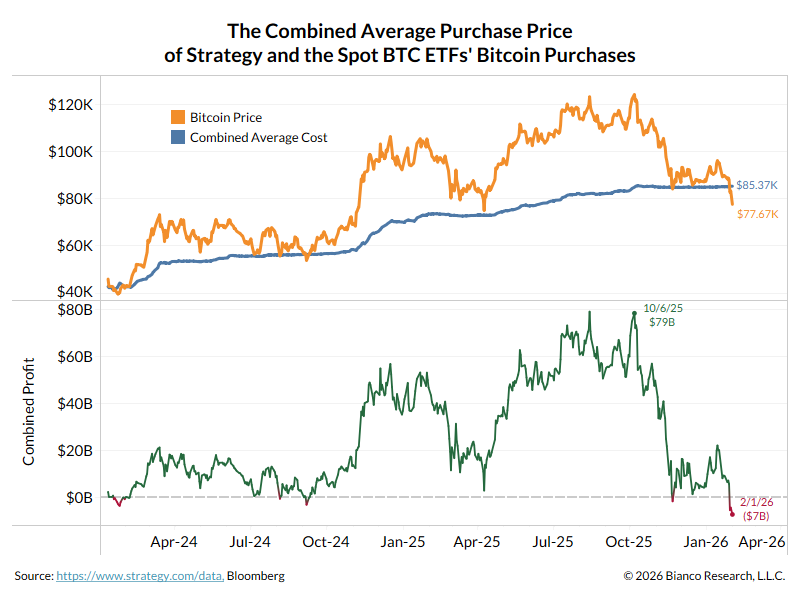
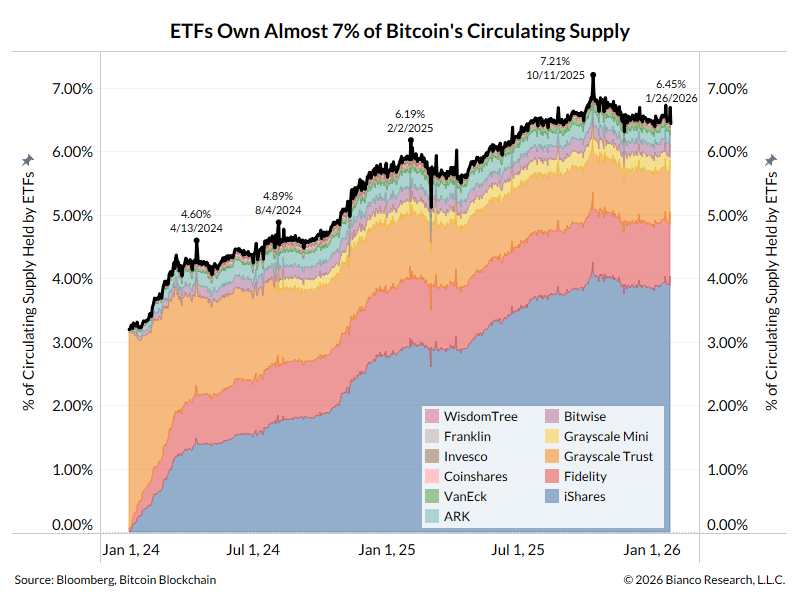
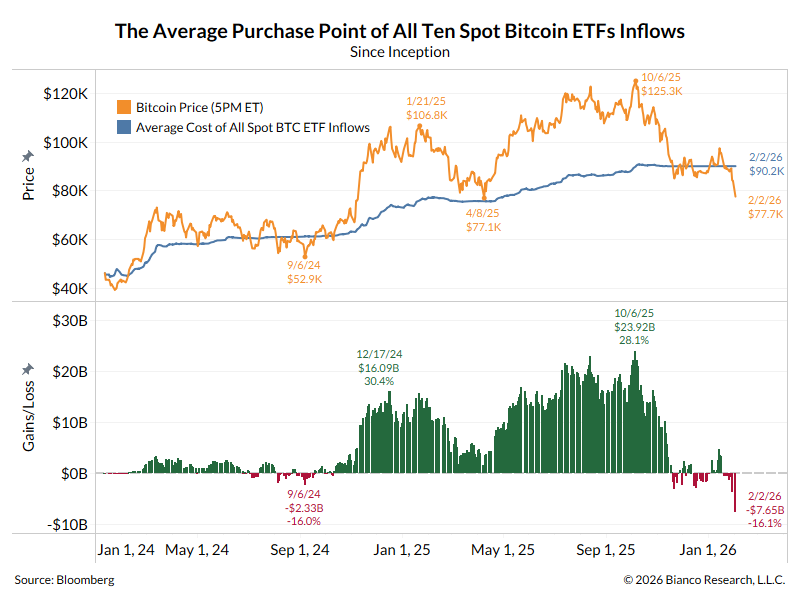
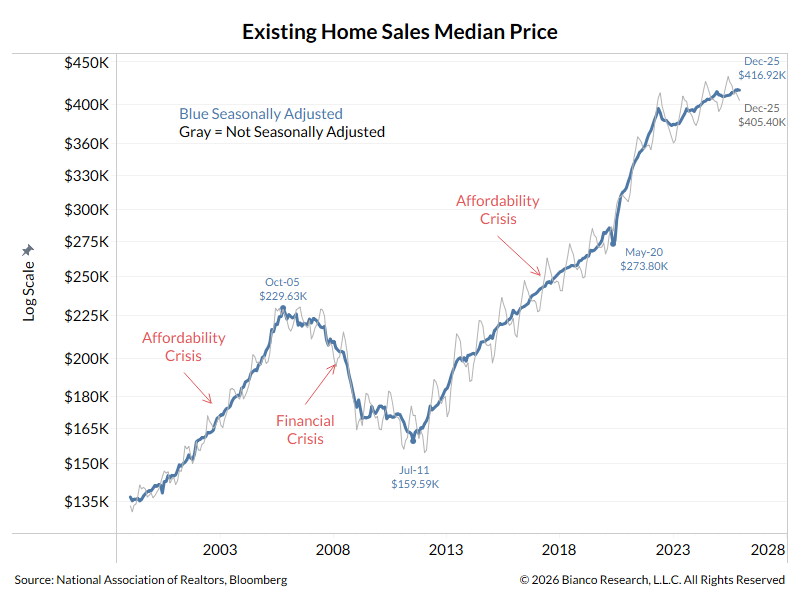
Tweet storm on stock market valuation.
Bottom line, companies have delivered earnings like a .300+ hitter with 35+ hrs. But you're paying that hitter $35m+/yr (record salary). Good for now. But will this hitter earn its pay next year, and the year after?
1/8
Bottom line, companies have delivered earnings like a .300+ hitter with 35+ hrs. But you're paying that hitter $35m+/yr (record salary). Good for now. But will this hitter earn its pay next year, and the year after?
1/8
As of August 23, 2021, 475 (95%) S&P 500 companies have reported Q2 2021 earnings with a beat rate of 87%, a new record. This compares to an average beat rate of 71% since the Great Recession ended.
2/8
2/8

Analysts expected YoY earnings of ~55%. The latest blended est. is ~ 95%. This jump of ~40% is record.
YoY earnings is compared to Q2 20220, the worst point of the lockdown, big base effect. This is why estimates for Q3 2021 earnings growth drop to 29% and 20% for Q4 2021.
3/8
YoY earnings is compared to Q2 20220, the worst point of the lockdown, big base effect. This is why estimates for Q3 2021 earnings growth drop to 29% and 20% for Q4 2021.
3/8

Company guidance, an index of which is shown below, shows companies continue to see strong earnings growth.
It remains to be seen if more COVID restrictions or rising inflationary costs will dampen expectations for earnings in the future.
4/8
It remains to be seen if more COVID restrictions or rising inflationary costs will dampen expectations for earnings in the future.
4/8

Hefty earnings growth is still needed. The 12-mo forward earnings P/E ratio, a Wall Street fav, is still quite high at 22.
Investors do not seemed bothered by these valuations. But should earnings disappoint, which has not been the case recently, investors may reconsider.
5/8
Investors do not seemed bothered by these valuations. But should earnings disappoint, which has not been the case recently, investors may reconsider.
5/8

@5thrule argues that SPX valuation is made up of 3 parts:
* The current value of assets, or the book value
* The NPV of expected future earnings. Or, the median SPX earnings forecast by WS analysts for the next 3 years
* A residual component he calls “Hopes and Dreams”
6/8
* The current value of assets, or the book value
* The NPV of expected future earnings. Or, the median SPX earnings forecast by WS analysts for the next 3 years
* A residual component he calls “Hopes and Dreams”
6/8

Normally a market should factor in “Hopes and Dreams” as companies have flexible structures and can re-make themselves as needed. How much should this be?
The next chart shows “Hopes and Dreams” make up the largest part of valuation since the bubble peak of 2000.
7/8
The next chart shows “Hopes and Dreams” make up the largest part of valuation since the bubble peak of 2000.
7/8

Finally, market capitalization to GDP is also at a new record (the so-called Buffett Indicator).
So nothing about this market is cheap. But companies are delivering on earnings and they expect to continue to do so.
How long will they continues to is the question.
8/8
So nothing about this market is cheap. But companies are delivering on earnings and they expect to continue to do so.
How long will they continues to is the question.
8/8

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh