Imagine a war-ravaged country, food crisis looming large, its desolate children, and a Messiah in the skies. This all came together once in post-WWII Germany when conflict among the Allied nations reached its peak and spawned Cold War's 1st crisis (1/n)
Soviet Union cut-off road, rail & canal links to Western bloc-held Berlin in the summer of 1948. Thus began Operation Berlin Airlift with US & UK air dropping supplies into the starving city. It is estimated that more than 250,000 sorties were flown (2/n) 

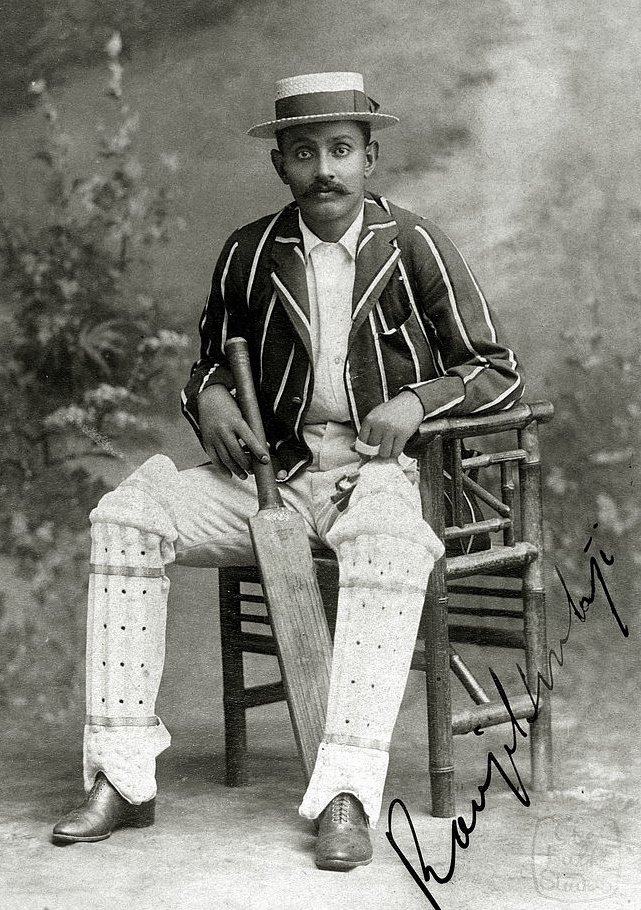
One of the many pilots engaged in the airdrops was Lt. Gail Halvorsen from Utah. In his spare time, he often flew into Berlin to do some photography. During one of those visits, he came across a bunch of kids in ragged condition across a barbed wire (3/n) 

Halvorsen gave them some toffees he was carrying. The kids distributed the toffees in the smallest of pieces - those who still didn't get one took the wrappers and sniffed them. The sight affected Halvorsen strongly (4/n)
He promised the kids he would be back with more. Gail Halvorsen prepared tiny parachutes with handkerchiefs & socks packing candies, chocolates & gums into them and #OTD in 1948, proceeded to drop them over Berlin. (5/n)
He repeated this several times over coming days and was joined by a few colleagues. Halvorsen rocked his plane a few times before the drops - his promised signal to the kids to help them identify his aircraft. (6/n) 

Soon, stacks of mail arrived at the base camp addressed to "Uncle Wiggly Wings", "The Chocolate Uncle" and "The Chocolate Flier." In no time, Halvorsen's initiative became a national project with several US confectionary cos. pitching in (7/n) 

The Chocolate Bomber Uncle of Berlin had a profound impact on the children of the war. They kept writing letters to him providing a map of their houses and mentioning their most favorite flavors. (8/n) 

One such little letter reads, “I'll be in the backyard every day at 2:00 PM. Drop the chocolate there". Gail Halvorsen showed that you don’t need guns, but a only a thriving conscience to win over a million hearts (9/n) 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh