Today's COVID vaccination update*:
- Total shots given: 11,813,201
- Shots per 100 people: 31.1
- Shots reported today: 286,263
- Inventory: 6.5 days (at avg pace)
- Adults w/ 1+ Shots: 34.2%
Source: covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…
* Weekend updates are incomplete
- Total shots given: 11,813,201
- Shots per 100 people: 31.1
- Shots reported today: 286,263
- Inventory: 6.5 days (at avg pace)
- Adults w/ 1+ Shots: 34.2%
Source: covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…
* Weekend updates are incomplete

Canada is now up to 11.8 million shots given -- which is 86.2% of the total 13.7M doses available. Over the past 7 days, 1,046,684 doses have been delivered to provinces.
And so far 1,009k are fully vaccinated with two shots.
And so far 1,009k are fully vaccinated with two shots.

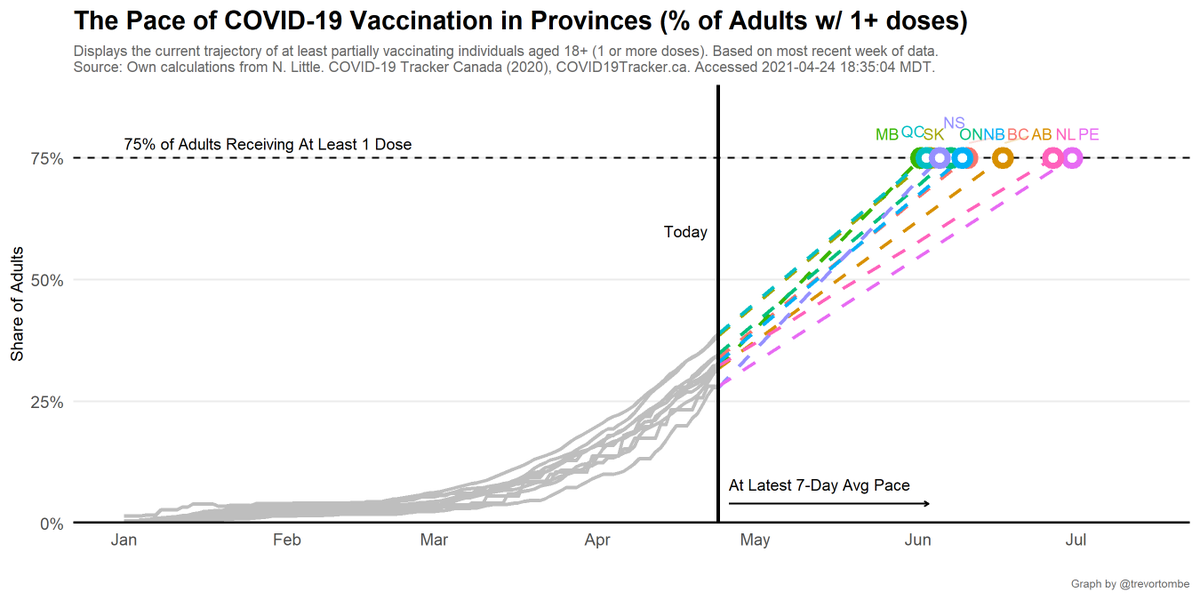
Canada's pace of vaccination:
Today's 286,263 shots given compares to an average of 290,470/day over the past week and 280,737/day the week prior.
- Pace req'd for 2 doses to 75% of Canadians by Sept 30: 284,269
- At current avg pace, we reach 75% by Sep 26
Today's 286,263 shots given compares to an average of 290,470/day over the past week and 280,737/day the week prior.
- Pace req'd for 2 doses to 75% of Canadians by Sept 30: 284,269
- At current avg pace, we reach 75% by Sep 26

Based on just the share of people with 1 or more doses (a weaker threshold), at Canada's current pace we reach 50% by May, and 75% by June 2021.
80% of *adults only* is reached by June 14
80% of *adults only* is reached by June 14

Turning to individual provinces, here's how each province's vaccination rate compared to the national average. Blue is above-average. Red is below. Dotted line is Canadian average rate. 

And here's total shots given and share of delivered doses used.
- Most shots given: YT at 111 doses per 100 people
- Fewest: NS at 27
- Highest share of delivered doses used: SK with 91%
- Lowest: NU with 64%
- Most shots given: YT at 111 doses per 100 people
- Fewest: NS at 27
- Highest share of delivered doses used: SK with 91%
- Lowest: NU with 64%

A more detailed look at provs/terrs:
- Highest overall: YT at 61% receiving at least one shot
- Most 1st doses only: QC at 31% receiving that shot
- Most Fully Vaccinated: YT at 51%
- Fewest Vaccinated: PE at 23%
- Highest overall: YT at 61% receiving at least one shot
- Most 1st doses only: QC at 31% receiving that shot
- Most Fully Vaccinated: YT at 51%
- Fewest Vaccinated: PE at 23%

Looking forward, here's time to reach 75% of *adults* w/ 1+ doses based on the latest 7-day average daily pace.
- MB fastest at 39 days.
- PE slowest at 67 days.
- MB fastest at 39 days.
- PE slowest at 67 days.
How does Canada compare to others? Currently, Canada ranks 6th out of 37 OECD countries in terms of the share of the population that is at least partially vaccinated. In terms of total doses per 100, Canada is 8th.
Source: ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinat…
Source: ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinat…

Canada/US comparison:
- Highest Prov: QC, 31.7% of pop w/ at least one dose
- Lowest Prov: PE, 22.9
- Highest State: NH, 59.2
- Lowest State: MS, 30.2
- Top CDN Terr: YT, 60.6
- Top US Terr: PW, 60.0
Sources: covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tra… and covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…
- Highest Prov: QC, 31.7% of pop w/ at least one dose
- Lowest Prov: PE, 22.9
- Highest State: NH, 59.2
- Lowest State: MS, 30.2
- Top CDN Terr: YT, 60.6
- Top US Terr: PW, 60.0
Sources: covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tra… and covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…

At Canada's latest 7-day avg daily pace, the share of people w/ 1 or more doses rises by 0.73% per day. The US rises by 0.39% per day.
- Projected out, we reach 75% 20 days before the US.
- We match the US share in 40 days.
- Reaching the current US share takes 18 days.
- Projected out, we reach 75% 20 days before the US.
- We match the US share in 40 days.
- Reaching the current US share takes 18 days.

But that's 1+ doses, here's a comparison of daily shots given per 100 people. In Canada, this rises by 0.76 per day. The US rises by 0.85 per day.
- Projected out, we reach 100 doses 52 days after the US.
- Reaching the current US rate takes 48 days.
- Projected out, we reach 100 doses 52 days after the US.
- Reaching the current US rate takes 48 days.

Finally, here's a selection across several metrics/groups of how Canada ranks globally. Pick your preferred measure! 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh