Today's ultrasound lecture by @mtabbut about ultrasound guided nerve blocks. #metroEUS #FOAMed #FOAMus #MedTwitter #POCUS @SLWerner_EM @DianeGramer @RJonesSonoEM @MetroHealth_EM 

Nerve blocks allow for the management of acute pain or painful procedures in the ED. Decreases need for opiates and sedations. Ultrasound guided vs blind decreases inadvertent vascular or nerve injection and allows targeted depot of anesthetic agent around the nerve. 





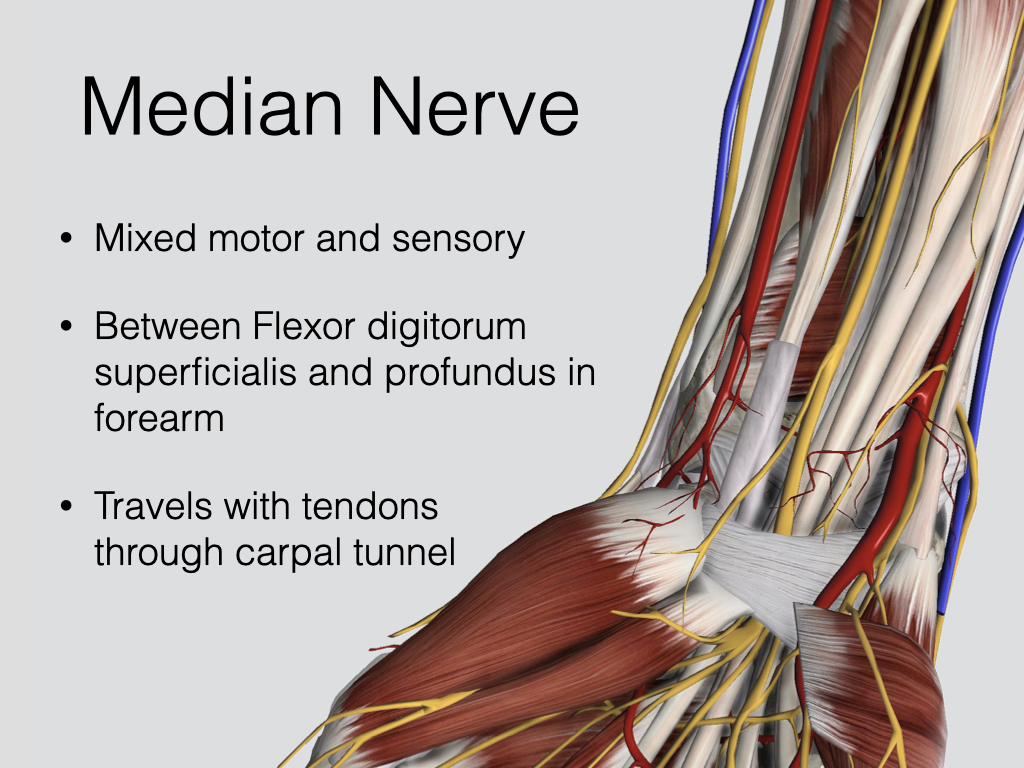
Characteristic appearance of a nerve = hyperechoic, honeycomb appearance, often triangular, may demonstrate anisotropy. 

Anesthetic agents work by blocking Na+ channels thereby preventing action potentials from generating a depolarization. 

Various agents will have different duration of actions and doses. Need to know the max dose. Lidocaine = 4.5mg/kg, Bupivocaine = 2 mg/kg. Determine your dose then dilute to reach the volume you need. 

Toxicity = Neuro and Cardiac. Think about what preventing depolarization of respective nerves will do. 





• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh