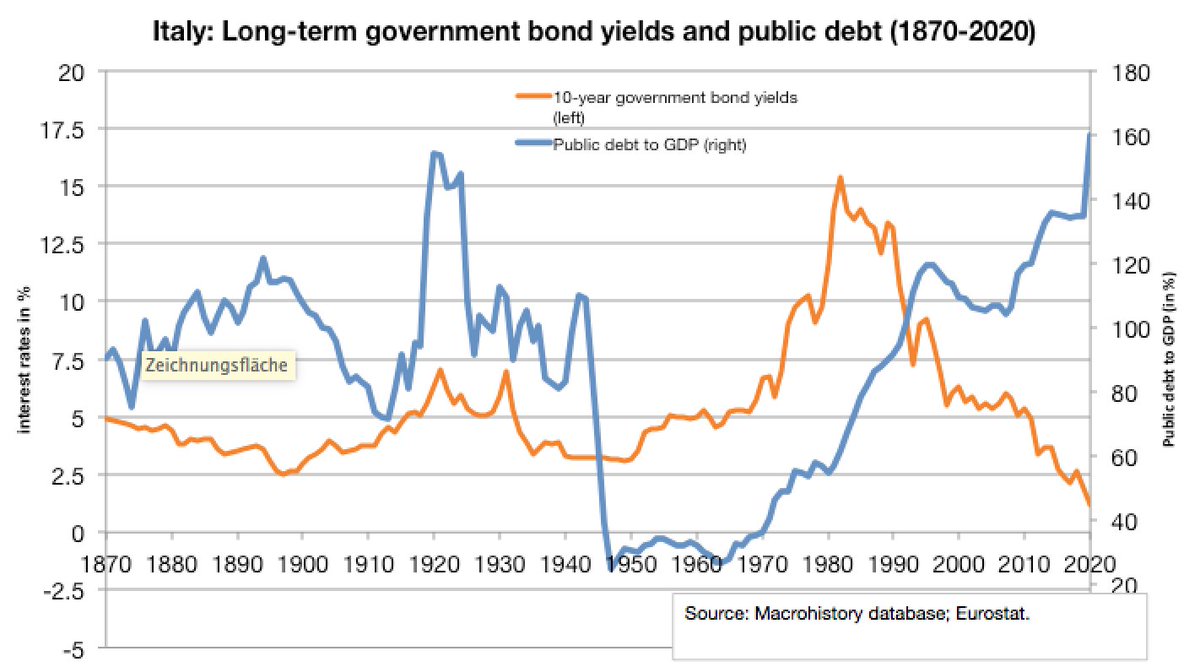
Due to Covid, Italy’s public debt has jumped to ~160% of GDP. It’s important to understand why Italy's public debt was high already before Corona: primarily because of the legacy of the 1980s and 1990s, when interest rates on government bonds skyrocketed. /3 
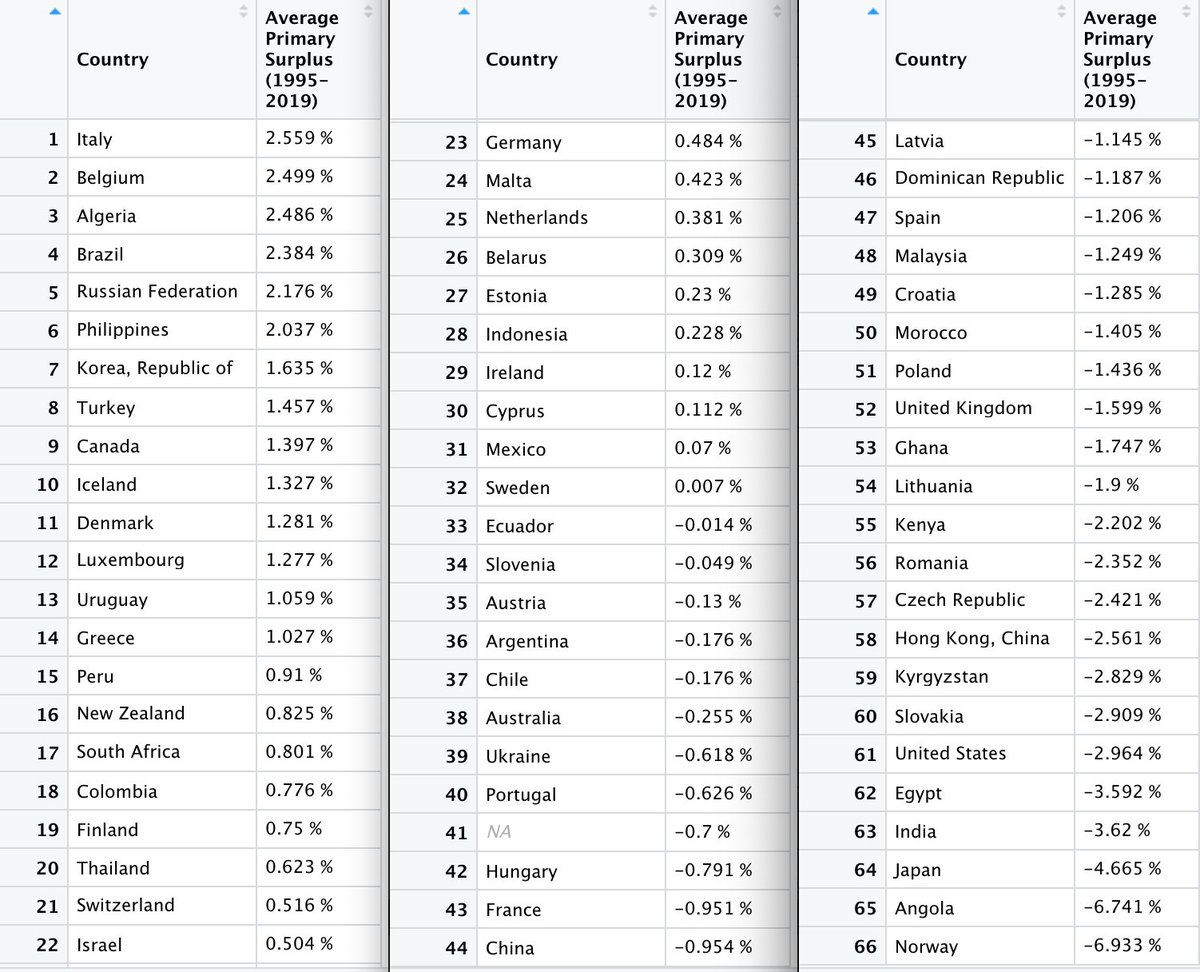
If we exclude the burden of interest payments, the Italian state is the world champion in running budget surpluses from the early 1990s up to Corona (“primary surpluses”). The "frugal" countries have shown much less fiscal discipline. /4 
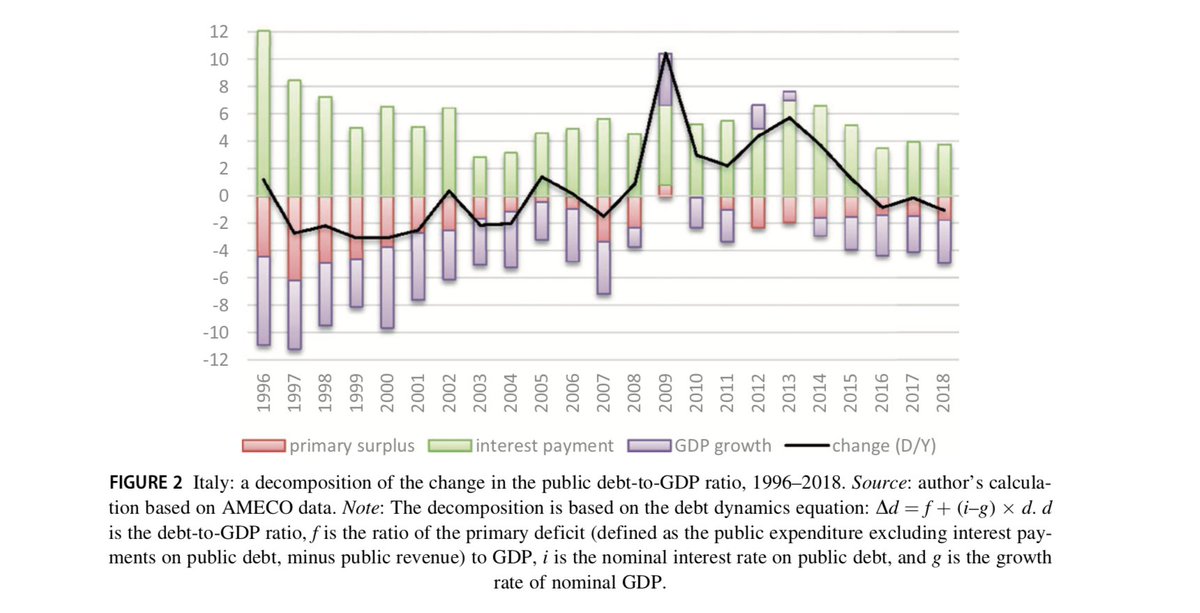
Running primary surpluses for 30 years had negative growth effects in Italy. Slow GDP growth relative to higher interest rates pushed up Italy's public-debt-to-GDP ratio. Too much fiscal consolidation is not good for debt sustainability. /4 
Public investment in Italy has fallen victim to fiscal austerity after the financial crisis. Italian net public investment has been cut more strongly than the €zone average, implying a decaying public capital stock - with negative short- and long-term growth effects. /5 
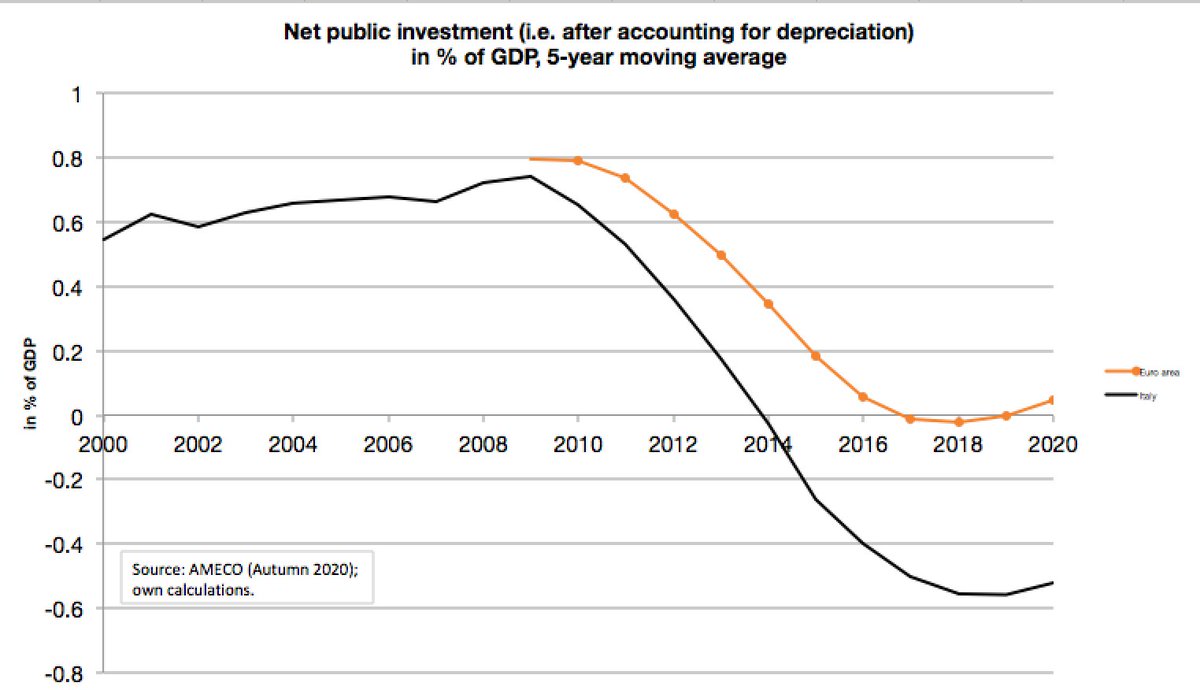
Italy's experience should serve as a cautionary tale: a one-sided focus on fiscal consolidation can lead to negative macroeconomic effects and relatively higher unemployment - and thus also undermine long-term debt sustainability. /6 

France and Spain will have similarly high government debt ratios after Corona as Italy had before Corona. Policy-makers must do their utmost to avoid driving these countries into a doom loop where fiscal consolidation undermines recovery and the achievement of fiscal targets. /7 
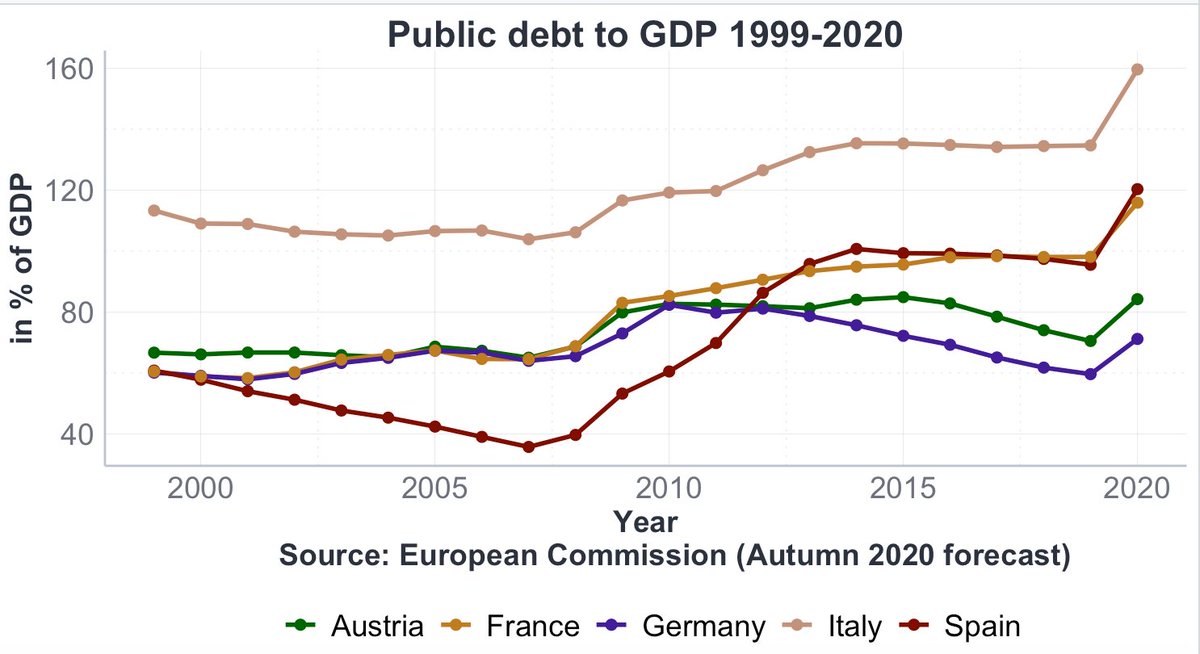
Successfully dealing with high public-debt-to-GDP ratios requires a departure from the mind-set that only running high primary surpluses can ensure debt sustainability. It's economically unsustainable - and also politically unsustainable, as I'll argue in a future thread. #CAIN 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















