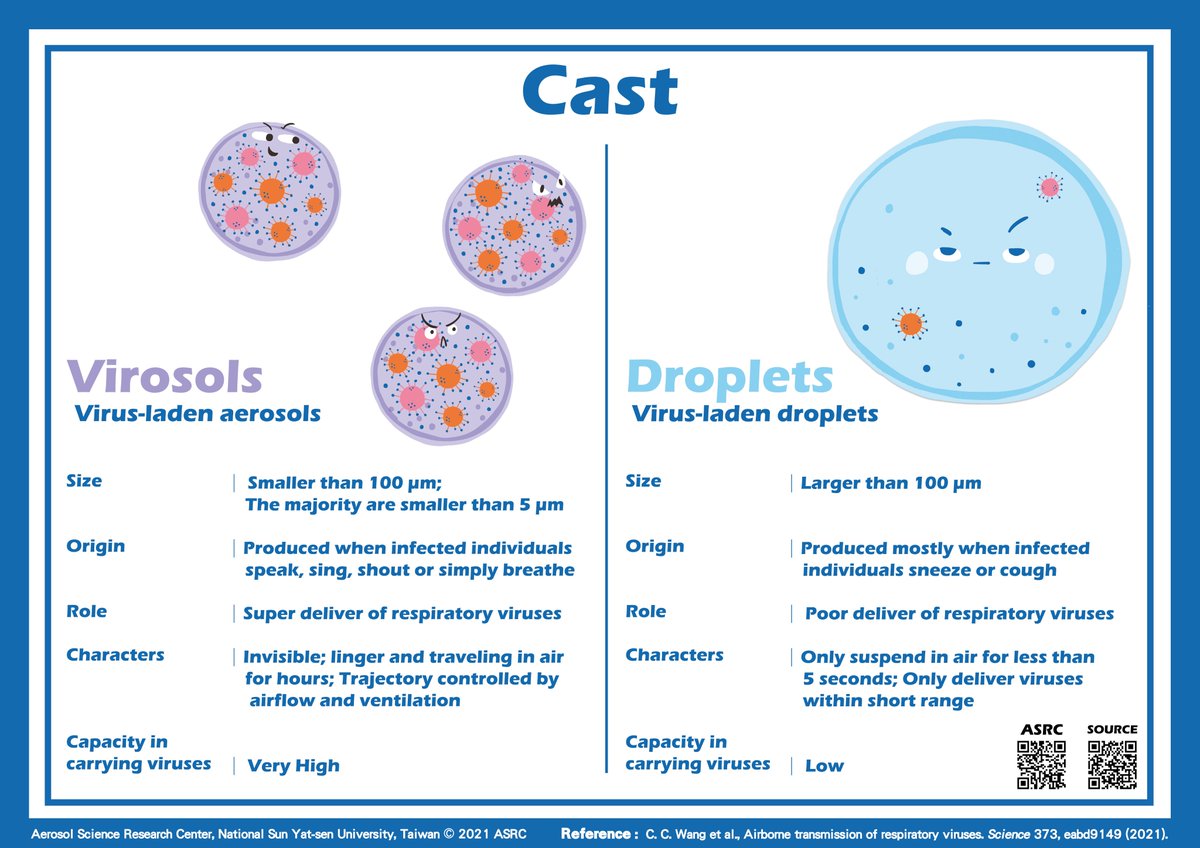
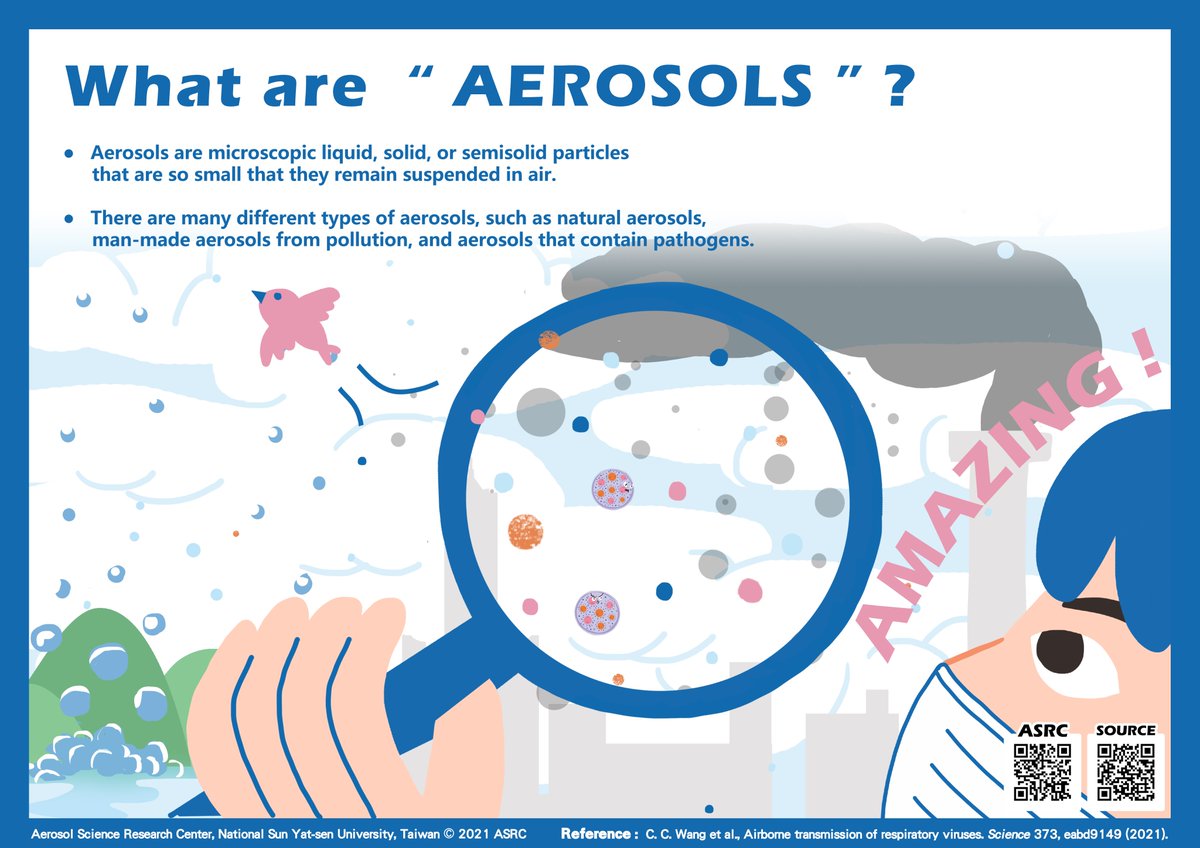
1/ AIRBORNE TRANSMISSION OF RESPIRATORY VIRUSES: THE COMIC VERSION
Supplementary multimedia prepared by lead author @ChiaWang8 to our recent @ScienceMagazine peer-reviewed paper
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
@kprather88 @linseymarr @zeynep @Lakdawala_Lab @zeynep
Supplementary multimedia prepared by lead author @ChiaWang8 to our recent @ScienceMagazine peer-reviewed paper
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
@kprather88 @linseymarr @zeynep @Lakdawala_Lab @zeynep

9/ Filters work well to remove infectious aerosols from the air (commercial HEPA or cheaper fan + filter like Corsi-Rosenthal box): 

10/ Solar radiation and artificial UV light disable aerosols by damaging their genetic material. (But ventilation and/or filters are preferable to artificial UV whenever possible) 

11/ Virus-laden aerosols can enter and deposit in the bronchiolar and alveolar regions of the lungs (also in the nose and upper respiratory tract): 

14/ Why did so many people get infected despite mask wearing? (not wearing it tight to the face, or low quality filter) 

16/ Plexiglas barriers may trap higher concentrations of aerosols! (and INCREASE, rather than decrease, transmission of the virus) 

17/ How to stop airborne transmission?
- Keep distance (helps but not enough by itself)
- Ventilation, filtration (+UV in some cases)
- Masks w/ attention to fit to the face
- Avoid indoor crowding
- Keep distance (helps but not enough by itself)
- Ventilation, filtration (+UV in some cases)
- Masks w/ attention to fit to the face
- Avoid indoor crowding

18/ More information:
- Our scientists'FAQs: bit.ly/FAQ-A
- @ScienceMagazine review: science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
- @TheLancet paper: thelancet.com/article/S0140-…
- @ScienceMagazine paradigm shift paper: science.org/doi/full/10.11…
- Transmission estimator: bit.ly/c-est
- Our scientists'FAQs: bit.ly/FAQ-A
- @ScienceMagazine review: science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
- @TheLancet paper: thelancet.com/article/S0140-…
- @ScienceMagazine paradigm shift paper: science.org/doi/full/10.11…
- Transmission estimator: bit.ly/c-est
19/ There are many requests to translate to other languages. So far they are only in English, but I am inquiring if we can make the editable files available, will post here if so.
20/ If you want to download all the comic images at once, they are available in this folder:
drive.google.com/drive/u/0/fold…
drive.google.com/drive/u/0/fold…
21/ And for people more inclined to learn about the details, check out the literature references etc., this thread explains the @ScienceMagazine paper in more detail:
https://twitter.com/jljcolorado/status/1430967286244970502
22/ A powerpoint version can be downloaded from this folder from @chiawang (it is the file that ends in "pptx"):
drive.google.com/drive/folders/…
drive.google.com/drive/folders/…
23/ TRANSLATIONS: if interested in translating the comics, pls complete agreement in folder below, & send it to @ChiaWang8 at chiawang@mail.nsysu.edu.tw:
Translation to Indonesian, Thai, Dutch, and Sinhala is already underway. Help for others needed
drive.google.com/drive/folders/…
Translation to Indonesian, Thai, Dutch, and Sinhala is already underway. Help for others needed
drive.google.com/drive/folders/…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh