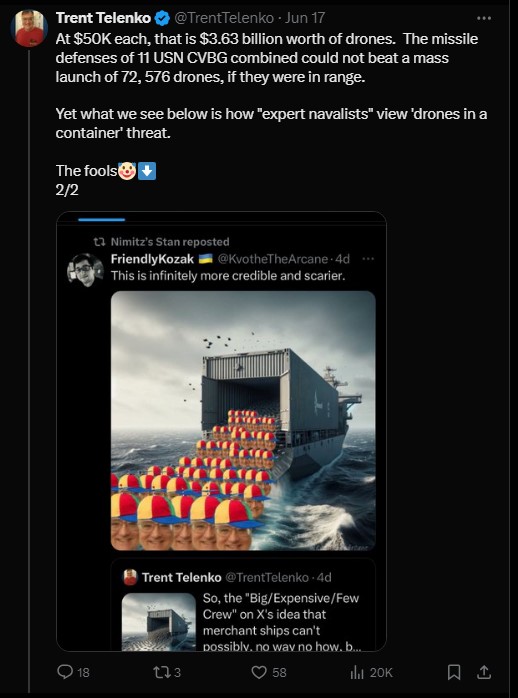
One of the crying shames of academic WW2 history is it's unwillingness to address what we now call electronic warfare.
The Ham radio community is both different & far more useful.
See:
German WW2 ECM
(Electronic Countermeasures)
Adam Farson
VA7OJ
ab4oj.com/nsprog/german_…
The Ham radio community is both different & far more useful.
See:
German WW2 ECM
(Electronic Countermeasures)
Adam Farson
VA7OJ
ab4oj.com/nsprog/german_…
Now to explain why Ham radio guys can be a whole lot more useful that academic & archival historians** for EW -- the 2 August 1939, LZ130 Graf Zeppelin flight.
**Note: Every field has it's weak points. Extremely few academic tract historians are radio geeks...
2/
**Note: Every field has it's weak points. Extremely few academic tract historians are radio geeks...
2/
...and being a radio geek is a better skill set for the subject matter than most PhD's not awarded to Dr Alfred Price.
LZ130 flew one of the first ELINT missions ever, against the UK Chain Home system with 25 RF engineers aboard.
3/
LZ130 flew one of the first ELINT missions ever, against the UK Chain Home system with 25 RF engineers aboard.
3/
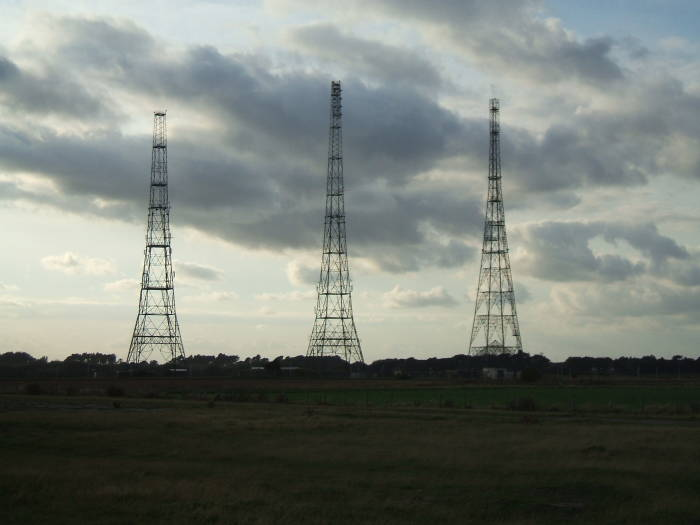

along with the engineers, LZ130 had broadband radio receivers covering 2 -100 MHz.
Luftwaffe General Wolfgang Martini thought that the British CH towers might be radar and put together this flight and an earlier on in May 1940.
Neither found radar.
4/
Luftwaffe General Wolfgang Martini thought that the British CH towers might be radar and put together this flight and an earlier on in May 1940.
Neither found radar.
4/

The German engineers believed that Britain was developing radars in the same 100-150 MHz
range as Germany, so the team concentrated on that band.
Up to this point, we are in the "standard narrative" historiography.
5/
range as Germany, so the team concentrated on that band.
Up to this point, we are in the "standard narrative" historiography.
5/
This is where Adam Farson being a Ham radio guy comes in for "non-standard" history.
He understands the affect of the Mains cycle or powerline hum.
This hum from the UK power grid played a huge role
6/
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mains_hum
He understands the affect of the Mains cycle or powerline hum.
This hum from the UK power grid played a huge role
6/
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mains_hum
...in why General Martini's boffins missed the CH signal.
The Luftwaffe signals boffins picked up pulsed signals of CH modulated by 'mains hum' in the 20-50 MHz range, but discounted these as ionosonde signals or mains powerline hum from the UK national grid.
7/
The Luftwaffe signals boffins picked up pulsed signals of CH modulated by 'mains hum' in the 20-50 MHz range, but discounted these as ionosonde signals or mains powerline hum from the UK national grid.
7/
According to Mr. Farson, the British grid was synchronous.
To avoid grid electromagnetic interference (EMI) interference, the 250 kW peak pulse CH transmitters were keyed from different points on the 50 Hz mains cycle to avoid co-channel interference between stations.
8/
To avoid grid electromagnetic interference (EMI) interference, the 250 kW peak pulse CH transmitters were keyed from different points on the 50 Hz mains cycle to avoid co-channel interference between stations.
8/
This clever synchronization scheme of the CH radar builders to avoid the UK National Grid's mains cycle/powerline hum from screwing up their radar ended up camouflaging the CH signal from the Luftwaffe radar signals intercept boffins.
9/
9/

Where have you heard that bit of electronic warfare history in the "Battle of Britain" narrative?
Even Dr Alfred Price and Dr. R. V. Jones missed this one.
/End
Even Dr Alfred Price and Dr. R. V. Jones missed this one.
/End
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh