
Meet Soyuz-5, the next-generation Russian crew and cargo launcher. 🚀
Below is a thread split into different parts going over how it works, what it is for, and any other important info. ℹ️
(1/8)
Below is a thread split into different parts going over how it works, what it is for, and any other important info. ℹ️
(1/8)

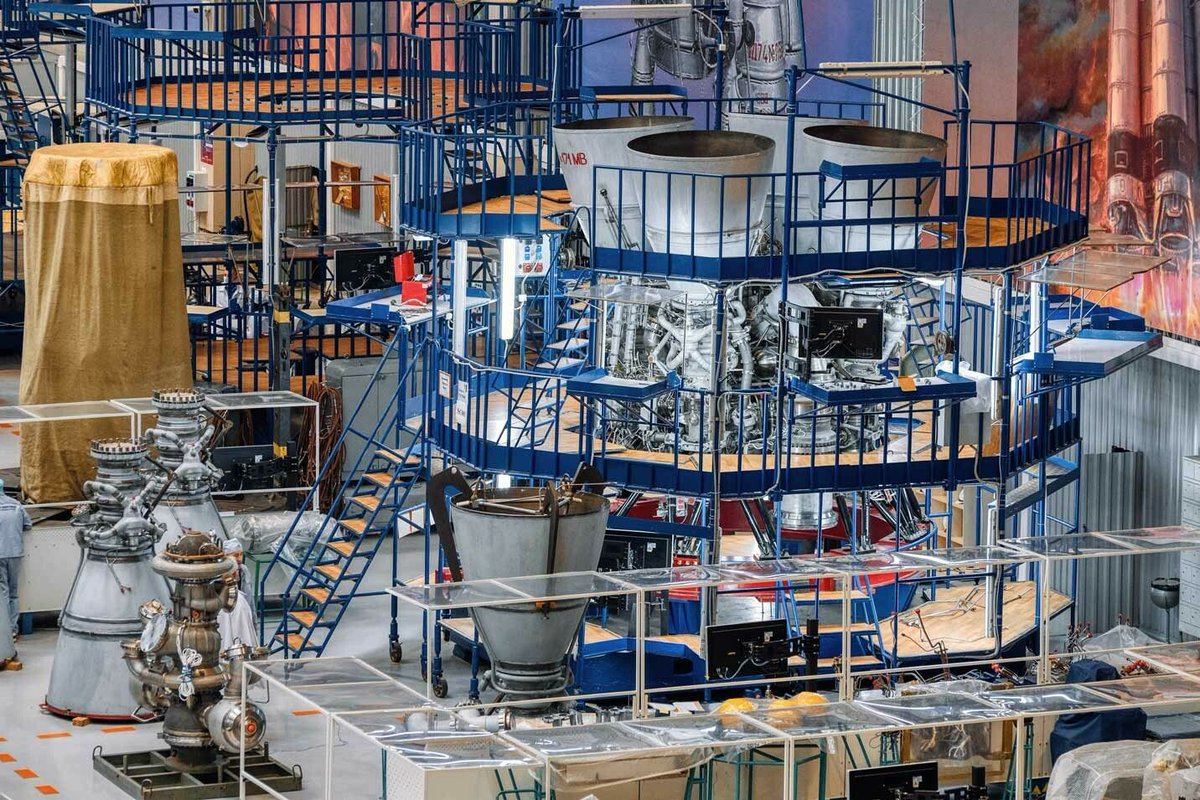
🚀 Launch
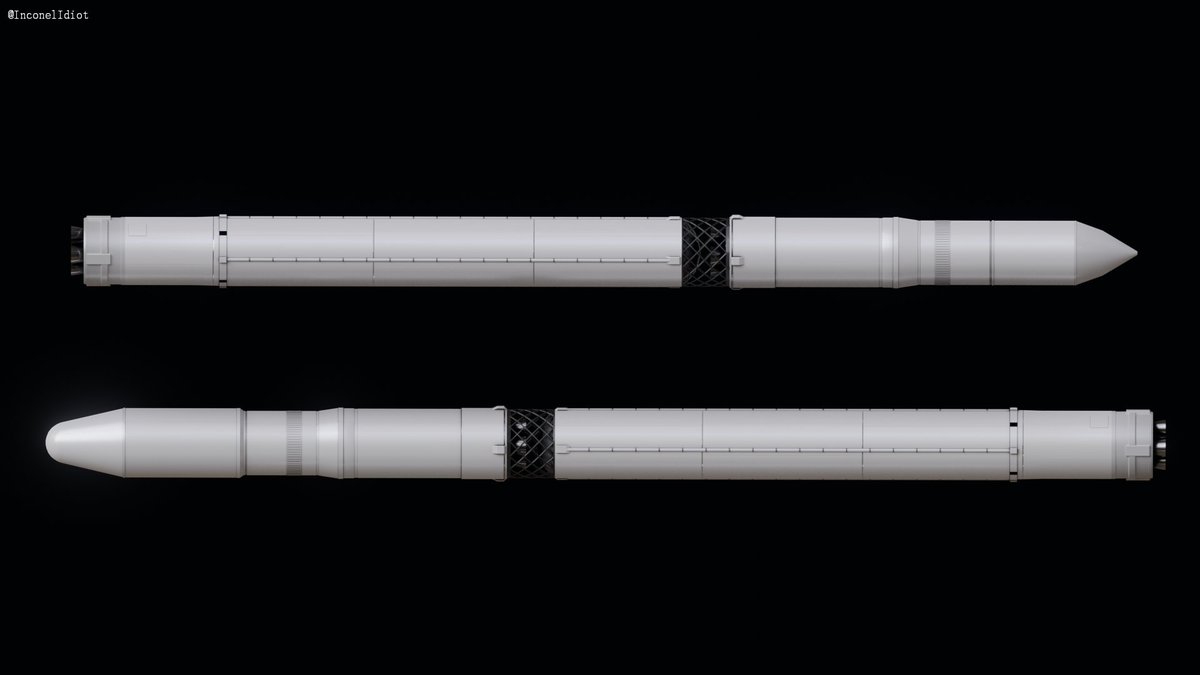
At launch, the rocket is powered by 1 RD-171MV engine creating 7,257 kN of thrust. This engine is similar to the RD-171 engine that was used on the Ukrainian/Soviet Zenit rocket. It features an upgraded control system and is all Russian made.
📸: NPO Energomash
(2/8)
At launch, the rocket is powered by 1 RD-171MV engine creating 7,257 kN of thrust. This engine is similar to the RD-171 engine that was used on the Ukrainian/Soviet Zenit rocket. It features an upgraded control system and is all Russian made.
📸: NPO Energomash
(2/8)

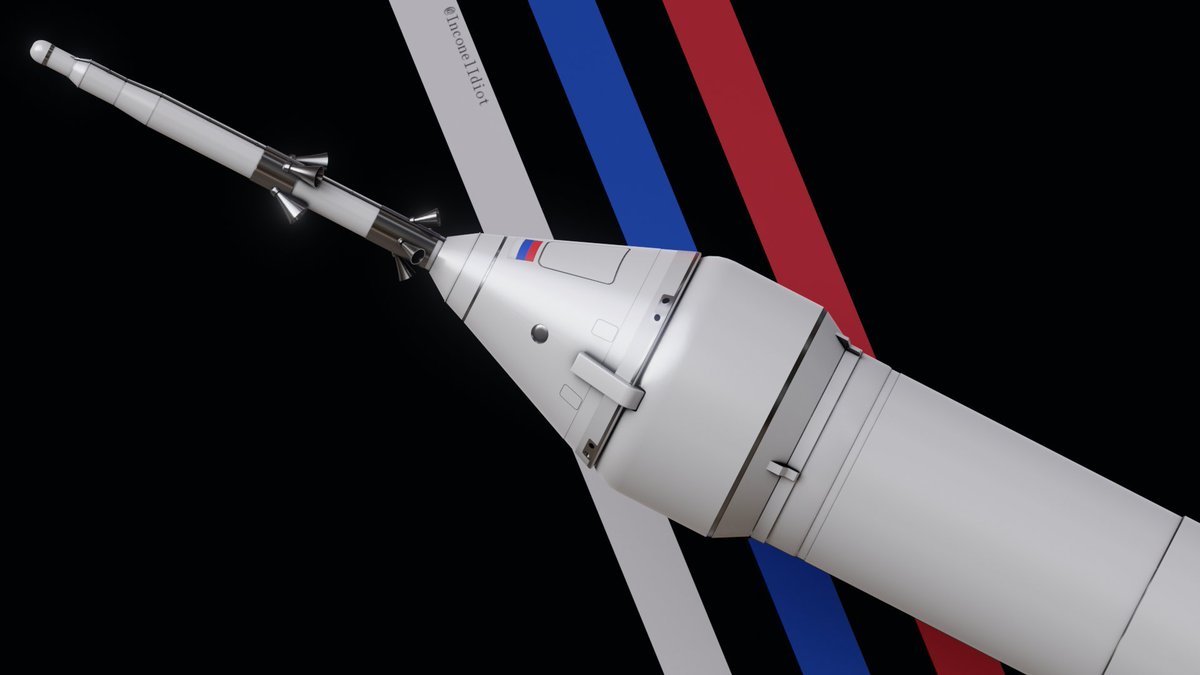
2⃣ Versions
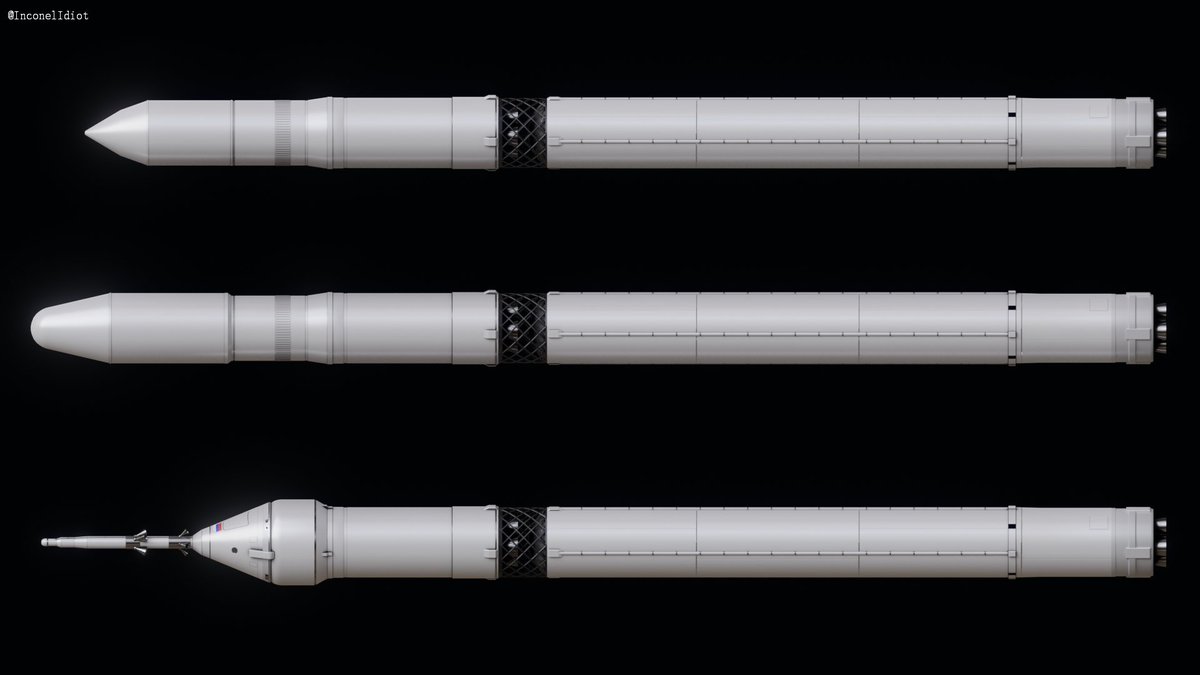
Soyuz 5 has 2 main versions, a cargo version and a crewed version. The crewed version shown here is Soyuz 5 with the Orel capsule on top (bottom). Soyuz 5 can also carry other crew vehicles, two of them being Orlenok and Pilot MMKK.
(3/8)
Soyuz 5 has 2 main versions, a cargo version and a crewed version. The crewed version shown here is Soyuz 5 with the Orel capsule on top (bottom). Soyuz 5 can also carry other crew vehicles, two of them being Orlenok and Pilot MMKK.
(3/8)
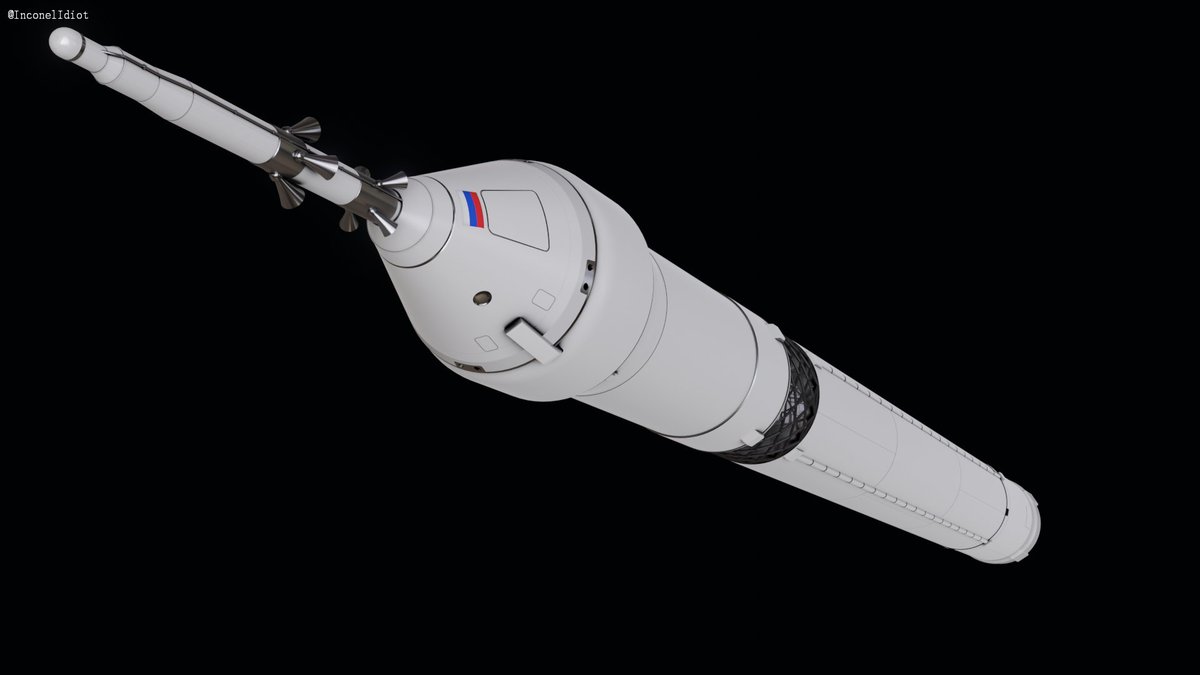
🧑🚀Crew
The Soyuz 5 rocket can carry multiple different crew vehicles with the main one being Orel. Orel has a launch mass of 17,000 kg for LEO missions and is capable of carrying 4-6 Cosmonauts to LEO and beyond (🌑!!!). It will replace Soyuz for crew flights to the ROSS.
(4/8)
The Soyuz 5 rocket can carry multiple different crew vehicles with the main one being Orel. Orel has a launch mass of 17,000 kg for LEO missions and is capable of carrying 4-6 Cosmonauts to LEO and beyond (🌑!!!). It will replace Soyuz for crew flights to the ROSS.
(4/8)

🛰️ Cargo
Soyuz 5 has multiple different fairing options. One of the options is the ST fairing (bottom), which is also used on the Soyuz 2 rocket. These fairings allow Soyuz 5 to be able to safely place payloads of up to 18,000 kg into Low Earth Orbit.
(5/8)
Soyuz 5 has multiple different fairing options. One of the options is the ST fairing (bottom), which is also used on the Soyuz 2 rocket. These fairings allow Soyuz 5 to be able to safely place payloads of up to 18,000 kg into Low Earth Orbit.
(5/8)
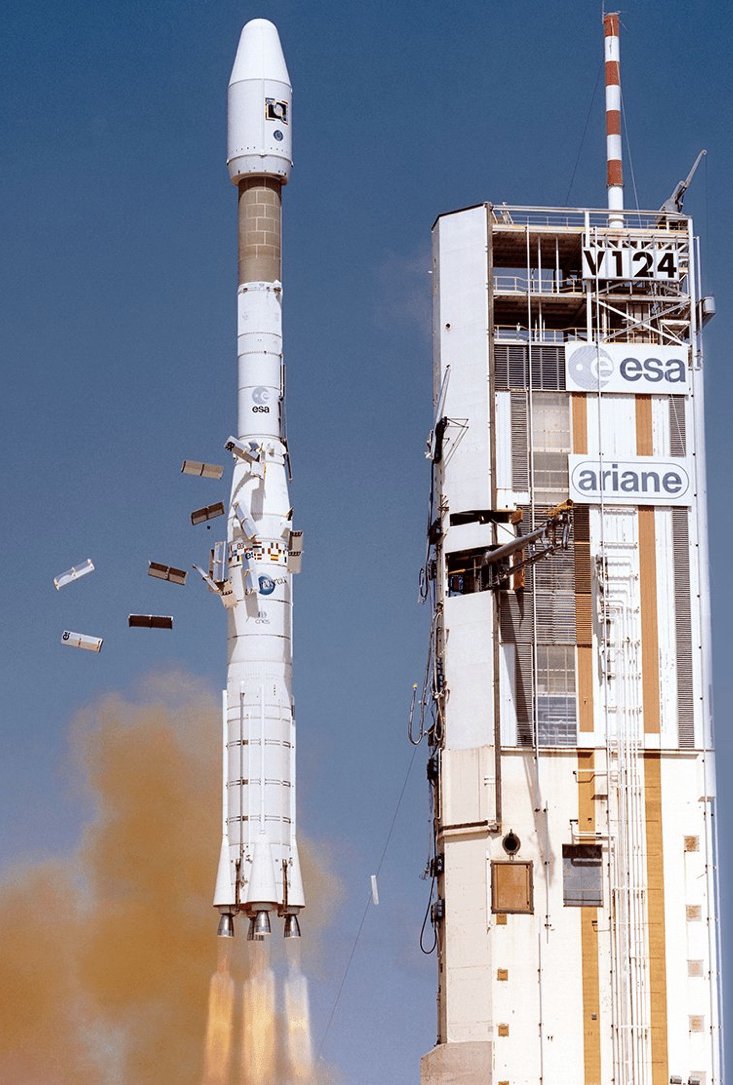
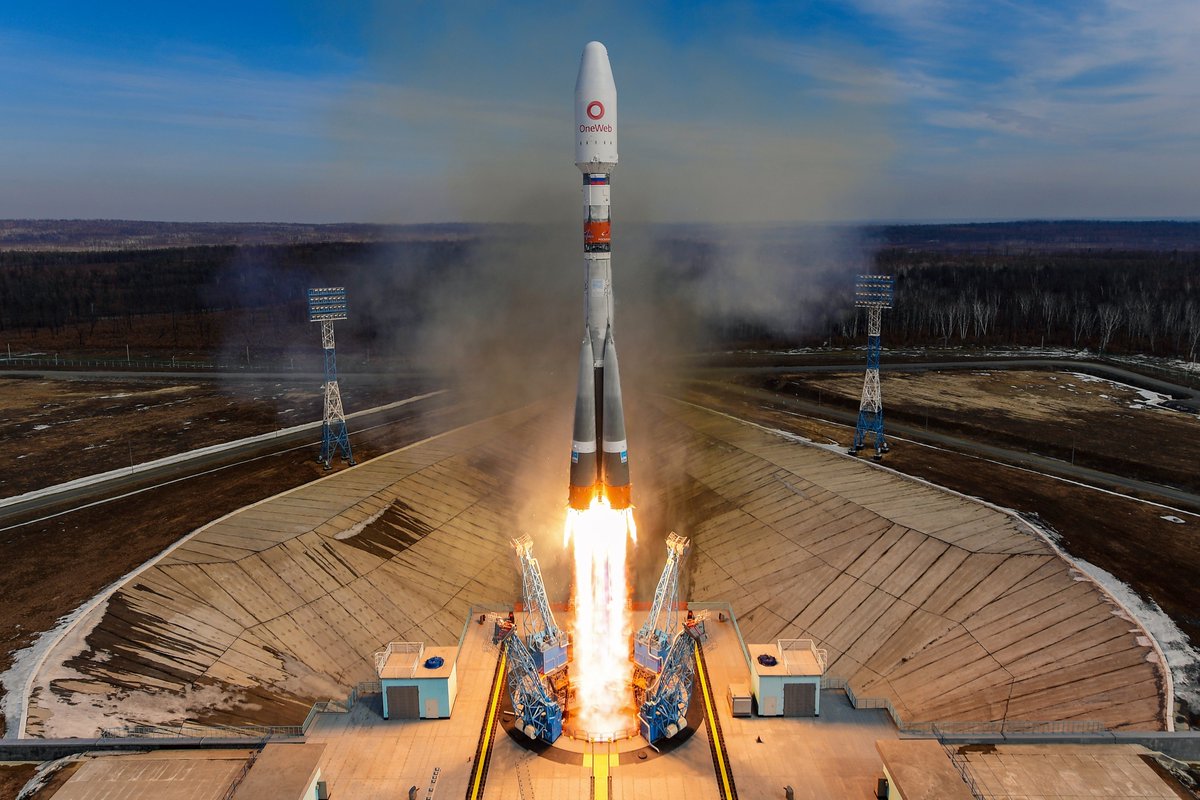
Similar designs to the ST fairing have also been used on vehicles like the commercial Titan III, Ariane 4 and Soyuz 2 🚀
📸: NASA, ESA, Roscosmos
(6/8)


📸: NASA, ESA, Roscosmos
(6/8)



ℹ️ Specs (for the cargo version)
Total height: 61.9m
First stage height: 37.14m
First stage width: 4.1m
Second stage height: 7.77m
Engines on the first stage: 1
Payload to LEO: 18,000 kg
Payload to GTO: 5,000 kg
(7/8)
Total height: 61.9m
First stage height: 37.14m
First stage width: 4.1m
Second stage height: 7.77m
Engines on the first stage: 1
Payload to LEO: 18,000 kg
Payload to GTO: 5,000 kg
(7/8)
📸: All media in tweets 1, 3, 4, and 5 are by @InconelIdiot. Other photo credits are in the tweets.
(8/8)
(8/8)
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh



