Today's COVID vaccine update:
- Shots reported today: 411,460
- Total shots: 24,933,524
- Age 12+ w/ a Shot: 67.9%
- Age 18+ w/ a Shot: 71.3% (est)
- Shots per 100 people: 65.6
- Inventory: 8.7 days
More: trevortombe.github.io/covidgraphs/
- Shots reported today: 411,460
- Total shots: 24,933,524
- Age 12+ w/ a Shot: 67.9%
- Age 18+ w/ a Shot: 71.3% (est)
- Shots per 100 people: 65.6
- Inventory: 8.7 days
More: trevortombe.github.io/covidgraphs/

Detailed data on vaccination rates by age comes with a long lag. I construct my own estimates. Here's the latest:
- Those 60+: 88.9% have at least one dose and 12.3% have two
- 18-59: it's 63.6% and 6.3%
- Adults: 71.3% and 8.1%
- Those 60+: 88.9% have at least one dose and 12.3% have two
- 18-59: it's 63.6% and 6.3%
- Adults: 71.3% and 8.1%

In total, Canada is now up to 24.9 million shots given -- which is 88.6% of the total 28.1 million doses available. Over the past 7 days, 2,161,060 doses have been delivered to provinces.
And so far 2.4 million are fully vaccinated with two shots.
And so far 2.4 million are fully vaccinated with two shots.

Canada's pace of vaccination:
Today's 411,460 shots given compares to an average of 369,459/day over the past week and 357,964/day the week prior.
- Pace req'd for 2 doses to 75% of Canadians by Sept 30: 269,567
- At current avg pace, we reach 75% by Aug 28
Today's 411,460 shots given compares to an average of 369,459/day over the past week and 357,964/day the week prior.
- Pace req'd for 2 doses to 75% of Canadians by Sept 30: 269,567
- At current avg pace, we reach 75% by Aug 28

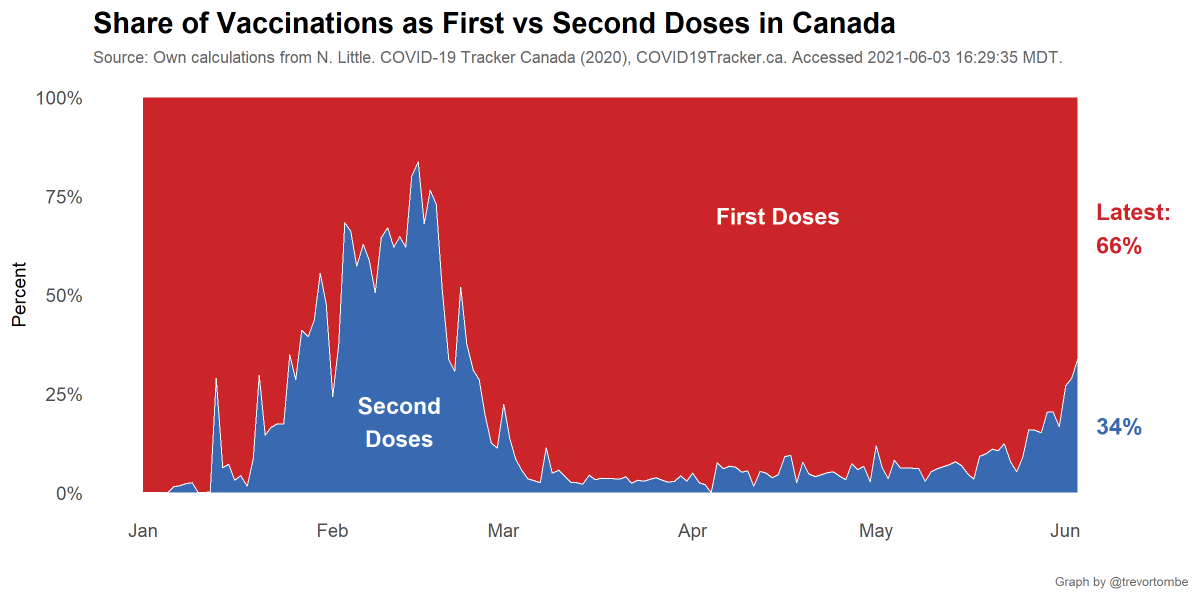
Canada's pace of vaccinations remains high, though shots are shifting towards more second doses. Currently, one in three shots is a second dose. Great to see!
This will slow the pace of % of pop with a first dose, which we've also gradually seen.
This will slow the pace of % of pop with a first dose, which we've also gradually seen.
Based on the share of people with 1 or more doses at Canada's current pace we reach 75% by June 24. We reach enough for 75% of those age 12+ by .
Gray lines are past projections.
Gray lines are past projections.

What about two doses? Here's when we'll have enough doses to reach different points:
- 75% of age 12+ w/ 1+ dose and 20% w/ 2: June 20
- 75% of 12+ w/ 2 doses: August 9
- 75% of age 12+ w/ 1+ dose and 20% w/ 2: June 20
- 75% of 12+ w/ 2 doses: August 9

Dose projections are informative, but effective protection is lower than the share with a shot. One dose is less effective than two, plus effects lag and are uncertain. Roughly, current "coverage" is ~19-39%
Useful research summary: publichealthontario.ca/-/media/docume…
Useful research summary: publichealthontario.ca/-/media/docume…

Turning to individual provinces, here's total shots given and share of delivered doses used.
- Most shots given: YT at 128 doses per 100 people
- Fewest: NL at 61
- Highest share of delivered doses used: NB with 94%
- Lowest: NU with 64%
- Most shots given: YT at 128 doses per 100 people
- Fewest: NL at 61
- Highest share of delivered doses used: NB with 94%
- Lowest: NU with 64%
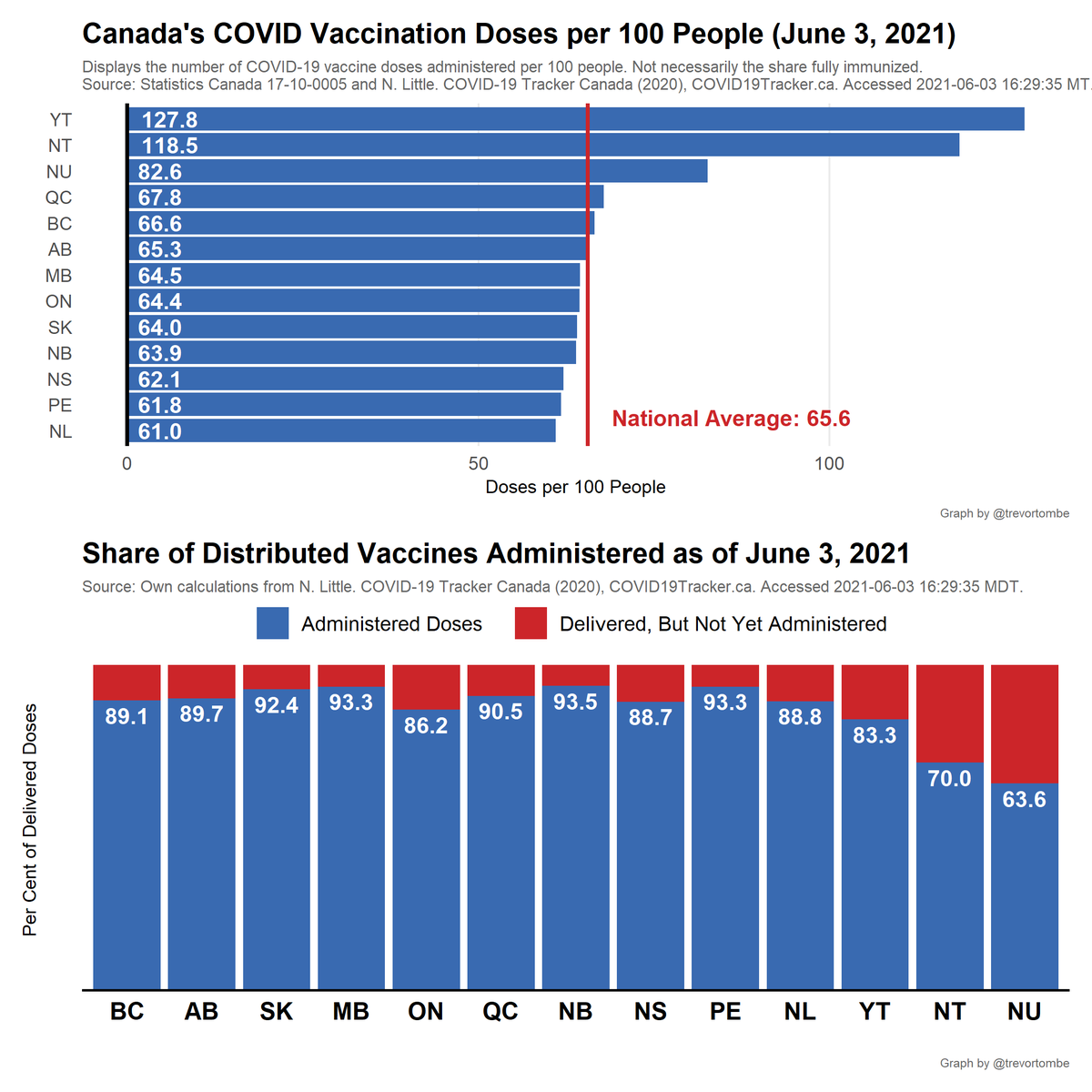
A more detailed look at provs/terrs:
- Highest overall: YT at 68% receiving at least one shot
- Most 1st doses only: BC at 58% receiving that shot
- Most Fully Vaccinated: YT at 60%
- Fewest Vaccinated: NU at 44%
- Highest overall: YT at 68% receiving at least one shot
- Most 1st doses only: BC at 58% receiving that shot
- Most Fully Vaccinated: YT at 60%
- Fewest Vaccinated: NU at 44%

Looking forward, here's time to reach 75% of people age 12+ w/ 1+ doses based on the latest 7-day average daily pace.
- QC fastest at 4 days.
- SK slowest at 18 days.
- QC fastest at 4 days.
- SK slowest at 18 days.
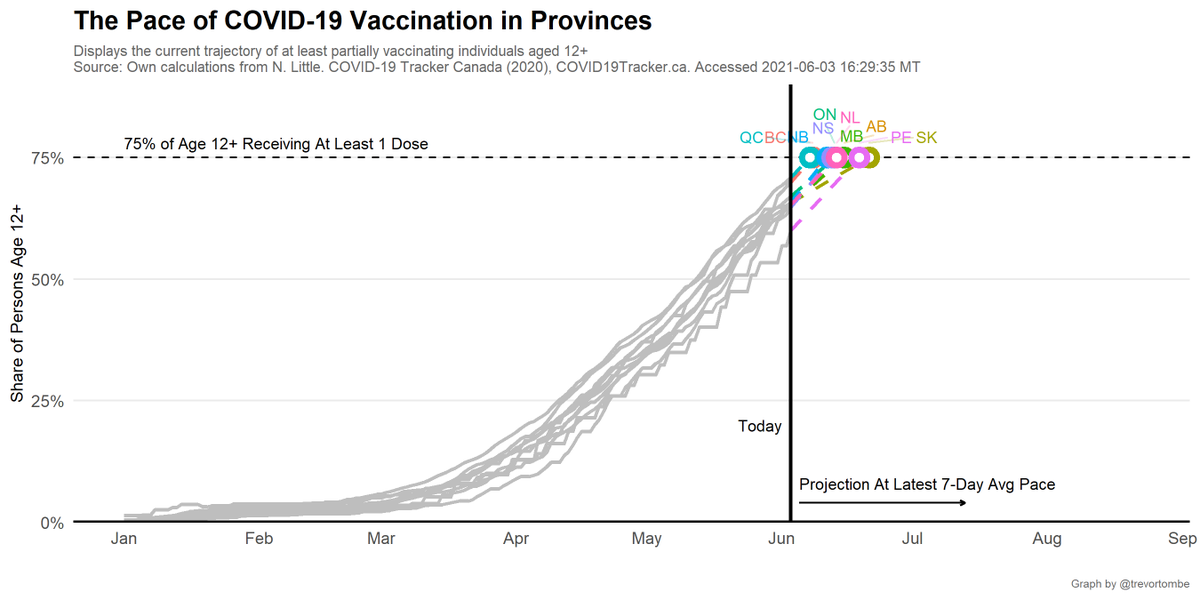
How does Canada compare to others? Here's all 37 OECD (i.e., developed) countries:
- Share of pop. w/ at least one dose: Canada ranks 2nd
- Total doses per 100: 7th
- Fully vaccinated: 32nd
- Share of pop. w/ at least one dose: Canada ranks 2nd
- Total doses per 100: 7th
- Fully vaccinated: 32nd

Going forward, here's a cdn/usa comparison of total doses per 100 people.
- In Canada, this rises by 0.97 per day. The US rises by 0.37 per day.
- Projected out, we match the US in 40 days
- Reaching the current US rate takes 25 days.
- In Canada, this rises by 0.97 per day. The US rises by 0.37 per day.
- Projected out, we match the US in 40 days
- Reaching the current US rate takes 25 days.

The gap in total doses per 100 with the US is closing fast. So too will the gap in second shots!
Today is the first day our average pace of increasing the number of second doses exceeded the US. Watch these two lines cross very very soon.
Today is the first day our average pace of increasing the number of second doses exceeded the US. Watch these two lines cross very very soon.

Of course, there's lots of countries and many ways to compare. Here's a selection across several metrics/groups of how Canada ranks globally. Pick your preferred measure! 

Fin.
Note: all graphs (and more!) are automatically updated and posted online for later review and easy sharing at the following site: trevortombe.github.io/covidgraphs/
Note: all graphs (and more!) are automatically updated and posted online for later review and easy sharing at the following site: trevortombe.github.io/covidgraphs/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh