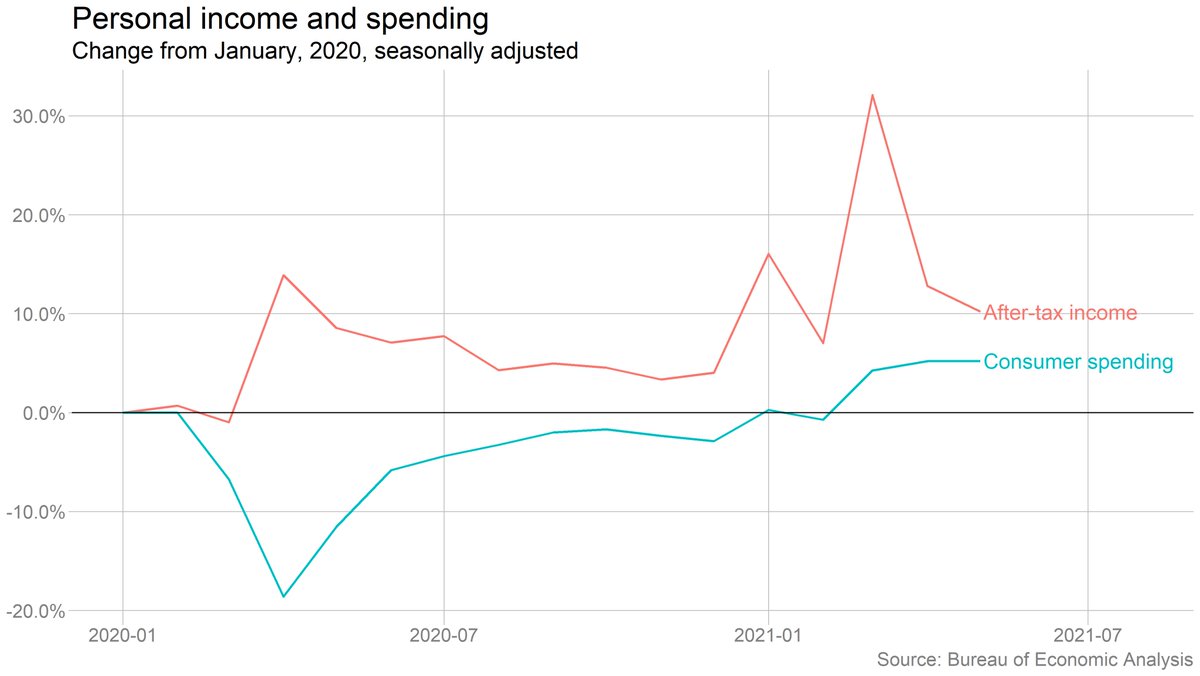
The drop in income was driven by a decline in government transfers (mostly the end of the direct checks under the American Rescue Plan). Wage and salary income rose, though more slowly than in April. 

Spending on goods fell and spending on services rose, but we still haven't seen anything close to a wholesale reversal of the big pandemic shifts in spending. Have to see what happens this summer. 

Sharper drop in spending on durable goods, which probably at least partly reflects the end of the ARP checks. 

Personal saving fell in May, and is way down from March (when most relief checks arrived), but still well above prepandemic levels. The caveat, as always: These savings are nothing close to evenly distributed. 

OK, inflation (you knew I'd get there eventually): The PCE price index rose 3.9% from a year earlier, the fastest pace since 2008. Excluding food and energy, prices were up 3.4%.
BUT
BUT

The year-over-year number is inflated by base effects (the drop in overall prices in the worst of the pandemic a year ago). The month-to-month increase in prices actually slowed. (Note chart shows annualized monthly change.) 

More on the inflation numbers from @jeannasmialek here: nytimes.com/2021/06/25/bus…
It's interesting to look at spending in some of the most pandemic-affected categories. Restaurants (including fast food, delivery, etc) have bounced back, but everything else is still way down. Movies, live entertainment have barely even begun to recover. 

Interesting to think through how much of this is capacity constraints vs health concerns vs behavior shifts (and, to the extent it's the latter, how long those last). Obviously varies substantially by category.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh