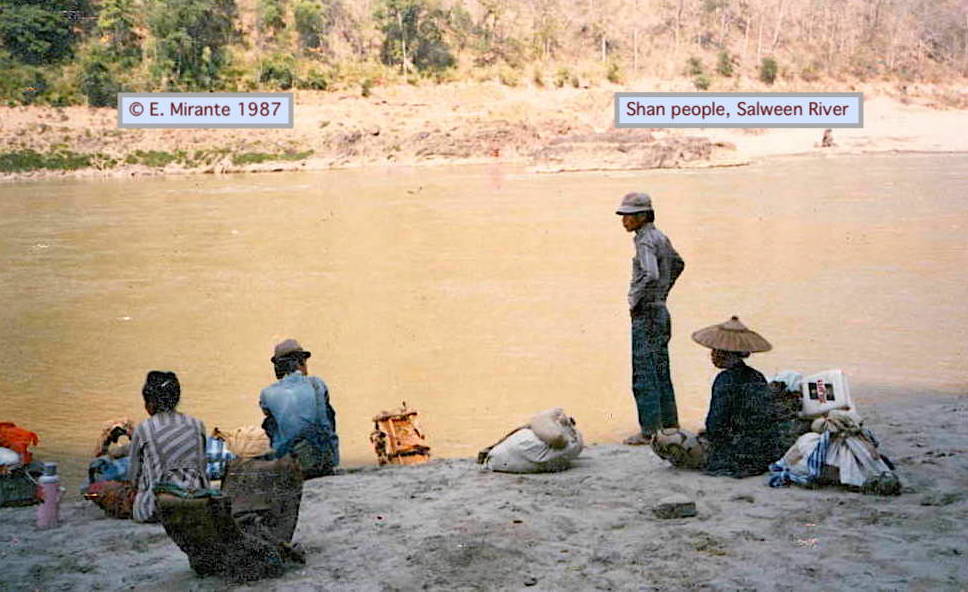
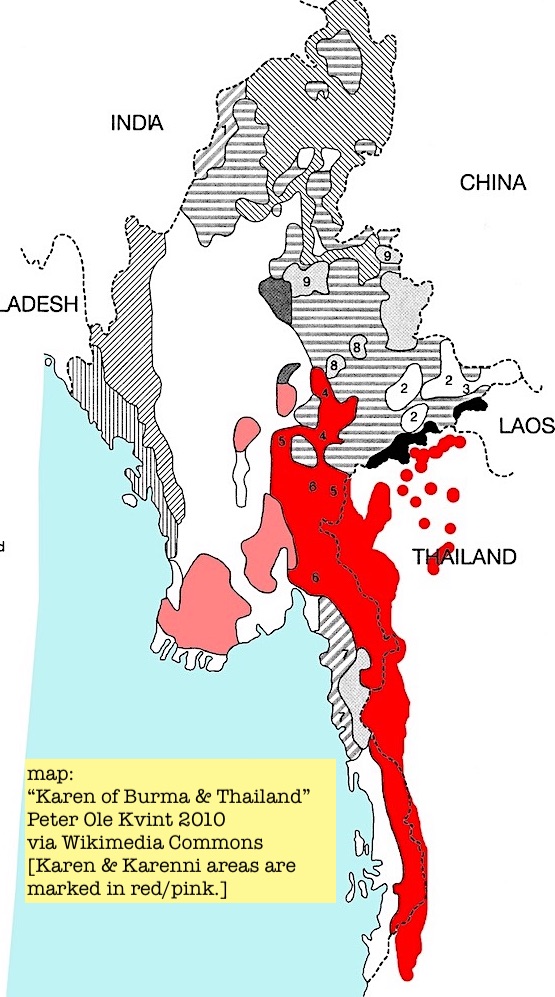
1. This History Thread is about relations between Burma (Myanmar) and China, the powerful & influential neighbor to the north. It’s a particularly long thread (30) but is still just an overview of this complex subject. #WhatIsHappeningInMyanmar 







2. Over millennia ancient migration routes along rivers connected lands that would become China with lands that would eventually be called Burma. Some peoples spoke languages of Sino-Thai family, others Tibeto-Burman languages; joined other ethnic groups inhabiting plains, hills. 

3. Ancient trade routes from Shan lands that would become Burma to Dali Kingdom (present day Yunnan, China.) Muslim traders' caravans from China. Sea trade, Chinese ships at ports in Pegu, Arakan, Martaban. By 15th C. precious stones, metals mined in Shan lands for China trade. 





4. 13th C. Kublai Khan’s Mongol Yuan Dynasty of China invaded Pagan Empire, Burma’s Irrawaddy plains. Turkic soldiers of the Khan conquered Pagan, renamed it Zhengmian. Marco Polo wrote about it. Yuan Mongols re-invaded northern Burma at start of 14th C. (unsuccessful, withdrew.) 

5. As China’s Ming Dynasty collapsed, in 1658 its last proclaimed Emperor Zhu Yongli fled Manchu Qing forces south to Sagaing (under Ava, later Burma.) Chinese Yongli loyalists followed. 1662 serial turncoat Gen. Wu Sangui's Manchu force captured Yongli in Sagaing & executed him. 

6. 1766-70 Sino-Burmese War: Qing dynasty (Manchu) invaders repelled by malaria & other diseases. 1856–73 Panthay Rebellion of Hui Muslims in Yunnan, China happened after British had conquered “Lower Burma.” When rebellion was suppressed, “Panthay” Hui refugees settled in Burma. 

7. During British colonial times, Chinese (particularly Cantonese & Fujianese) immigrated to Burma, settling in Rangoon & other cities, towns. Some prospered, notably Aw Boon Har & Aw Boon Par, brothers who marketed Tiger Balm brand salve. scmp.com/lifestyle/arti…
8. WW2 Japanese occupied Burma. US Gen. Stilwell, Allied commander for China/Burma/India emphasized supply routes from India through Burma to China (air supply & Ledo + Burma Rds) & using Chinese Expeditionary Force which fought in battles incl. Yenangyaung oil field & Myitkyina. 
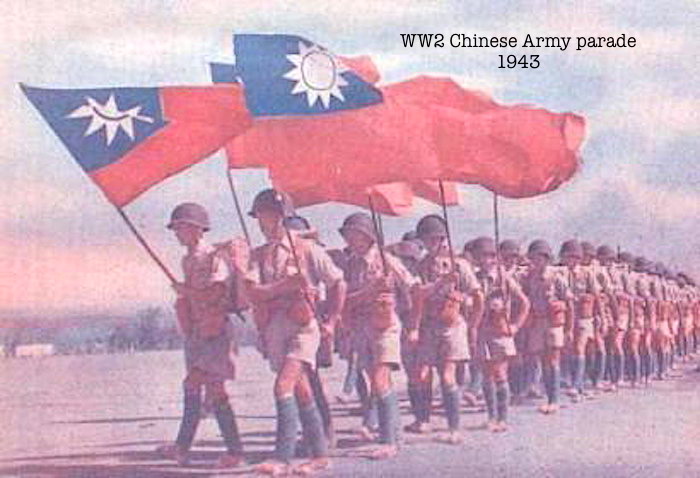





9. U Nu’s independent Burma govt recognized Peoples Republic of China in 1949. Chinese Nationalist Kuomintang (KMT) soldiers under Gen Li Mi fled China 1950-61 to Burma’s Shan St. US/Thai covert support until driven out by Sino-Burmese operation. KMT was prominent in opium trade. 



10. After Gen. Ne Win's 1962 Burma coup PRC didn’t trust Ne Win’s Cold War neutral stance & supported Communist Party of Burma (Maoist) on Shan St./China border. Also on China frontier, Kachin Independence Organization (Ethnic Armed Organization) financed by jade trade to China. 





11. 1967 Burmese mobs attacked Chinese Embassy & Chinese ethnic schools, businesses, homes in Rangoon & elsewhere (possible diversion tactic by Ne Win regime.) 30+ people of Chinese ethnicity or nationality killed. Citizenship of ethnic Chinese was diminished in 1982 Burma law. 

12. During post-1988 SLORC/SPDC junta rule China became main Myanmar (Burma) arms supplier. Tanks, vehicles, artillery, small arms, combat aircraft, ships. In recent years tech surveillance. Myanmar traded commodities for Chinese weapons or used hard currency from petroleum deals 
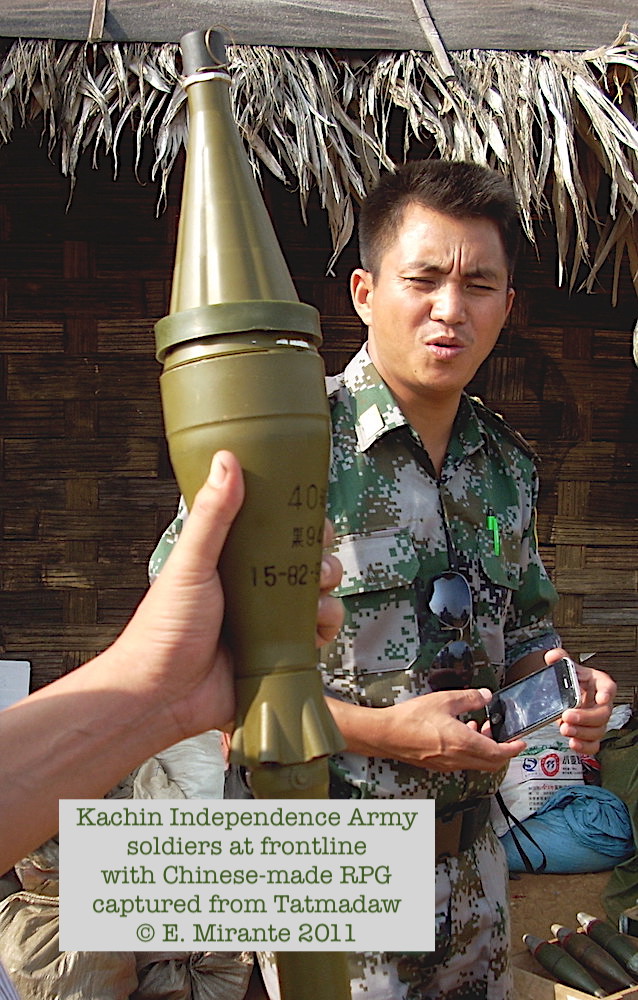





13. 1989 Communist Party of Burma overthrown in Shan St & leaders fled to China. Replaced by United Wa State Army & other Wa &/or ethnic Chinese forces involved in heroin & methamphetamine trade. UWSA, armed by China, has large autonomous zones in Myanmar. asiatimes.com/2019/09/why-my…
14. Myanmar’s China border towns incl. Nat. Dem. Alliance Army’s Mong La & Laukkai (Kokang) notorious for wildlife trade (tiger, elephant, pangolin etc.), gambling, sex tourism for Chinese border-crossers. Heroin, meth problems in China’s border towns. nytimes.com/2014/02/25/wor…
15. Since 1980s increasing numbers people from China trade, invest, live in Myanmar, particularly Mandalay, some obtaining citizenship. Chinese workers in Myanmar for infrastructure projects, resource extraction. Influx led to local resentment & conflict. scmp.com/news/asia/sout…
16. During Kachin Independence Army 1994-2011 ceasefire w. Myanmar military, northern forests were decimated by timber companies from China in deals w. govt/military, militias, KIO. Myanmar worst deforestation rate in world in 2003. @Global_Witness report: globalwitness.org/en/archive/con… 

17. Kachinland's precious jadeite 1st significantly traded to China in 1784. China remains main market for jade from Myanmar. Chinese companies use heavy equipment for mountaintop removal jade mining, increasing environment devastation & danger to workers. reuters.com/article/us-mya…
18. Companies from China mine/process minerals in Myanmar incl. gold, nickel, rare earths, etc. without environment protection, worker rights. Protests at Letpadaung copper mine operated since 2011 by Nornico (China state-owned arms co.) subsidiary Wanbao. frontiermyanmar.net/en/left-behind…
19. Kokang a Shan St., Myanmar region w. ethnic Chinese population. In 2009 Myanmar Gen. Min Aung Hlaing waged military offensive against a Kokang ceasefire force, his abuses causing 37,000 refugees to flee to China. Same Light Infantry Divisions he later unleashed on Rohingyas. 



20. Myanmar Air Force attacking Kokang’s Myanmar National Democratic Alliance Army in 2015 dropped bombs across China border killing 5 Chinese villagers. Cross-border China bombing by Myanmar Air Force also in Myanmar war against Kachin Independence Army. time.com/3745604/china-…
21. Highly unusual: Jan. 10, 2013, est. 1,500 Chinese citizens of Kachin-related Jingpo ethnicity marched through streets of 2 towns in Yunnan China to protest Myanmar military attacks on KIA territory then crossed border to KIA’s town Laiza for a combined protest with residents. 

22. China’s most controversial Myanmar development project: damming revered Myitsone confluence Irrawaddy River, Kachin St. to supply power to China. Opposed locally & nationally for enviro, seismic reasons. Suspended 2011 but China attempts to revive it. frontiermyanmar.net/en/myitsones-m…
23. China National Petroleum Corp. built Rakhine St. port & pipelines to bring oil (Middle East) & gas (offshore Myanmar) across Myanmar to China since 2013-14. Land-grabbing, fishing bans, pollution, labor conflict. Kyauk Pyu port project ongoing, report: unearthmyanmar.com/stories/rakhin… 

24. In 21st C. companies from China expanded agribusiness plantations in Myanmar with land grabbing, causing environmental harm with pesticides, chemical fertilizers & deforestation as they produced crops like rubber, tapioca & bananas for China market. frontiermyanmar.net/en/kachins-pla…
25. Since 2017 Chinese investors with Chinese workers building 3+ “megacities” to feature gambling & "blockchain tech" in Myanmar's Karen (Kayin) St. bordering Thailand. Criminal networks operating w. Myanmar military & other armed groups. Land grabbing. rfa.org/english/news/m…
26. Although replaced by Russia as top arms source, China remains most important relationship for Myanmar mil/govt, described as “pauk phaw” (sibling.) China + Russia block UN Sec. Council holding Myanmar mil/govt accountable for human rights violations. voanews.com/east-asia-paci…
27. As head of Myanmar government Aung San Suu Kyi kept friendly ties with China’s leaders with 2020 Xi Jinping state visit. China's “Belt & Road” international connectivity plans for Myanmar: infrastructure like the petroleum pipelines & transport links. thethirdpole.net/en/regional-co…
28. Myanmar/China border trade affected by COVID suspensions. China built partial border fence 2020-21. As COVID spreads through Myanmar under coup regime, Chinese vaccines reportedly mistrusted by some of public. China dispersing aid funds to coup junta. irrawaddy.com/news/burma/mya…
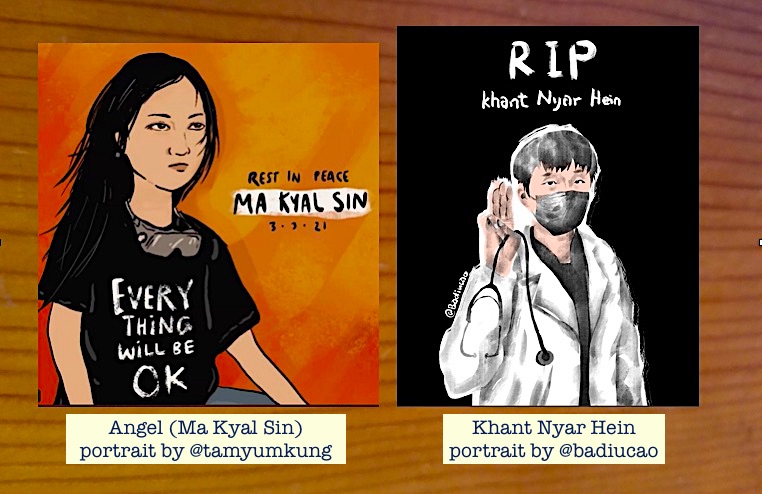
29. Since Feb. 1, 2021 Myanmar military coup, anti-coup demonstrations at Chinese embassy, Chinese goods boycotted. China-invested factories burned, pipeline sabotage threatened. Protesters of Chinese descent killed by Myanmar coup forces include Angel Kyal Sin & Khant Nyar Hein. 

30/30. China/Burma sources include: Yi Li 2017, Struve ’13, Thaw Kaung ’14, Jayde Lin Roberts ’16, Maung Aung Myoe, Hongwei Fan, @gardlunden, @Global_Witness,@pwinn5, Alvin Cheng-Hin Lim ’15, Nyi Nyi Kyaw ’20. My previous History Threads & reports are at projectmaje.org 







• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh