In @greatdismal's 1992 novel "Idoru," a media executive describes his company's core audience:
"Best visualized as a vicious, lazy, profoundly ignorant, perpetually hungry organism craving the warm god-flesh of the anointed.
1/
"Best visualized as a vicious, lazy, profoundly ignorant, perpetually hungry organism craving the warm god-flesh of the anointed.
1/

If you'd like an unrolled version of this thread to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
pluralistic.net/2021/06/05/lea…
pluralistic.net/2021/06/05/lea…
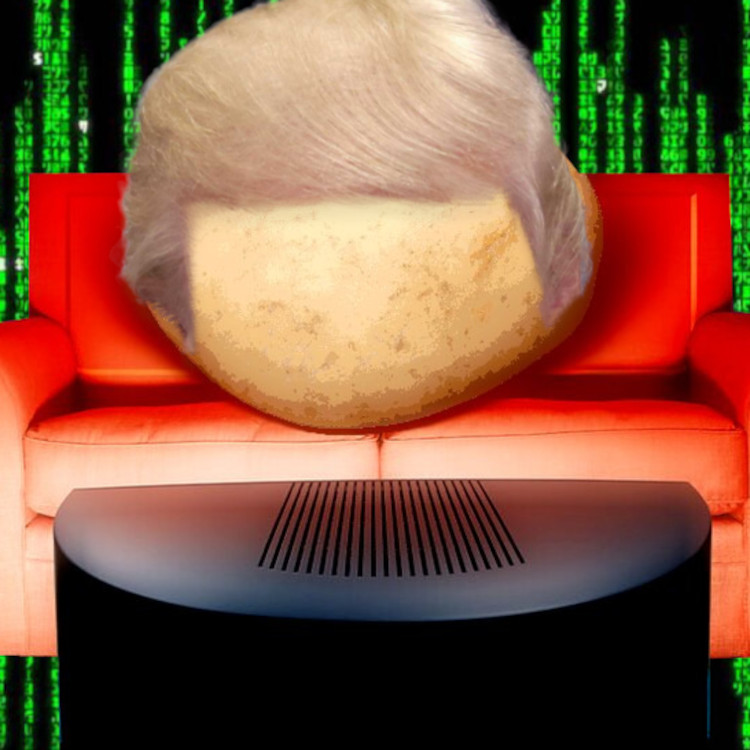
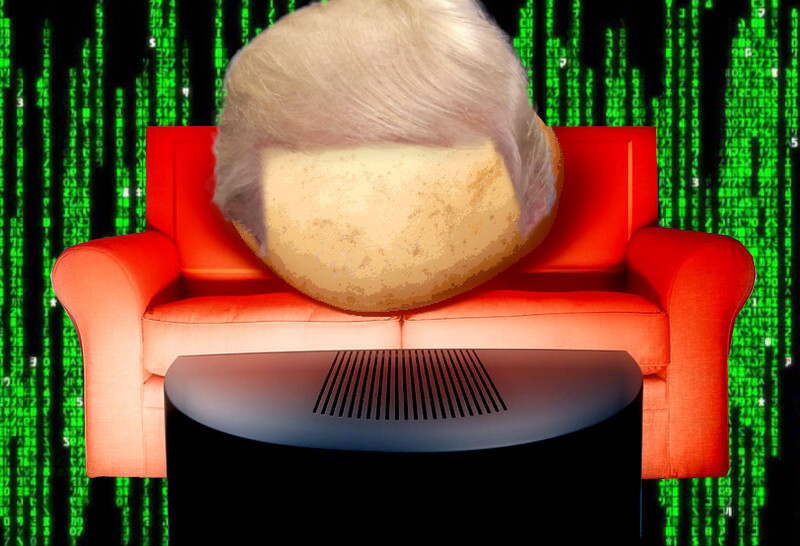
"Personally I like to imagine something the size of a baby hippo, the color of a week-old boiled potato, that lives by itself, in the dark, in a double-wide on the outskirts of Topeka.
2/
2/
"It's covered with eyes and it sweats constantly. The sweat runs into those eyes and makes them sting. It has no mouth...no genitals, and can only express its mute extremes of murderous rage and infantile desire by changing the channels on a universal remote.
3/
3/
"Or by voting in presidential elections."
It's an astonishingly great passage, not just for the image it evokes, but for how it captures the character of the speaker and his contempt for the people who made his fortune.
4/
It's an astonishingly great passage, not just for the image it evokes, but for how it captures the character of the speaker and his contempt for the people who made his fortune.
4/
It's also a beautiful distillation of the 1990s anxiety about TV's role in a societal "dumbing down," that had brewed for a long time, at least since the Nixon-JFK televised debates, whose outcome was widely attributed not to JFK's ideas, but to Nixon's terrible TV manner.
5/
5/
Neil Postman's 1985 "Amusing Ourselves To Death" was a watershed here, comparing the soundbitey Reagan-Dukakis debates with the long, rhetorically complex Lincoln-Douglas debates of the previous century.
6/
6/
(Incidentally, when I finally experienced those debates for myself, courtesy of the 2009 BBC America audiobook, I was more surprised by Lincoln's unequivocal, forceful repudiations of slavery abolition than by the rhetoric's nuance)
memex.craphound.com/2009/01/20/lin…
7/
memex.craphound.com/2009/01/20/lin…
7/
"Media literacy" scholarship entered the spotlight, and its left flank - epitomized by Chomsky's 1988 "Manufacturing Consent" - claimed that an increasingly oligarchic media industry was steering society, rather than reflecting it.
8/
8/
Thus, when the internet was demilitarized and the general public started trickling - and then rushing - to use it, there was a widespread hope that we might break free of the tyranny of concentrated, linear programming (in the sense of "what's on," and "what it does to you").
9/
9/
Much of the excitement over Napster wasn't about getting music for free - it was about the mix-tapification of all music, where your custom playlists would replace the linear album.
10/
10/
Likewise Tivo, whose ad-skipping was ultimately less important than the ability to watch the shows you liked, rather than the shows that were on.
11/
11/
Blogging, too: the promise was that a community of reader-writers could assemble a daily "newsfeed" that reflected their idiosyncratic interests across a variety of sources, surfacing ideas from other places and even other times.
12/
12/
The heady feeling of the time is hard to recall, honestly, but there was a thrill to getting up and reading the news that you chose, listening to a playlist you created, then watching a show you picked.
13/
13/
And while there were those who fretted about the "Daily Me" (what we later came to call the "filter bubble") the truth was that this kind of active media creation/consumption ranged far more widely than the monopolistic media did.
14/
14/
The real "bubble" wasn't choosing your own programming - it was everyone turning on their TV on Thursday nights to Friends, Seinfeld and The Simpsons.
15/
15/
The optimism of the era is best summarized in a taxonomy that grouped media into two categories: "lean back" (turn it on and passively consume it) and "lean forward" (steer your media consumption with a series of conscious decisions that explores a vast landscape).
16/
16/
Lean-forward media was intensely sociable: not just because of the distributed conversation that consisted of blog-reblog-reply, but also thanks to user reviews and fannish message-board analysis and recommendations.
17/
17/
I remember the thrill of being in a hotel room years after I'd left my hometown, using Napster to grab rare live recordings of a band I'd grown up seeing in clubs, and striking up a chat with the node's proprietor that ranged fondly and widely over the shows we'd both seen.
18/
18/
But that sociability was markedly different from the "social" in social media. From the earliest days of Myspace and Facebook, it was clear that this was a sea-change, though it was hard to say exactly what was changing and how.
19/
19/
Around the time Rupert Murdoch bought Myspace, a close friend a blazing argument with a TV executive who insisted that the internet was just a passing fad: that the day would come when all these online kids grew up, got beaten down by work and just wanted to lean back.
20/
20/
To collapse on the sofa and consume media that someone else had programmed for them, anaesthetizing themselves with passive media that didn't make them think too hard.
21/
21/
This guy was obviously wrong - the internet didn't disappear - but he was also right about the resurgence of passive, linear media.
But this passive media wasn't the "must-see TV" of the 80s and 90s.
22/
But this passive media wasn't the "must-see TV" of the 80s and 90s.
22/
Rather, it was the passivity of the recommendation algorithm, which created a per-user linear media feed, coupled with mechanisms like "endless scroll" and "autoplay," that incinerated any trace of an active role for the "consumer" (a very apt term here).
23/
23/
It took me a long time to figure out exactly what I disliked about algorithmic recommendation/autoplay, but I knew I hated it. The reason my 2008 novel LITTLE BROTHER doesn't have any social media? Wishful thinking. I was hoping it would all die in a fire.
24/
24/
Today, active media is viewed with suspicion, considered synonymous with Qanon-addled boomers who flee Facebook for Parler so they can stan their favorite insurrectionists in peace, freed from the tyranny of the dread shadowban.
26/
26/
But I'm still on team active media. I would rather people actively choose their media diets, in a truly sociable mode of consumption AND production, than leaning back and getting fed whatever is served up by the feed.
27/
27/
Today on @wired, Duke public policy scholar @pmnapoli writes about lean forward and lean back in the context of Trump's catastrophic failure to launch an independent blog, "From the Desk of Donald J Trump."
wired.com/story/opinion-…
28/
wired.com/story/opinion-…
28/
In a nutshell, Trump started a blog which he grandiosely characterized as a replacement for the social media monopolists who'd kicked him off their platforms. Within a month, he shut it down.
29/
29/
While Trump claimed the shut-down was all part of the plan, it's painfully obvious that the real reason was that no one was visiting his website.
Now, there are many possible, non-exclusive explanations for this.
30/
Now, there are many possible, non-exclusive explanations for this.
30/
For starters, it was a very bad social media website. It lacked even rudimentary social tools. The @washingtonpost called it "a primitive one-way loudspeaker," noting its lack of per-post comments, a decades old commonplace.
washingtonpost.com/technology/202…
31/
washingtonpost.com/technology/202…
31/
Trump paid (or more likely, stiffed) a grifter crony to build the site for him, and it shows: the "Like" buttons didn't do anything, the video-sharing buttons created links to nowhere, etc. From the Desk... was cursed at birth.
32/
32/
But Napoli's argument is that even if Trump had built a good blog, it would have failed. Trump has a highly motivated cult of tens of millions of people - people who deliberately risked death to follow him, some even ingesting fish-tank cleaner and bleach at his urging.
33/
33/
The fact that these cult-members were willing to risk their lives, but not endure poor web design, says a lot about the nature of the Trump cult, and its relationship to passive media.
34/
34/
The Trump cult is a "push media" cult, simultaneously completely committed to Trump but unwilling to do much to follow him.
That's the common thread between Fox News (and its successors like OANN) and MAGA Facebook.
35/
That's the common thread between Fox News (and its successors like OANN) and MAGA Facebook.
35/
And it echoes the despairing testimony of the children of Fox cultists, that their boomer parents consume endless linear TV, turning on Fox from the moment they arise and leaving it on until they fall asleep in front of it (also, reportedly, how Trump spent his presidency).
36/
36/
Napoli says that Trump's success on monopoly social media platforms and his failure as a blogger reveals the role that algorithmically derived, per-user, endless scroll linear media played in the ascendancy of his views.
37/
37/
It makes me think of that TV exec and his prediction of the internet's imminent disappearance (which, come to think of it, is not so far off from my own wishful thinking about social media's disappearance in Little Brother).
38/
38/
He was absolutely right that this century has left so many of us exhausted, wanting nothing more than the numbness of lean-back, linear feeds.
But up against that is another phenomenon: the resurgence of active political movements.
39/
But up against that is another phenomenon: the resurgence of active political movements.
39/
After a 12-month period that saw widescale civil unrest, from last summer's BLM uprising to the bizarre storming of the capital, you can't really call this the golden age of passivity.
40/
40/
While Fox and OANN consumption might be the passive daily round of one of Idoru's "vicious, lazy, profoundly ignorant, perpetually hungry organisms craving the warm god-flesh of the anointed," that is in no way true of Qanon.
41/
41/
Qanon is an active pastime, a form of collaborative storytelling with all the mechanics of the Alternate Reality Games that the lean-forward media advocates who came out of the blogging era love so fiercely:
pluralistic.net/2020/08/06/no-…
42/
pluralistic.net/2020/08/06/no-…
42/
Meanwhile, the "clicktivism" that progressive cynics decried as useless performance a decade ago has become an active contact sport, welding together global movements from Occupy to BLM that use the digital to organize the highly physical.
43/
43/
That's the paradox of lean-forward and lean-back: sometimes, the things you learn while leaning back make you lean forward - in fact, they might just get you off the couch altogether.
44/
44/
I think that Napoli is onto something. The fact that Trump's cultists didn't follow him to his crummy blog tells us that Trump was an effect, not a cause (something many of us suspected all along, as he's clearly neither bright nor competent enough to inspire a movement).
45/
45/
But the fact that "cyberspace keeps everting" (to paraphrase "Spook Country," another William Gibson novel) tells us that passive media consumption isn't a guarantee of passivity in the rest of your life (and sometimes, it's a guarantee of the opposite).
46/
46/
And it clarifies the role that social media plays in our discourse - not so much a "radicalizer" as a means to corral likeminded people together without them having to do much. Within those groups are those who are poised for action, or who can be moved to it.
47/
47/
The ease with which these people find one another doesn't produce a deterministic outcome. Sometimes, the feed satisfies your urge for change ("clicktivism"). Sometimes, it fuels it ("radicalizing").
48/
48/
Notwithstanding smug media execs, the digital realm equips us to "express our mute extremes of murderous rage and infantile desire" by doing much more than "changing the channels on a universal remote" - for better and for worse.
49/
49/
Image:
Ian Burt (modified)
flickr.com/photos/oddsock…
CC BY:
creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.…
eof/
Ian Burt (modified)
flickr.com/photos/oddsock…
CC BY:
creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.…
eof/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh