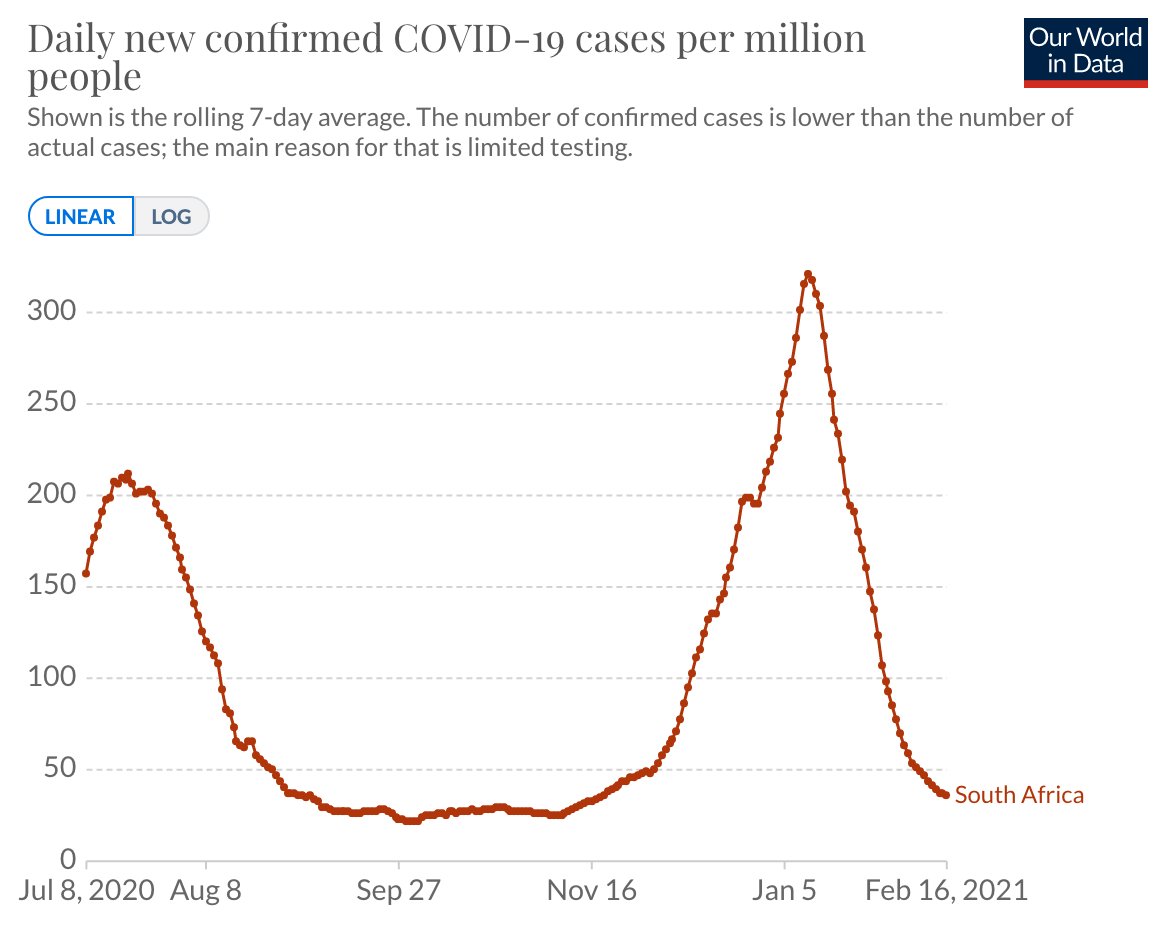
Shutting down half the economy and losing half a million lives anyway is totally unacceptable.
If we're gonna have 1 pandemic per decade—as we have this century—the U.S. must develop "institutional memory" to ensure this horror show never happens again.
theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/…
If we're gonna have 1 pandemic per decade—as we have this century—the U.S. must develop "institutional memory" to ensure this horror show never happens again.
theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/…
I asked experts what they considered the "original sin" of our COVID response.
To my surprise, there was strong unison: Our testing fiasco was the early failure that made every other failure worse and every hard decision harder.
theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/…
To my surprise, there was strong unison: Our testing fiasco was the early failure that made every other failure worse and every hard decision harder.
theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/…
With more and faster tests, the U.S. would have benefited, at least a little, in almost every thinkable capacity: We would have had greater and faster epidemiological knowledge, less stringent lockdowns, a more open economy, and fewer overall deaths. 

Having faced 2 pandemics in 21 years, it's a certainty that this will happen again. That's the bad news.
The good news is that, as bodies have immunological memory, societies have the capacity for institutional memory. They can learn from shame and death and loss. Let's learn.
The good news is that, as bodies have immunological memory, societies have the capacity for institutional memory. They can learn from shame and death and loss. Let's learn.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh