Today's COVID vaccination update:
- Total shots given: 16,258,155
- Shots per 100 people: 42.8
- Shots reported today *: 340,600
- Inventory: 6.4 days (at avg pace)
- Adults w/ 1+ Shots: 47.5%
Source: covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…
* Includes some weekend doses
- Total shots given: 16,258,155
- Shots per 100 people: 42.8
- Shots reported today *: 340,600
- Inventory: 6.4 days (at avg pace)
- Adults w/ 1+ Shots: 47.5%
Source: covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…
* Includes some weekend doses

Canada is now up to 16.3 million shots given -- which is 88.9% of the total 18.3 million doses available. Over the past 7 days, 3,202,370 doses have been delivered to provinces.
And so far 1.3 million are fully vaccinated with two shots.
And so far 1.3 million are fully vaccinated with two shots.

Canada's pace of vaccination:
Today's 340,600 shots given compares to an average of 315,238/day over the past week and 249,101/day the week prior.
- Pace req'd for 2 doses to 75% of Canadians by Sept 30: 284,992
- At current avg pace, we reach 75% by Sep 16
Today's 340,600 shots given compares to an average of 315,238/day over the past week and 249,101/day the week prior.
- Pace req'd for 2 doses to 75% of Canadians by Sept 30: 284,992
- At current avg pace, we reach 75% by Sep 16
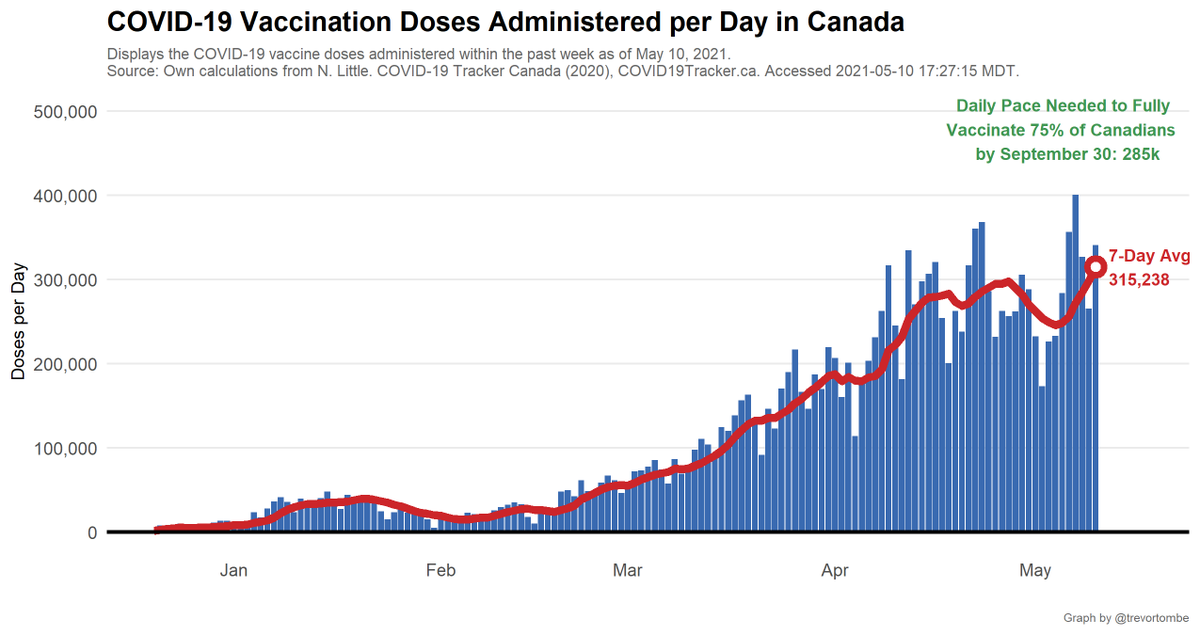
Based on the share of people with 1 or more doses (a weaker threshold), at Canada's current pace we reach 50% by May 23 and 75% by June 24. We reach 75% of *adults only* (age 16+) by June 7.
Gray lines are past projections. This illustrates the extent of recent changes.
Gray lines are past projections. This illustrates the extent of recent changes.

Recent modeling suggests health rules may be safely eased once 75% of adults have at least one dose and 20% have two canada.ca/content/dam/ph…
This requires ~30M shots. We're on pace for that by June 22.
But deliveries are accelerating. If shots keep up, could be early-June
This requires ~30M shots. We're on pace for that by June 22.
But deliveries are accelerating. If shots keep up, could be early-June

Turning to individual provinces, here's total shots given and share of delivered doses used.
- Most shots given: YT at 119 doses per 100 people
- Fewest: NS at 37
- Highest share of delivered doses used: SK with 97%
- Lowest: NU with 66%
- Most shots given: YT at 119 doses per 100 people
- Fewest: NS at 37
- Highest share of delivered doses used: SK with 97%
- Lowest: NU with 66%

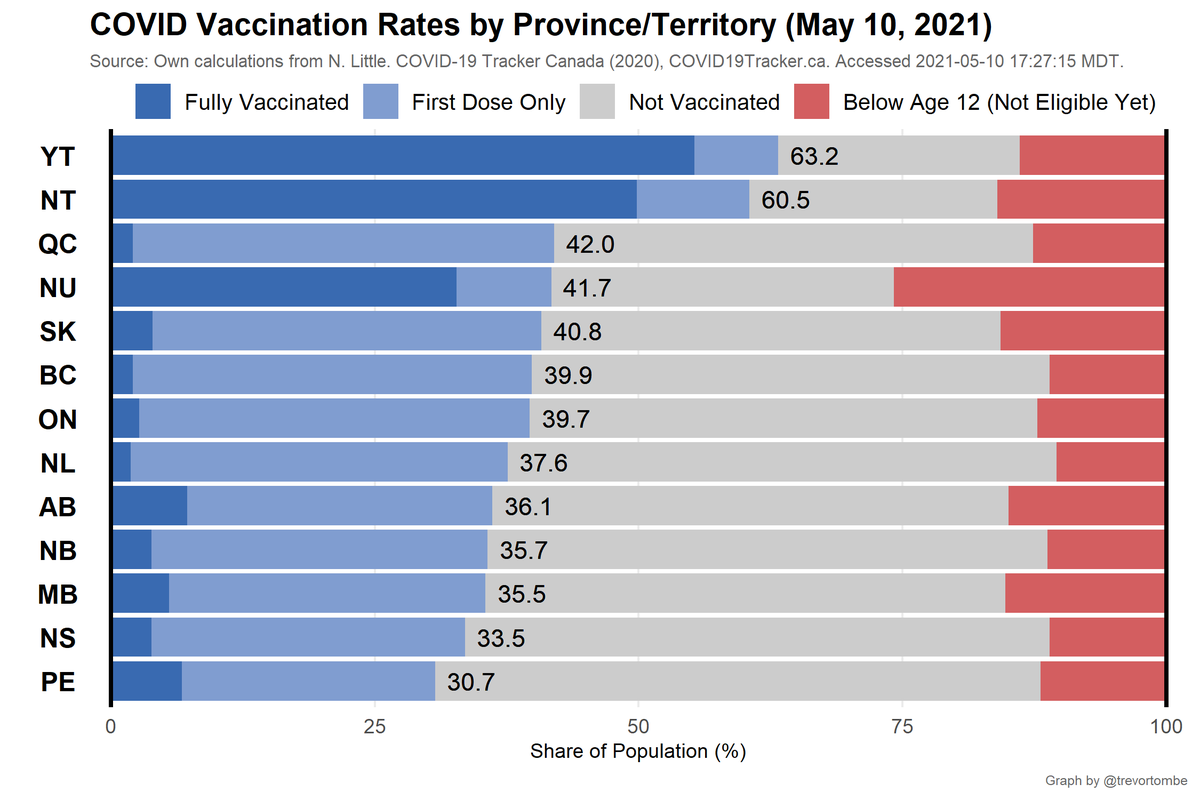
A more detailed look at provs/terrs:
- Highest overall: YT at 63% receiving at least one shot
- Most 1st doses only: QC at 40% receiving that shot
- Most Fully Vaccinated: YT at 55%
- Fewest Vaccinated: PE at 31%
- Highest overall: YT at 63% receiving at least one shot
- Most 1st doses only: QC at 40% receiving that shot
- Most Fully Vaccinated: YT at 55%
- Fewest Vaccinated: PE at 31%
How does Canada compare to others? Currently, Canada ranks 7th out of 37 OECD countries in terms of the share of the population that is at least partially vaccinated. In terms of total doses per 100, Canada is 7th.
Source: ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinat…
Source: ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinat…

Canada/US comparison.
Received at least one dose:
- Top Prov: QC, 42.0% of pop
- Top State: VT, 61.9
- Top Terr: YT, 63.2
Fully vaccinated:
- Top Prov: AB, 7.2% of pop
- Top State: CT, 45.0
- Top Terr: YT, 55.3
Sources: covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tra… and covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…
Received at least one dose:
- Top Prov: QC, 42.0% of pop
- Top State: VT, 61.9
- Top Terr: YT, 63.2
Fully vaccinated:
- Top Prov: AB, 7.2% of pop
- Top State: CT, 45.0
- Top Terr: YT, 55.3
Sources: covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tra… and covid19tracker.ca/vaccinationtra…

At Canada's latest 7-day avg daily pace, the share of people w/ 1 or more doses rises by 0.78% per day. The US rises by 0.23% per day.
- Projected out, we reach 75% 81 days before the US.
- We match the US share in 12 days.
- Reaching the current US share takes 8 days.
- Projected out, we reach 75% 81 days before the US.
- We match the US share in 12 days.
- Reaching the current US share takes 8 days.

But that's 1+ doses, here's a comparison of daily shots given per 100 people. In Canada, this rises by 0.83 per day. The US rises by 0.64 per day.
- Projected out, we reach 100 doses 36 days after the US.
- Reaching the current US rate takes 43 days.
- Projected out, we reach 100 doses 36 days after the US.
- Reaching the current US rate takes 43 days.

Finally, here's a selection across several metrics/groups of how Canada ranks globally. Pick your preferred measure! 

That's it... but if you're hungry for more, I've thrown together a collection of international projections and comparisons to Canada (and more) at trevortombe.github.io/covidgraphs/in…
The couple weeks will be big, and soon we'll see the second dose rates accelerate rapidly too! 💉



The couple weeks will be big, and soon we'll see the second dose rates accelerate rapidly too! 💉




• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh