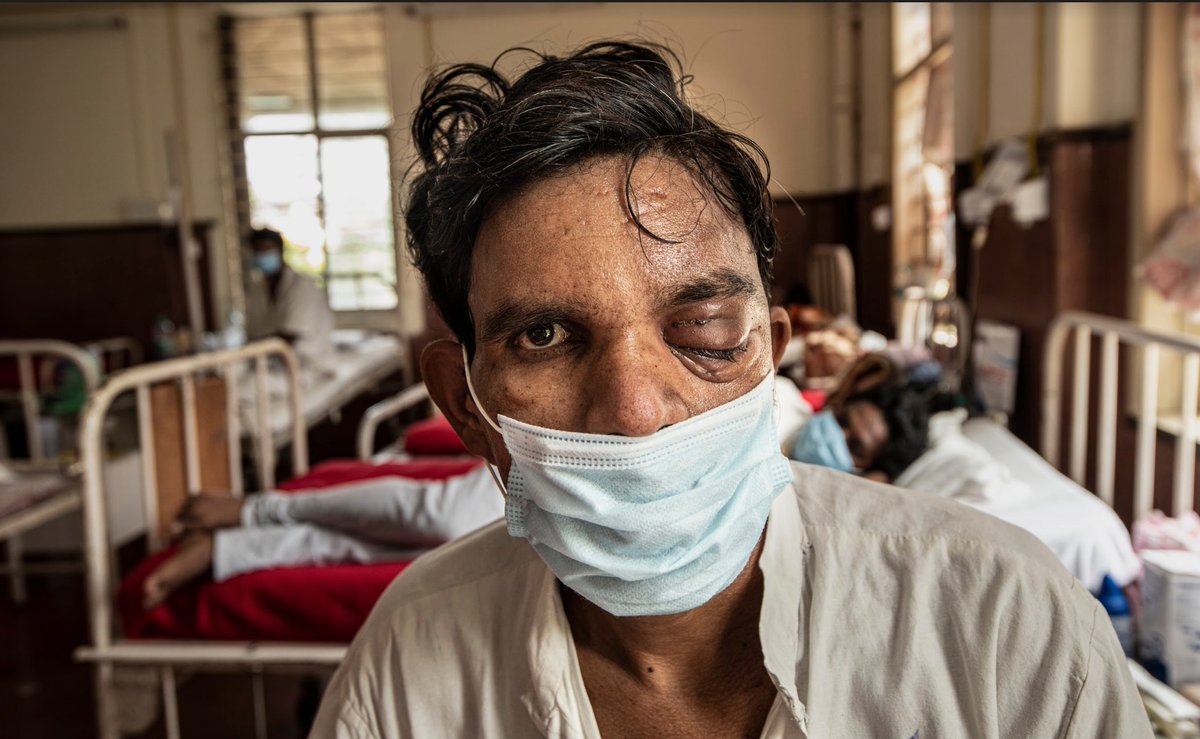
The world has missed all of the targets for tackling Aids by 2020 and "time is running out" to end the disease in the next ten years, according to a new United Nations report.
@jriggers has the latest ~ 🧵
telegraph.co.uk/global-health/…
@jriggers has the latest ~ 🧵
telegraph.co.uk/global-health/…
📈Despite some major achievements, including cutting deaths by 43% in the last decade and infections by 30%, progress has been patchy and in some regions – such as Eastern Europe and Central Asia – new HIV infections are actually on the rise
🌐 Globally, there were three times as many new infections in 2020 – a total of 1.5 million – than the hoped for 500,000, the report from @UNAIDS found
🔴Despite the fact that Aids has been "one of the deadliest pandemics of modern times" – killing more than 30 million people since it was first reported 40 years ago – it remained "unfinished business," @Winnie_Byanyima said of the findings
⌛️By 2020, the aim was for the "90-90-90" target to have been reached: 90% of HIV-positive people knowing they have the virus; 90% of them on medication; and 90% of them with viral levels suppressed to a level low enough to mean they could not pass it on
📉Those targets have not been universally met, either: instead they are at 84, 87 and 90% respectively.
Ms Byanyima said the criminalisation of gay sex, drug use and sex work in many countries continued to "stand in the way" of testing and treatment
Ms Byanyima said the criminalisation of gay sex, drug use and sex work in many countries continued to "stand in the way" of testing and treatment
🔊Campaigners said that the world is "sleepwalking towards a new Aids emergency" and action needs to be taken now
@jriggers reports
telegraph.co.uk/global-health/…
@jriggers reports
telegraph.co.uk/global-health/…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh