Today I will talk about the epic 1288 battle of Worringen in which the renowned knight John, Duke of Brabant, excelled! He fought against the forces of Siegfried II of Westerburg, the Archbishop of Cologne! They fought for the possession of the disputed wealthy Duchy of Limburg! 

John I, Duke of Brabant, was one of the most gifted and chivalrous princes of his time. He was described as a perfect model of a feudal prince in the days of chivalry, brave, adventurous, excelling in every form of active exercise, fond of display, generous in temper. 
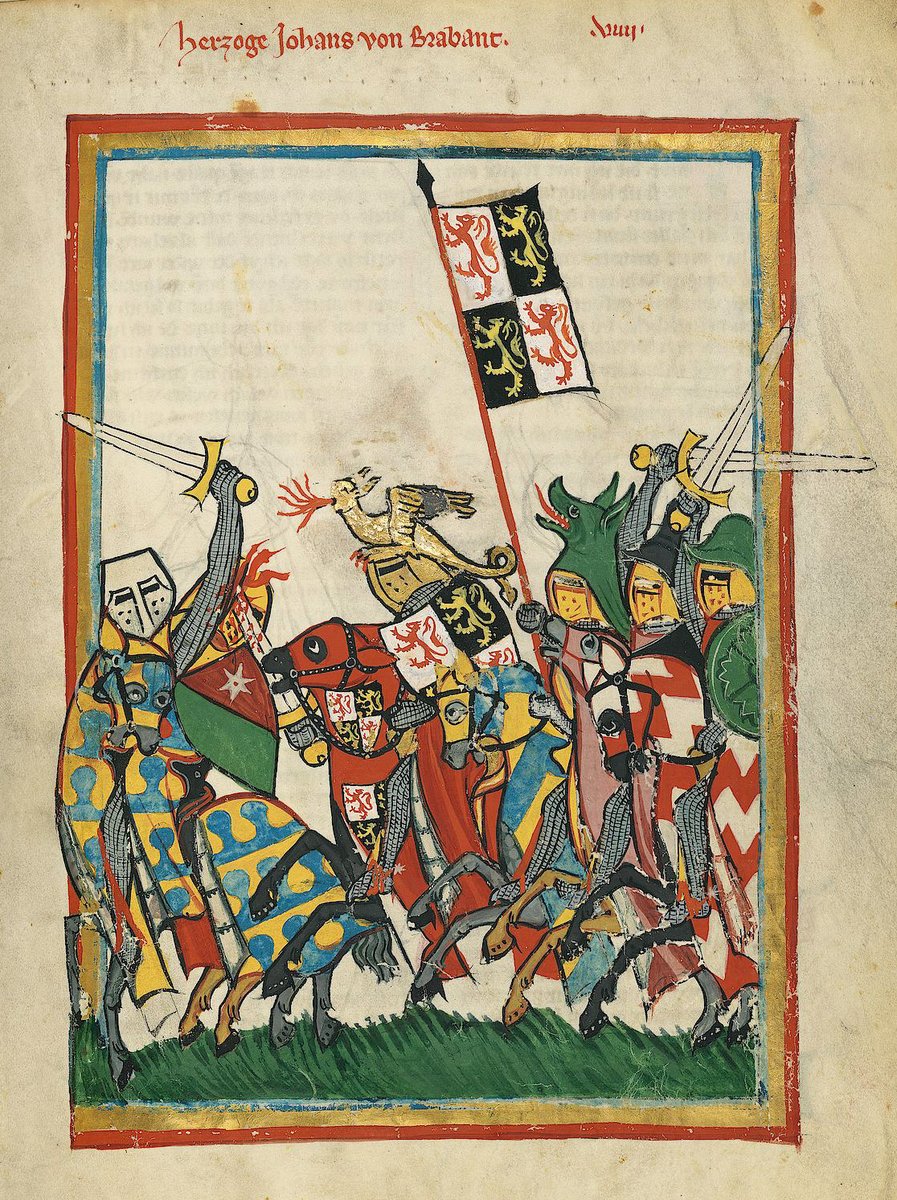



John of Brabant who would be called "the Victorious", delighted in tournaments, and was always eager personally to take part in jousts! This would also later lead to his death as he was mortally wounded on a brutal tournament held as part of some marriage festivities.
John came from the mighty Reginar family, a family of magnates in Lower Lotharingia! He became the Duke of Brabant in 1267 as his older brother Henry IV was deposed due to being mentally deficient. John intended to enlarge his territory and in 1283 laid claims to lands of Limburg 



The Duchy of Limburg was disputed territory ever since Ermengarde, the daughter of the deceased duke Waleran IV of Limburg, died in 1283. She had no children with her husband Count Reginald I of Guelders whose claim to duchy was disputed by Waleran's nephew Adolf VIII of Berg. 



John of Brabant bought the claim from Adolf VIII of Berg in that same year and in a display of power and might invaded the duchy with his forces after the local nobles who were loyal to Reginald of Guelders opposed him. From 1283 to 1288 tensions increased rapidly.
A large scale conflict was emerging as the neighboring powers began to choose sides, each having their own personal interests. John's increasing power worried the powerful Archbishop of Cologne Siegfried II of Westerburg who led the coalition against him, allying with Reginald.
The Archbishop of Cologne wielded immense power as he was one of the seven electors of the Holy Roman Empire. Besides having the dignity of prince-elector, he was also the Arch-chancellor of Italy. Archbishop Siegfried was a man of big ambitions, willing to back them up by force! 



Siegfried gathered an alliance of nobles, joined by Henry VI of Luxembourg, his brother Waleran I of Ligny, count Adolf of Nassau, and of course the already mentioned Reginald I of Guelders who saw himself as the rightful ruler of Limburg! Their magnificent coats of arms: 







On John's side were Adolf VIII of Berg who joined with Westphalian counts of County of Mark, together with the Counts of Loon, Tecklenburg and Waldeck. They gathered an army that was slightly larger than Siegfried's, but not by much. 







Hostilities before the battle of Worringen started in May 1288 when John started a campaign and marched against the castle of Worringen that belonged to Archbishop of Cologne, located north of Cologne. He was supported by local citizens who disliked the archibishop's harsh rule! 

The chronicle "Deeds of the Abbots of St. Trond" reports that in this castle, Archbishop Siegfried of Cologne had stationed robbers who plundered and imprisoned merchants! The local people of Cologne wanted the castle gone for these same reasons and supported John's siege.
The Chronicle of the Dukes of Brabant also reports that once John entered Archibishop's lands he "had the vines of Bonn cut down, and he entered the forest of the archbishop to enjoy the hunting there" to provoke his mighty rival, which incited his wrath against him! 

The siege started and Siegfried responded by gathering his own army, supported by the troops of Henry of Luxembourg. They would arrive to Worringen on 5 June and Henry's troops would face John's right away. A fierce fight followed in which Henry and two of his brothers died!
Siegfried entered the battle in a bold manner and was able to rout Berg's troops and the treacherous Cologne militia but did not have proper support from the rest of his army. John's army counterattacked and won the battle, taking Reginald of Guelders and Siegfried as prisoners! 

The chronicle "Deeds of the Abbots of St. Trond" reports of 900 dead on Siegfried's side. Supposedly only 40 John's men died. After his victory he demolished the sinister castle of Worringen where the robbers had been gathering to secure a safe passage for merchants in the future
The victory started the rise of power of Duchy of Brabant which added Limburg. The city of Cologne also benefited as it gained its independence from the Archbishopric. Siegfried and Reginald were released after they renounced their claims on Limburg. Glory to the mighty Brabant! 

Here is a collection of contemporary sources for the battle of Worringen!
ims.leeds.ac.uk/wp-content/upl…
ims.leeds.ac.uk/wp-content/upl…
@TalentEvaluator What do you think about archbishops personally fighting in bloody battles like this?
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh