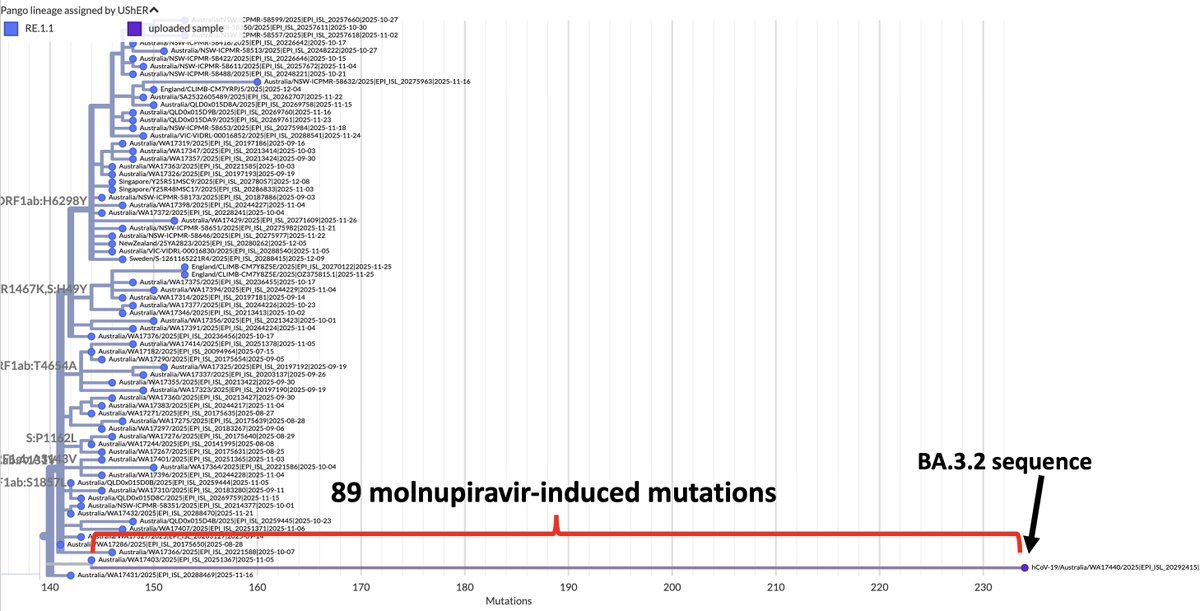
1/ This is unreal. The study title is "Same-day SARS-CoV-2 antigen test screening in an indoor mass-gathering live music event: a randomised controlled trial." It is being cited as evidence that rapid antigen tests can make social events safe. But there are a couple problems...
https://twitter.com/TheLancetInfDis/status/1398047212576378889
2/ They gave rapid tests to over 1000 people and randomly divided those who tested negative into two groups. One went to a concert, where they were encouraged to dance and sing, and the others stayed home. I encourage you to read the entire abstract in the 2 pictures below. 



3/ Results: None who went to the concert tested positive for Covid eight days later, but two of those who stayed home tested positive. Yay for rapid tests, right? Not exactly. 

4/ You see, when they screened study participants with rapid antigen tests before the concert, NONE tested positive. That is to say, the rapid tests had ZERO effect on the results here. 

5/ One would think this would merit a mention in the abstract, but the study authors apparently didn't think so. The study title indicates it's an RCT of rapid test screening for an indoor concert, yet there's no mention in the abstract that the rapid tests were irrelevant.
6/ Perhaps even more astonishing, nowhere in the discussion section of the paper do they mention that none of the rapid antigen tests were positive and that therefore no one was screened out of participating in the concert. Instead, they sing the praises of rapid tests. 





7/ The authors do not let a little thing like the total irrelevance of the rapid antigen tests to the study's results prevent them from concluding their study provides evidence of the effectiveness of rapid tests as screening tools for indoor social events. You can't make it up. 

8/ Though not mentioned in the study abstract, we are eventually told that concert attendees were required to wear an N95 mask at all times, except when drinking. I'm 100% for wearing N95 masks, but this is not likely to ever be adapted as policy in the real world. 

9/ The ventilation was also extraordinarily good at the concert, maintaining CO2 at or below 800 ppm, much lower than the typical school classroom. 

10/ In other words, the study was designed to give a result indicating the effectiveness of rapid antigen tests, & despite its failure to provide that result, the authors manage to come to the conclusion they wanted anyway. 

11/ I should add that I'm open to the possibility that rapid antigen tests could be effective in preventing Covid transmission. But this study is a joke. It's disturbing that it was published by the Lancet & is apparently being taken seriously by prominent experts.
Addendum/ This study was funded by the events company Primavera Sound Group and YoMeCorono, which I know nothing about, but which appears to be funded by dozens of (mostly) Spanish corporations. yomecorono.com/en/empresas-qu… 



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh