Battle of Bicocca was another crucial and bloody battle in the Italian Wars, fought on 27 April 1522. Imperial-Spanish forces crushed the French and their Swiss mercenaries, in a battle that marked yet another important step in the evolution of the pike and shot warfare. 
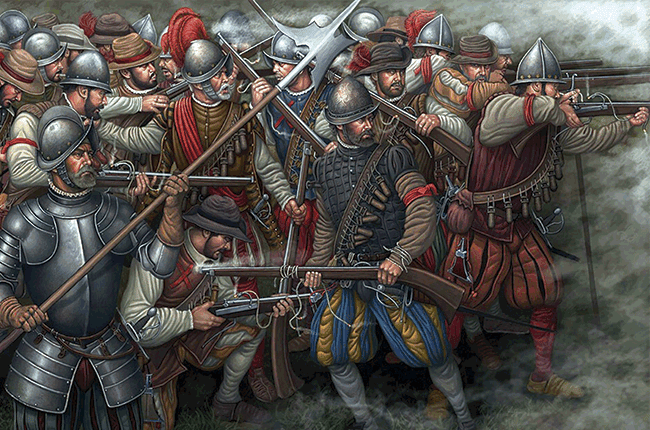

The Italian wars began in 1494 and in the next three decades they were fought with only brief interruptions. The War of the League of Cambrai (1508-1516) was particularly bloody, with practically all the European superpowers at the time joining coalitions against each other. 

In 1516 peace was made that ended the War of the League of Cambrai and pretty much returned things to the 1508 status quo ante bellum. However like it was common in the Italian Wars, peace would not last long as tensions among the European superpowers increased again soon. 

The Italian wars marked a new era in many ways. It was the first European conflict where large diplomatic coalitions of superpowers were made to keep the balance of power. Italian city states were top weak on their own to stop their country becoming a battlefield of entire Europe 



Secondly, Italian Wars were the beginning of the pike and shot era where gunpowder weapons started increasingly playing a decisive role, backed by pikemen. Veteran mercenaries were sought and these ferocious men plundered Italian cities and caused a lot of devastation. 



Furthermore, the canons and firearms made the battles more lethal than what was common in the middle ages. Despite this, the superpowers like France could afford to keep recruiting new armies and send them to Italy, and the conflict just kept going, with each new war more brutal. 

The major event that caused new tensions was the death of Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I in 1519 and the new Imperial elections that took place. The Habsburg Spanish king Charles was elected, becoming the Holy Roman Emperor as Charles V, uniting his vast domains under one ruler! 



French king Francis I did not like the course of development as his fears of France becoming cornered by Habsburgs came true. Charles V now ruled over Spain and its overseas possessions, and directly ruled over Burgundian lands, the Low Countries and lands of Austrian Habsburgs. 



Charles' rule was not completely consolidated though as rebellions broke out in Spain and in German speaking lands, he had to deal with the outbreak of heresy by Martin Luther. Francis I wanted to use this situation and decided for aggressive approach. 



Francis I didn't want the English King Henry VIII to have a diplomatic excuse to attack him, so instead of open aggression he supported wars in Navarre and Low Countries by proxy, sending troops and funding enemies of Habsburgs in those lands. These French allies failed, however. 



Italy would once again become the main battlefield between France and Imperial-Spanish forces supported by the Papal States. Papal general and condottiere Prospero Colonna moved to northern Italy with a large Spanish contingent from Naples, joined by Imperial Landsknechts. 



French Milan was defended by Odet of Foix, Viscount of Lautrec. He had a considerable army, but was lacking resources to pay his mercenaries and Colonna patiently avoided battle until Lautrec's army disbanded due to lack of pay. Lautrec had to flee to allied Venetian territory. 



In 1522, Lautrec finally received money to raise a new Swiss mercenary contingent as well as employing the famed Giovanni de Medici and his notorious Italian Black Bands. He moved towards Milan to try to face Colonna in a decisive battle again. Colonna once again patiently waited 
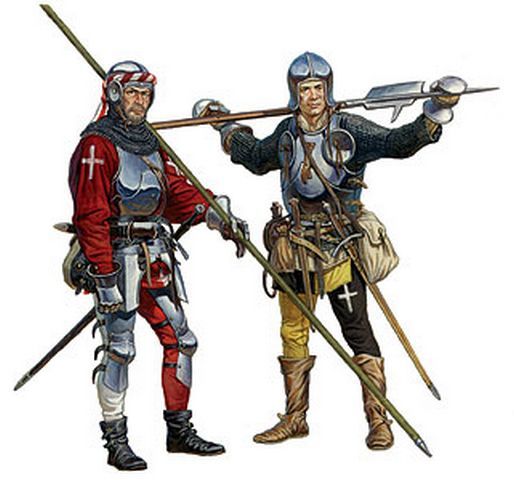



Instead of engaging the large French force, Colonna took a defensive position. Lautrec made a wise decision not to engage and tried to cut off Colonna's supplies instead. However his Swiss mercenaries were once again restless as they haven't received pay and wanted to fight. 

The Swiss mercenaries were too important for Lautrec and he had to cave in to their demands. He had no choice but to fight Colonna near Bicocca, a manor park north of Milan. The battlefield was perfect for the defensive minded Imperial-Spanish forces, with marshy ground. 

The park where Imperial-Spanish army was stationed was also bordered by ditches and irrigation canals, making the terrain even more suitable to defend from charges. Colonna used a typical pike and shot formation to await the french, putting arquebusiers ahead of pikemen to shoot. 



Colonna ordered the arquebusiers to be formed in four lines so that they could shoot uninterrupted while the other line would reload, supported also by Imperial artillery and protected by Landsknecht pikemen. Trusting the infantry, Colonna placed cavalry far away in the rear. 

The cavalry was mainly meant to protect the infantry from being attacked from behind by enemy cavalry. With this formation of his around 18000 men strong army, Colonna awaited the bigger French army and the notorious Swiss pikemen who would meet their rivals Landsknechts again! 

The French plan was to use their own artillery to bombard the Imperial-Spanish forces, but the Swiss mercenaries refused to obey. Out of overconfidence and their fierce pugnacious character, they charged at the enemy army, blocking the French artillery and heading straight on! 

It was a hopeless charge, the Swiss lost many men by artillery fire before they even reached the Imperial positions, then they were met with the trench and arquebusiers behind a rampart firing at them. One has to give credit to their bravery for attempting that in the first place 

The Imperial infantry was well prepared and led by charismatic capable men Fernando d'Avalos (commanding the Spanish detachment) and the legendary Landsknecht commander Georg von Frundsberg. They dealt with the Swiss who managed to climb over the ditch and the ramparts. 



Meanwhile the French cavalry reached the bridge in the south attempting to attack the Imperials from behind, but they were met there by Imperial cavalry led by Antonio de Leyva and allied Milanese led by Federico Sforza. The French were pushed backed and returned to the main army 



This was a perfect victory for Colonna. With brilliant pike and shot tactics he managed to win the battle with minimal casualties, while inflicting heavy losses on the enemy. A veteran of the 1503 battle of Cerignola, he learned from the pioneer of this tactic Gonzalo de Cordoba. 
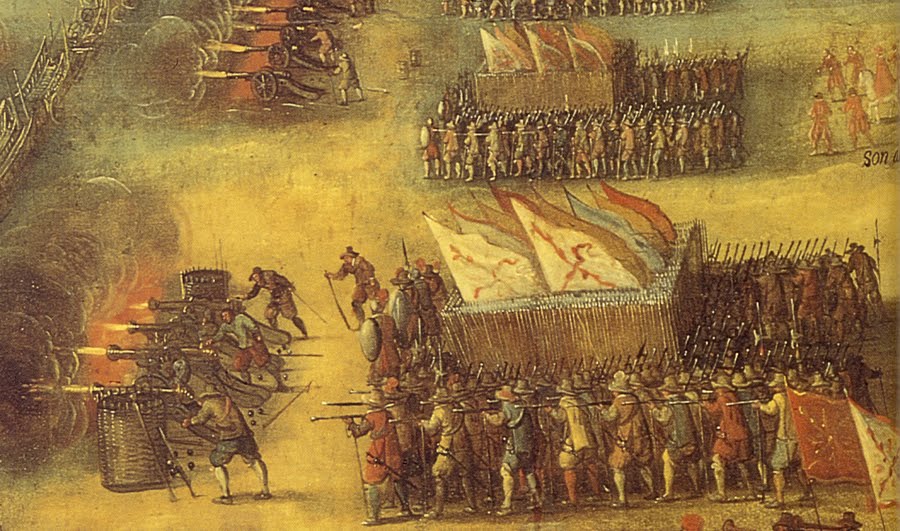

After this battle the Swiss who suffered a lot of casualties marched home and lacking quality infantry, Lautrec was unable to continue his offensive. The French returned to allied Venetian territory. Imperial-Spanish forces won an important victory for young emperor Charles V! 



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh