Fresh analysis thread 🙌
Chelsea fell to defeat at Juventus after a fine defensive display from the Italians. Juve took the lead just 11 seconds into the second half through Federico Chiesa – a goal Thomas Tuchel later desrcibed as “cheap”... 🧐🧵
#JuventusChelsea • #UCL
Chelsea fell to defeat at Juventus after a fine defensive display from the Italians. Juve took the lead just 11 seconds into the second half through Federico Chiesa – a goal Thomas Tuchel later desrcibed as “cheap”... 🧐🧵
#JuventusChelsea • #UCL
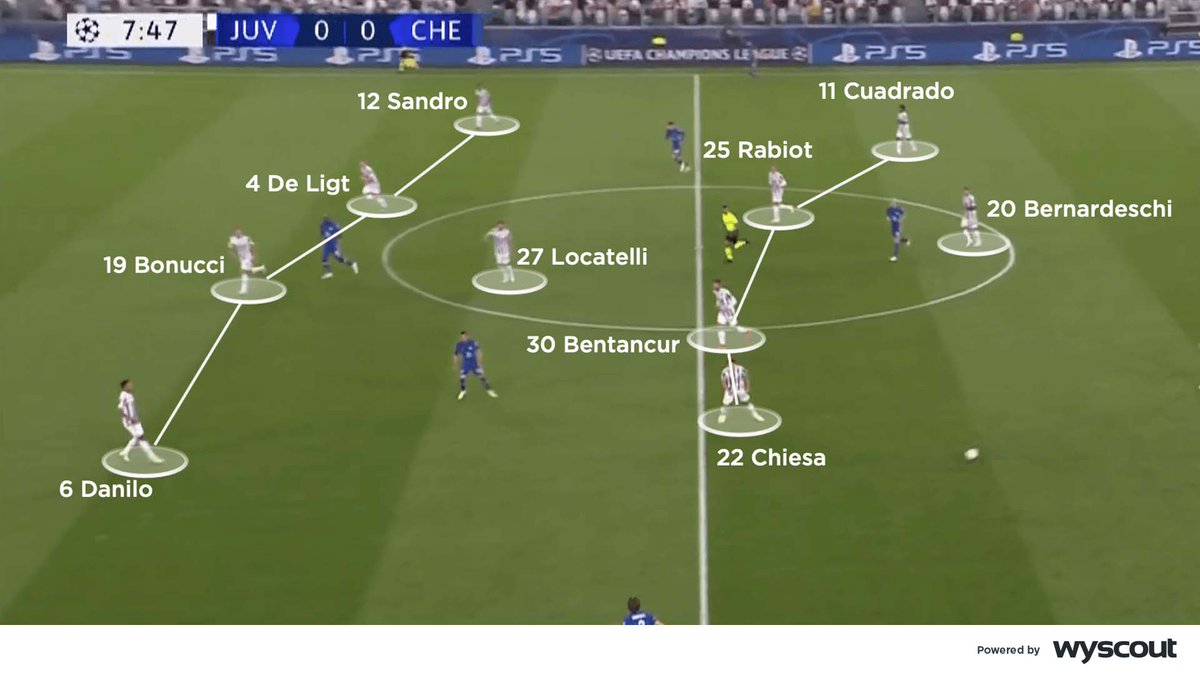
Bentancur dropped alongside Locatelli to form a double pivot. Bernardeschi then dropped into midfield, while Cuadrado moved into a narrow position. Chiesa then moved across the front line, attacking centrally to threaten the space in behind Chelsea’s back three 🧐🧵 

Juventus initially defended with a 4-1-4-1. The hosts’ two number eights – Rabiot and Bentancur – pushed forwards to press Chelsea’s double pivot, with wingers Chiesa and Cuadrado pressing from out to in 🧐🧵 
Chiesa remained as Juve’s highest threat throughout the game, and they defended incredibly deep but remained ready to counter-attack. In the moments where Cuadrado did break forward, they looked to release him or Chiesa following Bernardeschi dropping into a 10 position 🧐🧵 

Cuadrado dropped so deep that Juventus ended up in a 5-4-1 with a diamond midfield, which stopped Chelsea finding their way into the inside channels, and forced play out wide. Any resulting crosses were dealt with well by Juventus’ back line 🧐🧵 

Chelsea were set up by their manager Thomas Tuchel in a 3-4-2-1 formation when in possession, with the width held by wing-backs Alonso and Azpilicueta. Lukaku was supported by penetrative runs from number 10s, Ziyech and Havertz through the inside channels 🧐🧵 

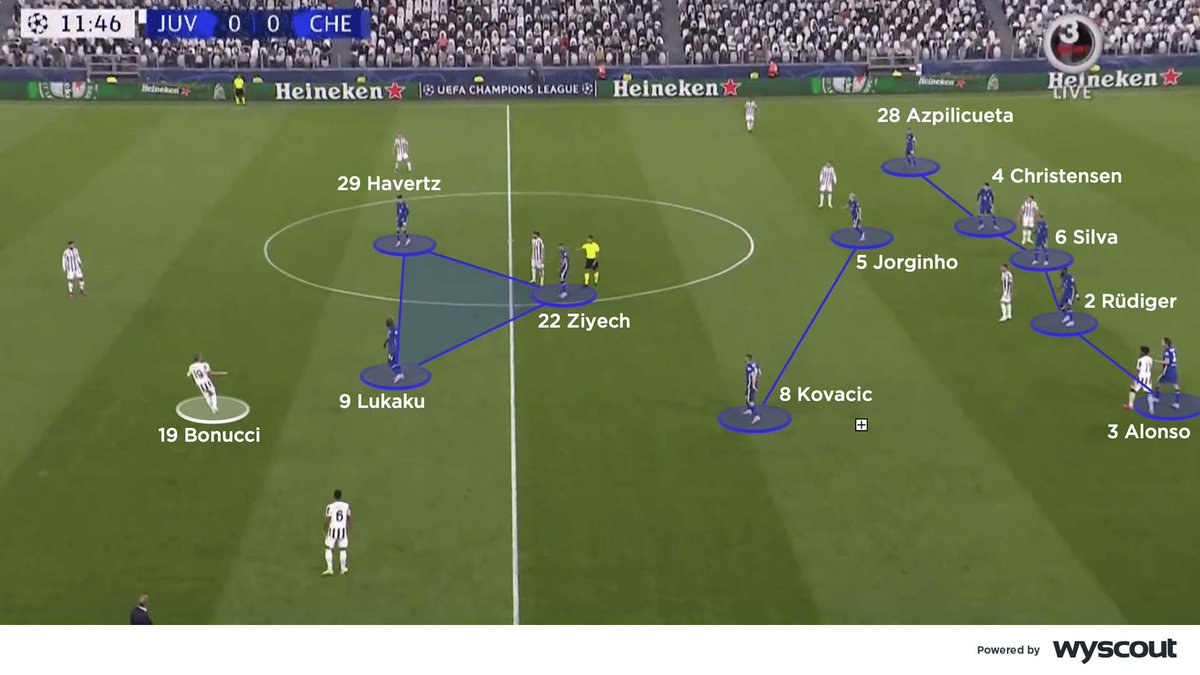
Chelsea defended with a 5-2-3 mid-block where Ziyech moved into the centre as a defensive number 10 behind Lukaku and Havertz to cover Juventus’ single pivot, Locatelli. Jorginho and Kovacic, as Chelsea’s double pivot, held their positions to occupy Juventus’ two number 8s 🧐🧵 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh