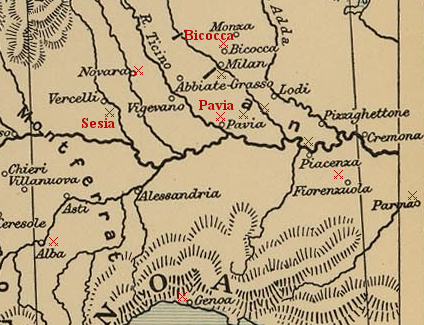
Battle of the Sesia River in 1524 was another defeat of the French in the Italian War of 1521-26, defeated by Imperial forces. During this battle, they also lost one of the finest French knights Pierre Terrail, seigneur de Bayard, who fell on the battlefield, shot by an arquebus. 

Despite their crushing defeat at Bicocca in 1522, the French king Francis I managed to send another big army to Italy in late 1523 led by Guillaume Gouffier, Lord of Bonnivet. Francis gained money for this new army by seizing properties of Charles III, Duke of Bourbon. 



Charles of Bourbon was angered by this and abandoned the French king Francis, switching sides and entering emperor Charles V's service instead. Meanwhile a huge French army under Bonnivet, numbering around 35000 men including Swiss mercenaries marched into Italy to conquer Milan. 



The Imperial forces under Prospero Colonna had barely half as many men, but Colonna was an experienced leader who patiently avoided battles and eventually stationed his army in the fortified city of Milan. Once again he wanted the French to exhaust themselves before battles. 
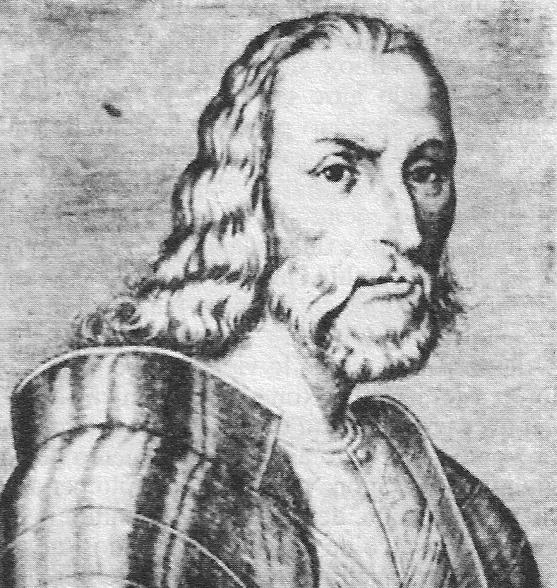



The French once again had a problem of poor leadership as Bonnivet played into Colonna's game and had his army retreat to winterquarters to the west of Milan and delaying the campaign to next year. Meanwhile Imperial army received reinforcements by arrivals of Bourbon and Lannoy. 

Charles de Lannoy arrived from Naples with fresh troops. He would assume command after the aged Colonna died that same year, and he continued using the same pragmatic and defensive approach while the French army was decimated by disease and lack of pay. A lot of Swiss left. 



Lannoy now had a larger army than Bonnivet and decided to look for a decisive engagement on the open field. However this time, it was Bonnivet who didn't want it. Realizing the abysmal condition of his army, he decided to retreat to France. Lannoy was determined to pursue him. 

As the French were crossing the river Sesia, Lannoy sent a vanguard consisting of light cavalry and mounted arquebusiers to catch the retreating French forces. This small force of Imperials was able to successfully harass the French who were retreating over the river very slowly. 


The French prepared a counterattack on the Spanish and Italian arquebusiers who had dismounted uphill and assumed a defensive position. The French heavy cavalry charged, but on boggy terrain the charge was not as effective and arquebusiers managed to shoot down many. 

Next the Swiss pikemen went on offensive but they too had a lot of casualties and were not effective as the arqubusiers retreated from them and then shot again from safer positions. They were also threatened by light cavalry from the flanks and had to retreat back. 

In this situation, the French prepared another heavy cavalry attack, led by Pierre Terrail de Bayard, an inspiring veteran warrior reputed as the most chivalrous French. The charge was once again unsuccessful and Bayard himself died in the charge! He was shot down by an arquebus. 



At that point, the main Imperial army had arrived and the French had no choice but to retreat in disorder and flee. Bonnivet's 1523-24 campaign was a total fiasco, a waste of money and men and another humiliating defeat for the French in a battle, on top of losing Bayard's life. 

What makes this battle interesting is that is proved the effectiveness of skirmish gunpowder attacks which would continue to be used by Giovanni de Medici's Black Bands Italian mercenaries in the years that followed to great effect, as the wars would continue. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh