HTML tips - hidden gems.
🧵
🧵
1. The `loading=lazy` attribute
You can use the `loading=lazy` attribute to defer the loading of the image until the user scrolls to them.
You can use the `loading=lazy` attribute to defer the loading of the image until the user scrolls to them.

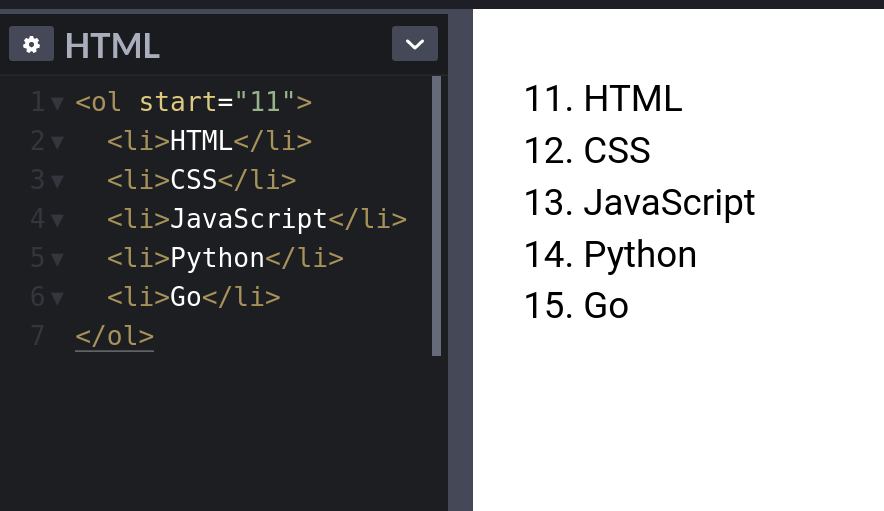
3. Ordered lists `start` attribute.
Use the `start` attribute to change the starting point for your ordered lists.
Use the `start` attribute to change the starting point for your ordered lists.
4. The `meter` element
You can use the `<meter>` element to display quantities. No JavaScript/CSS needed.
You can use the `<meter>` element to display quantities. No JavaScript/CSS needed.

5. `window.opener`
Pages opened with `target="_blank"` allow the new page to access the original’s `window.opener`. This can have security and performance implications. Include `rel="noopener"` or `rel="noreferrer"` to prevent this.
Pages opened with `target="_blank"` allow the new page to access the original’s `window.opener`. This can have security and performance implications. Include `rel="noopener"` or `rel="noreferrer"` to prevent this.

6. Base Element
If you want to open all links in the document in a new tab, you can use <base> element:
If you want to open all links in the document in a new tab, you can use <base> element:

7. Favicon cache busting
To refresh your website’s favicon you can force browsers to download a new version by adding ?v=2 to the filename.
This is especially helpful in production to make sure the users get the new version.
To refresh your website’s favicon you can force browsers to download a new version by adding ?v=2 to the filename.
This is especially helpful in production to make sure the users get the new version.

11. `download` attribute
You can use the `download` attribute in your links to download the file instead of navigating to it.
You can use the `download` attribute in your links to download the file instead of navigating to it.

12. Performance tip
Use the `.webp` image format to make images smaller and boost the performance of your website.
Use the `.webp` image format to make images smaller and boost the performance of your website.

If you liked this thread, maybe you'd love to bookmark it as a post.
P.S. You can find a few more tips there.
markodenic.com/html-tips/
P.S. You can find a few more tips there.
markodenic.com/html-tips/
If you're learning HTML, CSS or JavaScript be sure to follow me and never miss tips like this.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










