Accounting is the language of business.
If you buy stocks, you MUST learn how to read a balance sheet.
Here’s everything you need to know:
If you buy stocks, you MUST learn how to read a balance sheet.
Here’s everything you need to know:
The balance sheet is one of the 3 major financial statements.
It shows company’s:
▪️Assets: What it owns
▪️Liabilities: What it owes
▪️Shareholders Equity: It's net worth attributable to its owners
At a fixed point in time
It shows company’s:
▪️Assets: What it owns
▪️Liabilities: What it owes
▪️Shareholders Equity: It's net worth attributable to its owners
At a fixed point in time
That “at a point in time” part is key!
A balance sheet is a SNAPSHOT of a company’s net worth.
It is usually measured at the end of a quarter/year.
That’s different from an income statement or cash flow statement, both of which are measured over periods of time
A balance sheet is a SNAPSHOT of a company’s net worth.
It is usually measured at the end of a quarter/year.
That’s different from an income statement or cash flow statement, both of which are measured over periods of time
All balance sheets follow the same formula:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders Equity
This formula must be in balance at all times
(Hence the term “balance sheet”)
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders Equity
This formula must be in balance at all times
(Hence the term “balance sheet”)

Side Note:
This formula can be easily re-arranged into the “net worth” formula that you are already familiar with
Assets - Liabilities = Shareholders Equity (Net worth)
This formula can be easily re-arranged into the “net worth” formula that you are already familiar with
Assets - Liabilities = Shareholders Equity (Net worth)

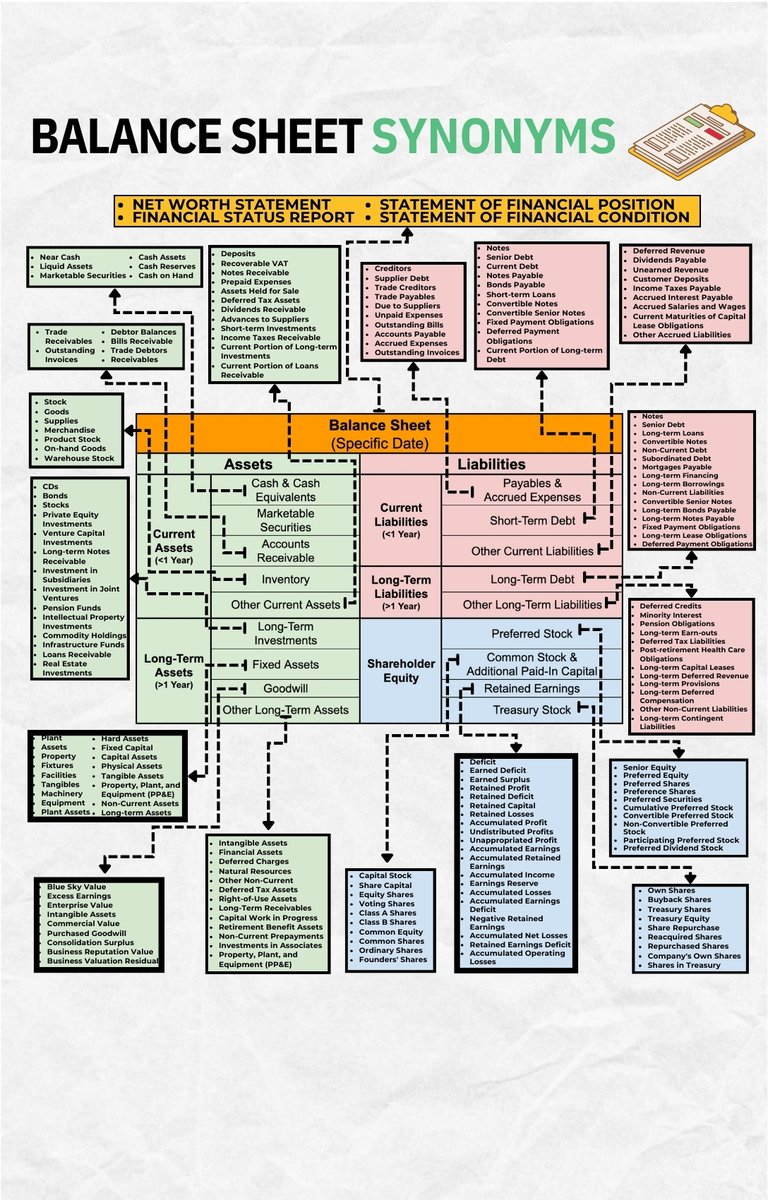
Companies get soe leeway in how they categorize each item on their balance sheet
This graphic shows some of the most commonly used categories & terms
This graphic shows some of the most commonly used categories & terms

Let’s start with assets, which is what a company OWNS
Assets are listed in order of liquidity
(Liquidity means how quickly a security can be turned into cash)
The most liquid assets are at the top, the least liquid on the bottom
Assets are listed in order of liquidity
(Liquidity means how quickly a security can be turned into cash)
The most liquid assets are at the top, the least liquid on the bottom

There are two categories of assets:
Current assets:
▪️Assets that are expected to be used in <1 year
Long-term assets:
▪️Assets that a company will benefit from for >1 year
Current assets:
▪️Assets that are expected to be used in <1 year
Long-term assets:
▪️Assets that a company will benefit from for >1 year

Common current assets:
▪️Cash: Checking account, t-bills, CDs w/ <3 maturity
▪️Marketable Securities: Stocks, bonds...etc that can easily become cash
▪️Accounts Receivable: Money it is owed by its customers
▪️Inventory: Unsold goods
▪️Prepaid expenses: Insurance, rent, etc…
▪️Cash: Checking account, t-bills, CDs w/ <3 maturity
▪️Marketable Securities: Stocks, bonds...etc that can easily become cash
▪️Accounts Receivable: Money it is owed by its customers
▪️Inventory: Unsold goods
▪️Prepaid expenses: Insurance, rent, etc…
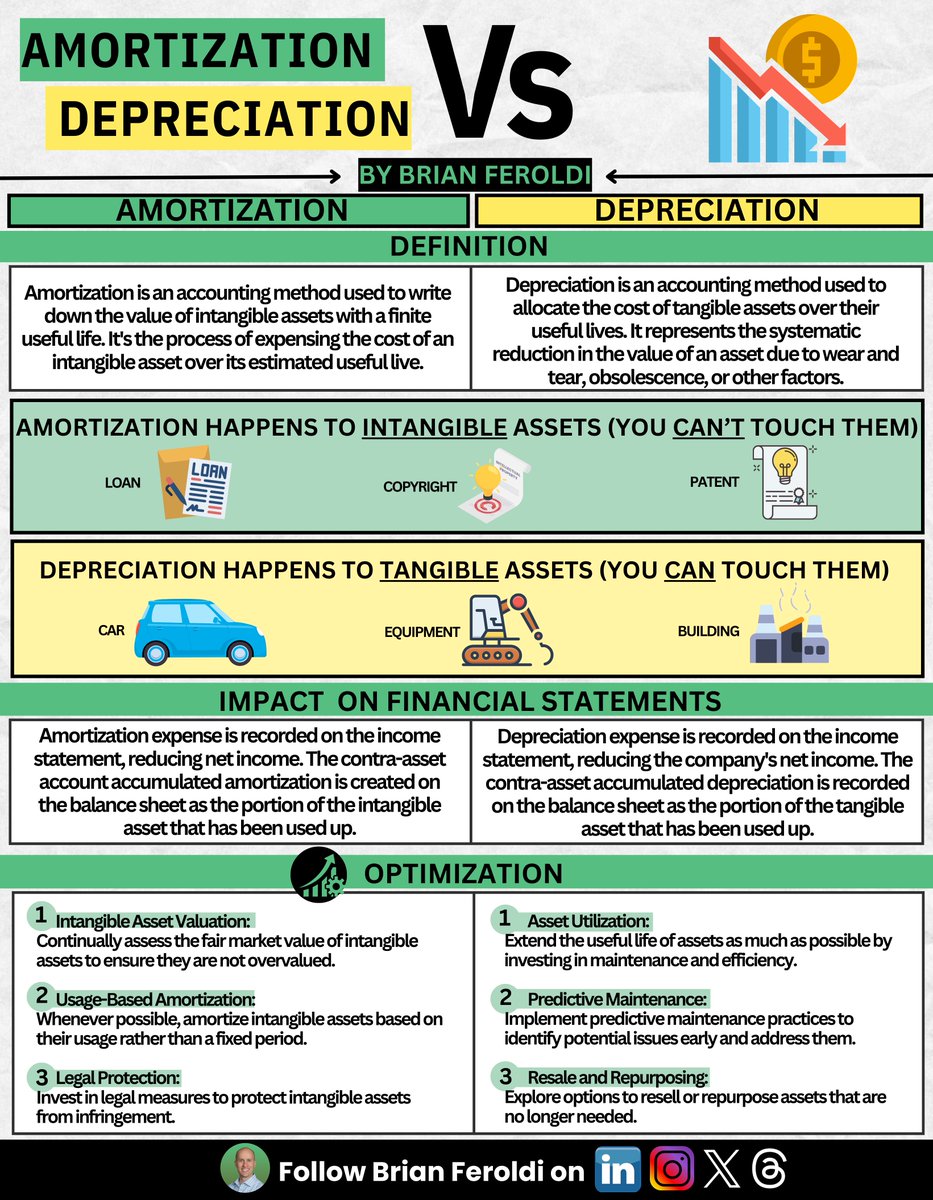
Long-term assets come in 2 forms:
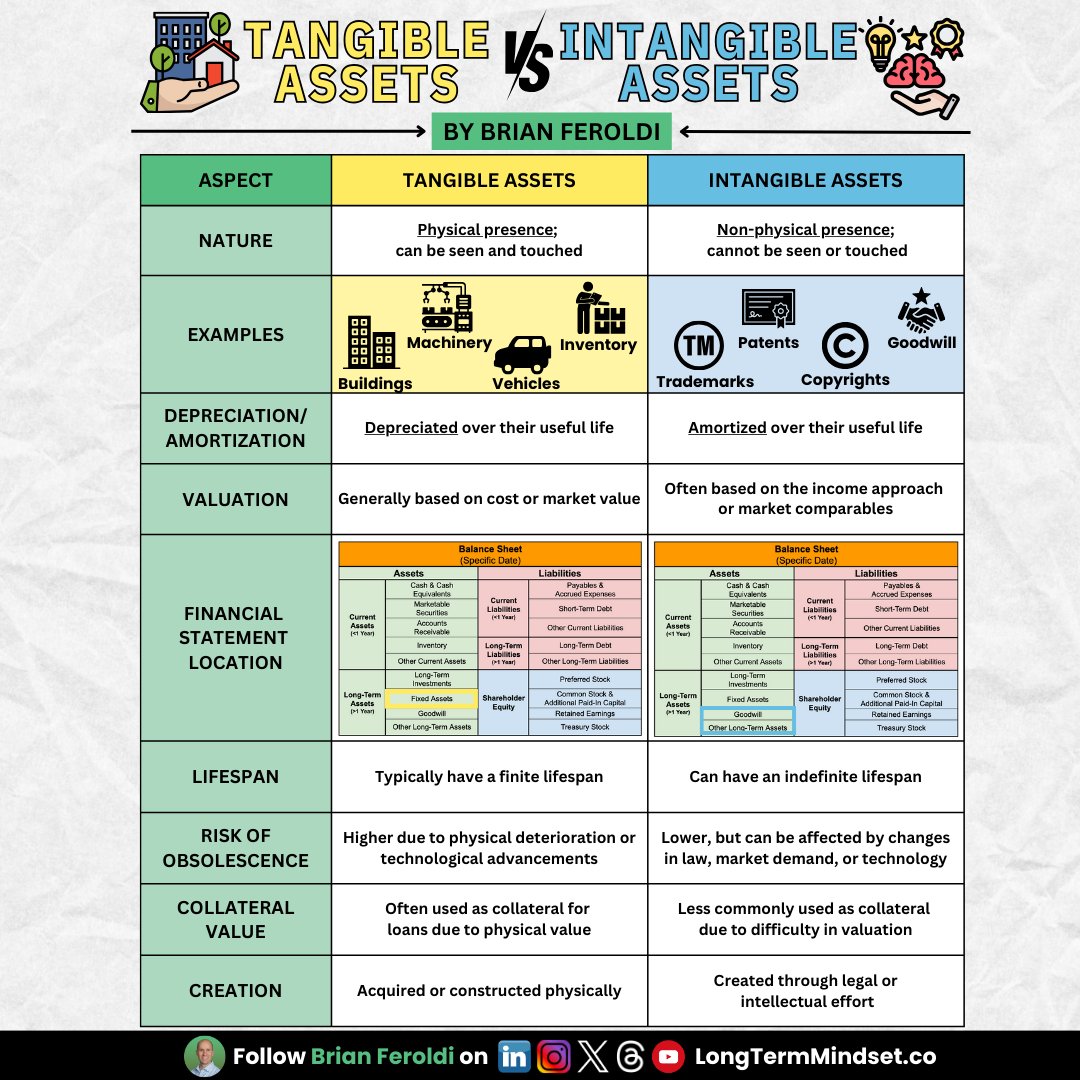
1: Tangible Assets
▪️Buildings
▪️Equipment
▪️Property
▪️Stores
2: Intangible Assets
▪️Trademarks
▪️Goodwill (premiums paid to make an acquisition)
▪️Patents
▪️Stocks/Bonds held >1 Year
1: Tangible Assets
▪️Buildings
▪️Equipment
▪️Property
▪️Stores
2: Intangible Assets
▪️Trademarks
▪️Goodwill (premiums paid to make an acquisition)
▪️Patents
▪️Stocks/Bonds held >1 Year
Now for Liabilities, which are what a company OWES
There are 2 categories of liabilities:
1: Current liabilities:
▪️Bills that will be paid in <1 year
2: Long-term liabilities:
▪️Bills that are due in >1 year
There are 2 categories of liabilities:
1: Current liabilities:
▪️Bills that will be paid in <1 year
2: Long-term liabilities:
▪️Bills that are due in >1 year

Common current liabilities (due <1 year):
▪️Short-term debt
▪️Accounts payable (money owed to suppliers)
▪️Interest
▪️Unpaid Wages
▪️Dividends
▪️Taxes
Common long-term liabilities (due >1 year):
▪️Long-term debt (also called "Notes")
▪️Customer pre-payment
▪️Taxes
▪️Pension
▪️Short-term debt
▪️Accounts payable (money owed to suppliers)
▪️Interest
▪️Unpaid Wages
▪️Dividends
▪️Taxes
Common long-term liabilities (due >1 year):
▪️Long-term debt (also called "Notes")
▪️Customer pre-payment
▪️Taxes
▪️Pension
Common categories:
▪️Retained Earnings: Net profits a company reinvests in the business
▪️Treasury Stock: Money used to buy back stock
▪️Additional Paid-In Capital: Amount shareholders have invested beyond common/preferred stock
▪️Retained Earnings: Net profits a company reinvests in the business
▪️Treasury Stock: Money used to buy back stock
▪️Additional Paid-In Capital: Amount shareholders have invested beyond common/preferred stock
This thread is just a broad overview of the balance sheet
Want specifics & and a helpful example?
We did a deep dive into the balance sheet on my YouTube channel using $AAPL's recent numbers as an example
Want specifics & and a helpful example?
We did a deep dive into the balance sheet on my YouTube channel using $AAPL's recent numbers as an example
Want to learn more about the income statement?
I have a thread on that too:
I have a thread on that too:
https://twitter.com/BrianFeroldi/status/1420377260222296066?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh