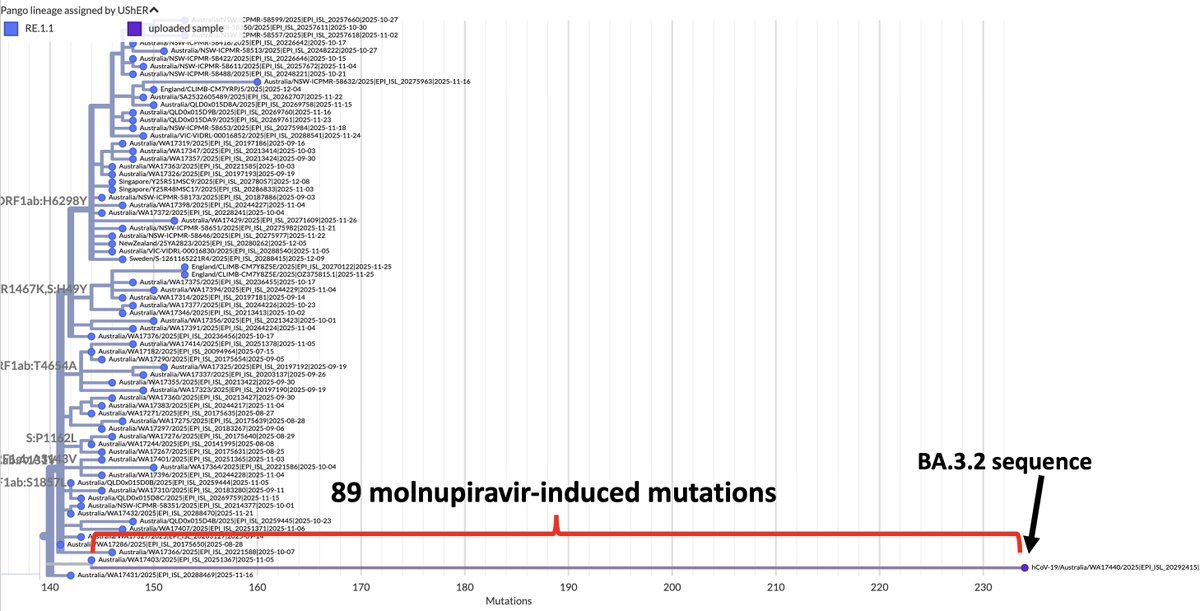
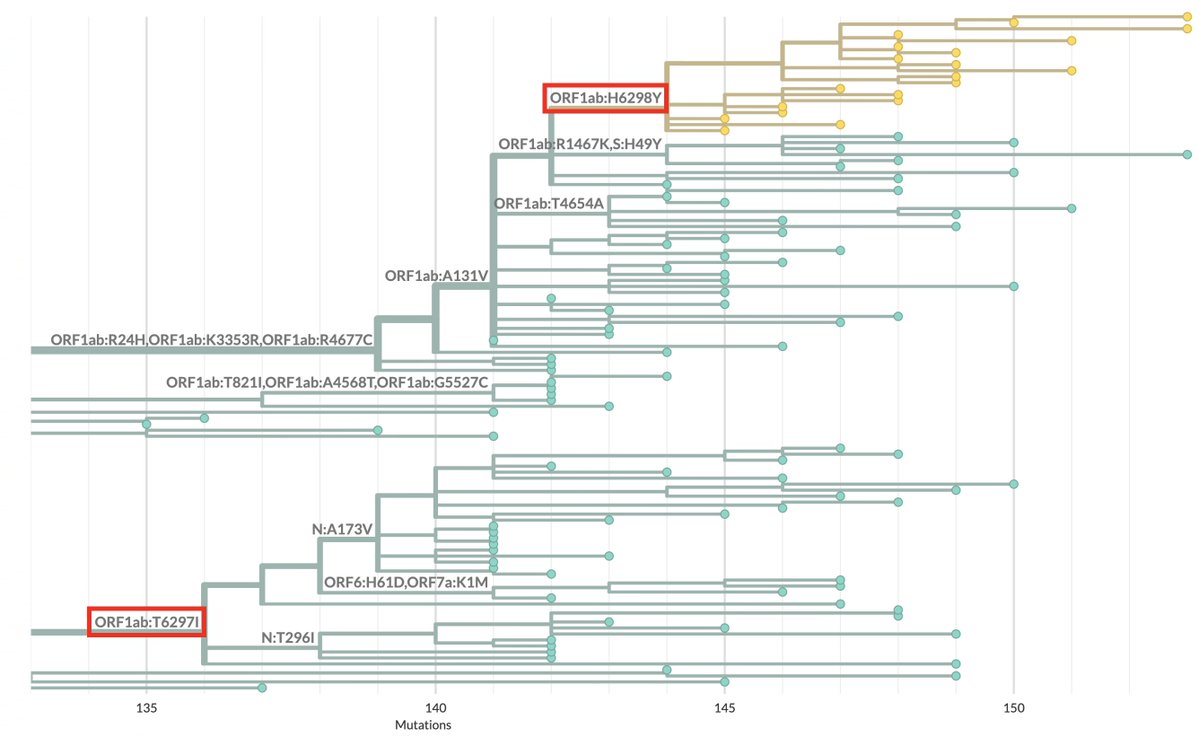
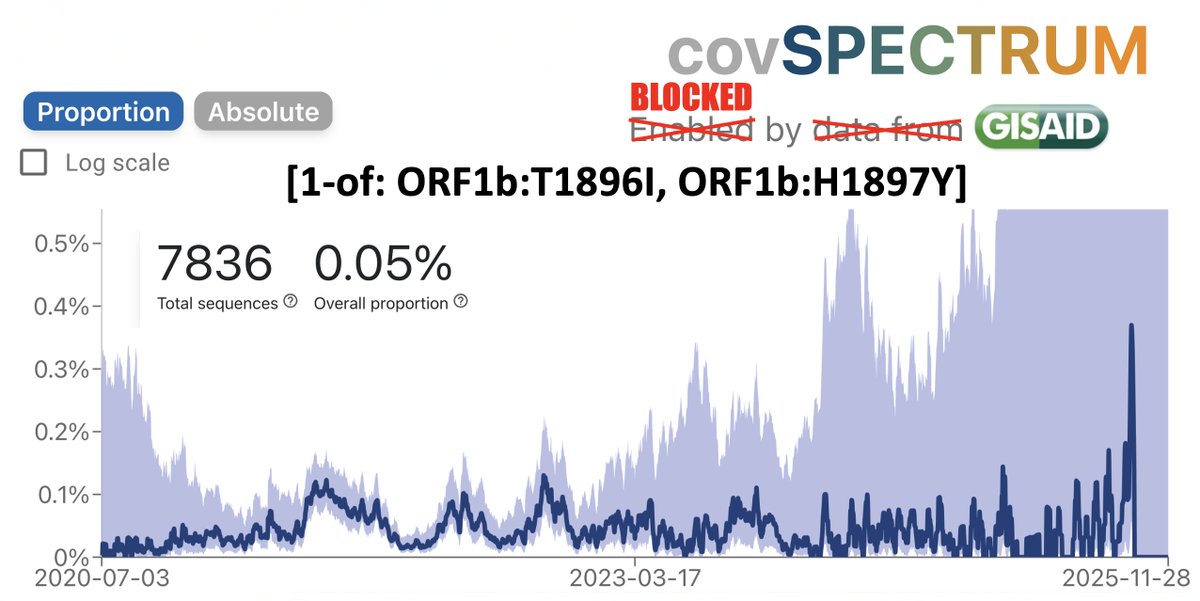
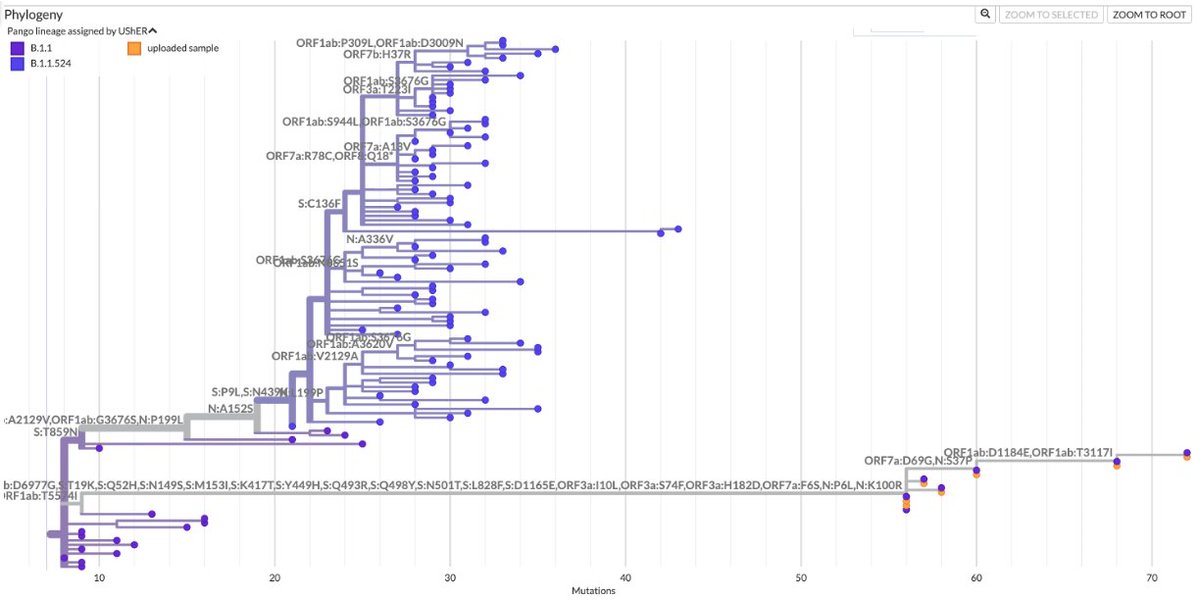
1/10 This shouldn't even be a debate. Who could argue against this? Knowledge is the ultimate public good, & to restrict access to scientific papers to those at academic institutions w/subscriptions to journals is a crime.
https://twitter.com/cg_canning/status/1431419802371899393
2/10 Out-of-control, continually strengthening copyright & patent laws are an economic weapon wielded by the rich against the poor and by enormous, monopolistic firms against small firms. This is a major driver of inequality that receives scant attention.
cepr.net/technology-pat…
cepr.net/technology-pat…

3/10 The alleged justification for strong IP laws is that they incentivize & facilitate innovation. But as @DeanBaker13 points out in his indispensable (& free) book Rigged, in their current form, IP protections greatly impede innovation. See Ch. 5 deanbaker.net/books/rigged.h… 

4/10 How much has medical progress been stifled by the patent-driven secrecy under which private research is cloaked? And by the gross distortions that drive companies to pursue expensive, patentable treatments & ignore cheap, often greatly superior treatments? (Rigged, Ch. 5) 

5/10 Apart from the baleful economic & scientific effects of our IP laws, it's worth considering some more indirect effects these laws have on public health. Patent monopolies unquestionable cause corruption in the pharmaceutical industry. @DeanBaker13 on the opioid crisis: 

6/10 Understandably, the rampant corruptions & recurrent scandals in the pharma industry have led to public distrust. Skepticism about Big Pharma claims is of course justified, but it has led some to reject anything connected to pharma, including vaccines. statnews.com/2019/02/26/ant…
7/10 The anti-vaccine movement's claims are of course absurd & tremendously harmful to public health, but their outright rejection of all scientific evidence largely stems from the never-ending flow of pharma-industry scandals, which are a predictable result of patent monopolies. 

8/10 There's been much discussion of how to combat misinformation during the pandemic, but little talk of one of the root causes: patent-monopolies. Public financing of drug research could eliminate patent monopolies & allow drugs to be sold at generic, free-market prices. 

9/10 Until we reform our rotten, corrupt, patent-monopoly-driven pharma industry, public skepticism of even impeccable medical research will remain, and such distrust will continue to be exploited by charlatans & mountebanks peddling noxious nonsense, w/grave public consequences.
10/10 Chart in tweet #8 is from chapter 5 of @DeanBaker13's book 'Rigged.' The book is freely available in digital form, & an awesome intro into some of the most pressing economic issues of our time. Definitely give Ch. 5 a read if nothing else. deanbaker.net/books/rigged.h…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh