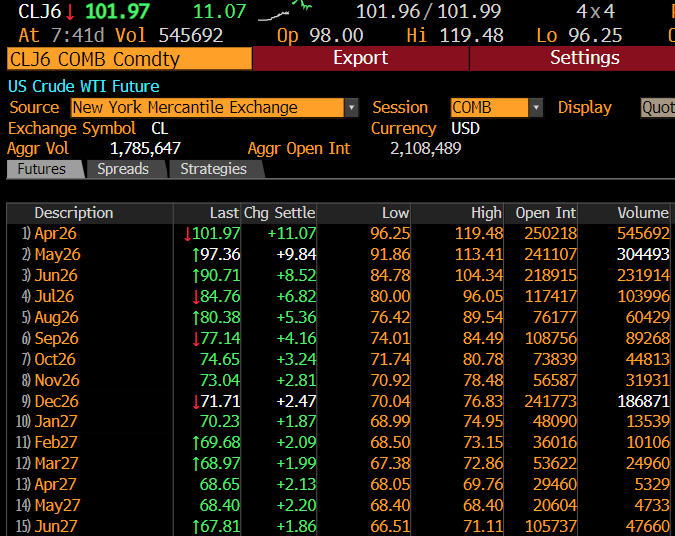
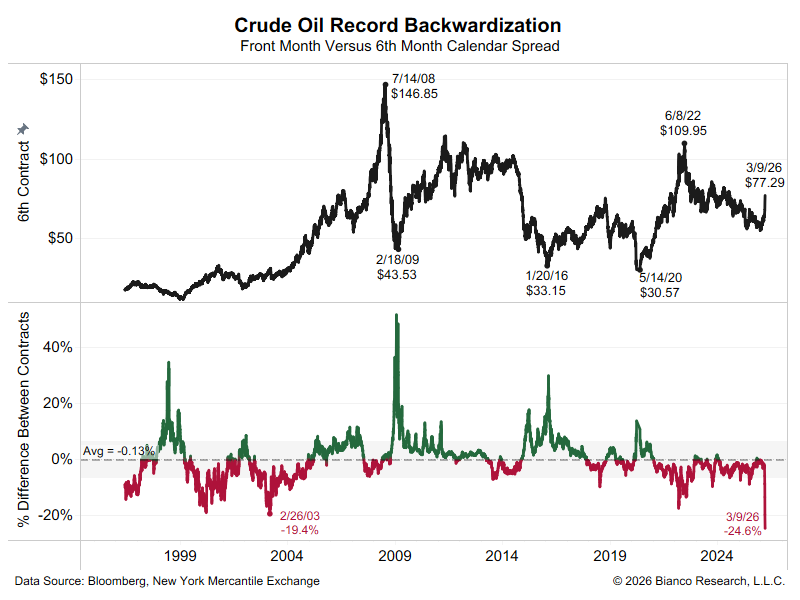
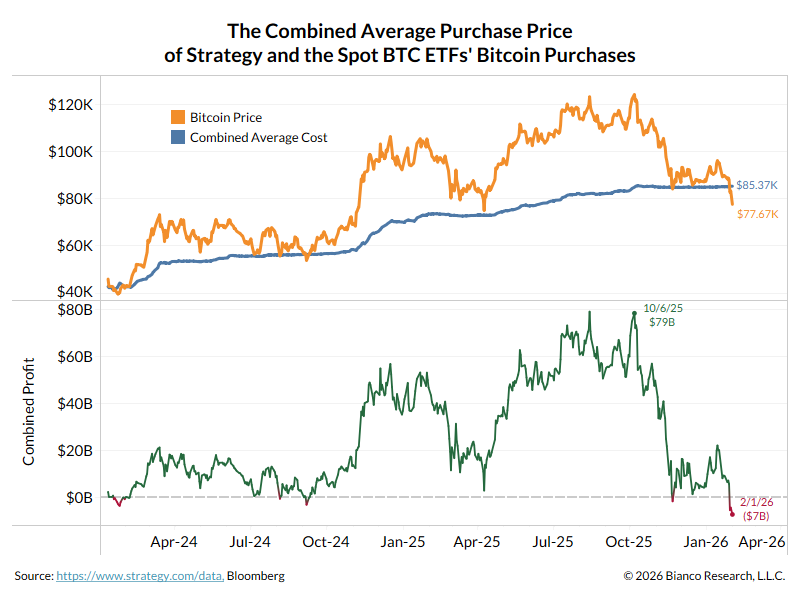
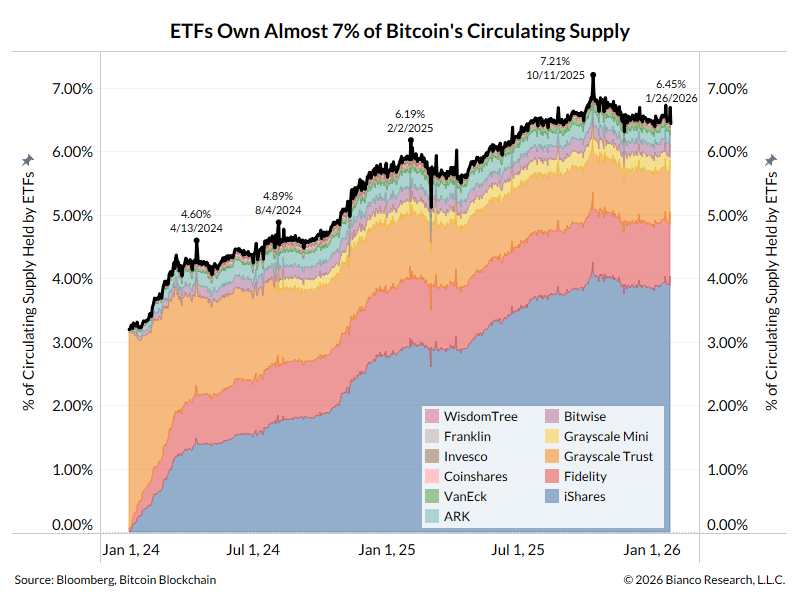
A thread about transitory vs persistent inflation and why persistent might be actually be winning.
This comes from @economics And it breaks down CPI by reopening and non-reopening components.
Of the 5.25% inflation rate in the last year, only 1.62% was reopening components.
1/6
This comes from @economics And it breaks down CPI by reopening and non-reopening components.
Of the 5.25% inflation rate in the last year, only 1.62% was reopening components.
1/6

Breaking it down for August we find that reopening CPI components (or transitory inflation) FELL by 0.22% while CPI non-reopening components (or persistent inflation) ROSE by 0.35%
2/6
2/6

Detailing this we find that CPI non-reopening (persistent) components are surging to its highest monthly level since at least 2016.
Restated, this series of persistent inflation is trending higher, and is 78% of overall CPI.
3/6
Restated, this series of persistent inflation is trending higher, and is 78% of overall CPI.
3/6

The CPI reopening components (transitory) fell by the most since the lockdown.
Restated, this series of transitory inflation is falling and is just 14% of overall CPI.
4/6
Restated, this series of transitory inflation is falling and is just 14% of overall CPI.
4/6

So, why are the CPI reopening components falling? Is the Delta variant hurting the economy and sapping demand?
Consider these two charts.
Airline ticket prices collapsed by 9% annualized in August. Why? Because demand is also collapsing as measured by the TSA?
5/6

Consider these two charts.
Airline ticket prices collapsed by 9% annualized in August. Why? Because demand is also collapsing as measured by the TSA?
5/6


In sum transitory components are falling and their demand is off as Delta is hurting economic activity.
Meanwhile persistent inflation components are surging higher and higher.
Is this why stocks turnaround today? Weakening demand and higher inflation squeezing margins?
6/6
Meanwhile persistent inflation components are surging higher and higher.
Is this why stocks turnaround today? Weakening demand and higher inflation squeezing margins?
6/6
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh