
Let's dive further into SQL to help you through the most demanding skill required in the Data Science Industry.
A Beginner's Guide to Filter Results in MySQL - Part 5!!
Thread 🧵
A Beginner's Guide to Filter Results in MySQL - Part 5!!
Thread 🧵
☑️ LIMIT Clause
To restrict the number of rows in the final result, we use the LIMIT clause.
That means if you have 10,000 rows in the data, you can fetch only 10 rows using this clause in your query.
To restrict the number of rows in the final result, we use the LIMIT clause.
That means if you have 10,000 rows in the data, you can fetch only 10 rows using this clause in your query.
👉 Query: select * table_name LIMIT limit_no;
For e.g., Consider a table PAYMENTS. It has more than 1000 rows. [See the image]
For e.g., Consider a table PAYMENTS. It has more than 1000 rows. [See the image]
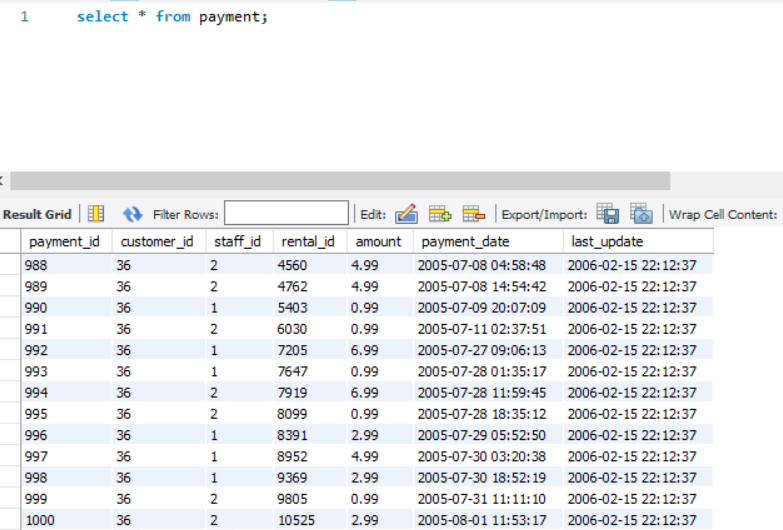
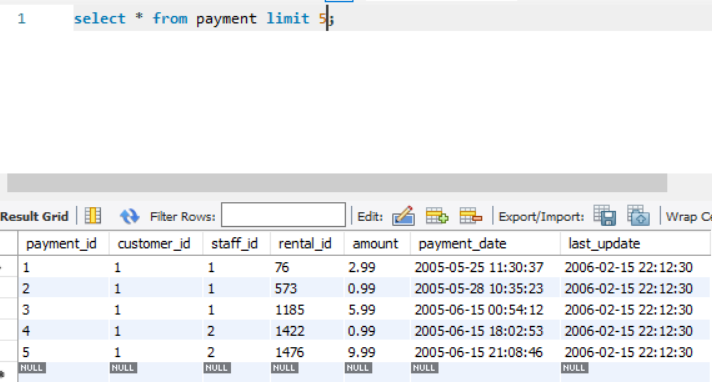
To fetch only 5 rows from the PAYMENTS table, we write a query as follows:-
Query: select * from payments limit 5;
[We get the result as shown in the image.]
Query: select * from payments limit 5;
[We get the result as shown in the image.]
☑️ DISTINCT Clause
This clause is used to filter out results based on unique values, i.e., the distinct clause is used to get UNIQUE results only.
👉 Query: select DISTINCT column_name from table_name;
This clause is used to filter out results based on unique values, i.e., the distinct clause is used to get UNIQUE results only.
👉 Query: select DISTINCT column_name from table_name;
Considering the same PAYMENTS table, we use the DISTINCT clause to find all the unique AMOUNTs.
Query: select DISTINCT amount from payments;
Despite 1000 records, the distinct (unique) amount values are only 19.
Query: select DISTINCT amount from payments;
Despite 1000 records, the distinct (unique) amount values are only 19.

☑️ WHERE Clause
Using this clause, we can specify selection criteria to select the required records from the table.
It works like an IF CONDITION.
You can specify conditions using:-
1. Relational Operators (>,<,=)
2. Logical Op (AND, OR)
3. IS NULL or IS NOT NULL
Using this clause, we can specify selection criteria to select the required records from the table.
It works like an IF CONDITION.
You can specify conditions using:-
1. Relational Operators (>,<,=)
2. Logical Op (AND, OR)
3. IS NULL or IS NOT NULL
Example:-
Selecting records where the amount is less than 5.99.
👉 Query: select * from payment where amount < 5.99;
Selecting records where the amount is less than 5.99.
👉 Query: select * from payment where amount < 5.99;

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh







