1/
🚨Is sodium bicarbonate useful to prevent Rhabdomyolysis induced AKI ❓❓🚨
We get asked this all the time! But in order to understand it, let's start with a simple question
What is the mechanism of AKI in rhabdomyolysis ❓❓
🚨Is sodium bicarbonate useful to prevent Rhabdomyolysis induced AKI ❓❓🚨
We get asked this all the time! But in order to understand it, let's start with a simple question
What is the mechanism of AKI in rhabdomyolysis ❓❓
2/
1⃣What happens in rhabdo?
⚡️Muscle necrosis → release of intracellular components (enzymes-CK, electrolytes & myoglobin)
⚡️Fluid sequestration within damaged muscle → volume depletion →🚨 RAAS➕SNS
⚡️Oxidative injury →⬆️ in vascular mediators → ⬇️renal blood flow
1⃣What happens in rhabdo?
⚡️Muscle necrosis → release of intracellular components (enzymes-CK, electrolytes & myoglobin)
⚡️Fluid sequestration within damaged muscle → volume depletion →🚨 RAAS➕SNS
⚡️Oxidative injury →⬆️ in vascular mediators → ⬇️renal blood flow
3/
We might see ⬆️Creatine Kinase (CK) levels somewhat frequently...
BUT...
Is there a CK level that predicts AKI❓
⚡️There is no defined threshold value of CK
⚡️CK levels < 15,000 to 20,000 U/ L on admission usually have a low risk of AKI
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16490621/
We might see ⬆️Creatine Kinase (CK) levels somewhat frequently...
BUT...
Is there a CK level that predicts AKI❓
⚡️There is no defined threshold value of CK
⚡️CK levels < 15,000 to 20,000 U/ L on admission usually have a low risk of AKI
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16490621/

4/
More on pathophys...
2⃣What is MYOGLOBIN?
⚡️17.8 kDa protein
⚡️Enters tubular epithelial cells through endocytosis
⚡️⬆️Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and free radicals
⚡️Precipitates with the Tamm-Horsfall protein (THP) in the distal tubular lumen
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19571284/
More on pathophys...
2⃣What is MYOGLOBIN?
⚡️17.8 kDa protein
⚡️Enters tubular epithelial cells through endocytosis
⚡️⬆️Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and free radicals
⚡️Precipitates with the Tamm-Horsfall protein (THP) in the distal tubular lumen
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19571284/

5/
The pathophysiology of AKI involves
⚡️Renal Vasoconstriction
⚡️Myoglobin induced oxidative injury
⚡️Intratubular cast obstruction
🚨Myoglobin induced direct cytotoxicity AND the formation of pigmented granular casts are favored by an ACIDIC URINE!! 🚨
The pathophysiology of AKI involves
⚡️Renal Vasoconstriction
⚡️Myoglobin induced oxidative injury
⚡️Intratubular cast obstruction
🚨Myoglobin induced direct cytotoxicity AND the formation of pigmented granular casts are favored by an ACIDIC URINE!! 🚨
6/
Before we dive into prevention 🚫 & treatment 💊 of AKI
🧪Beware of electrolyte complications...
- There is a ⬆️in serum K, Phos, Mg, uric acid
- There is a ⬇️in serum bicarbonate & Ca (initially⬇️then⬆️)
Before we dive into prevention 🚫 & treatment 💊 of AKI
🧪Beware of electrolyte complications...
- There is a ⬆️in serum K, Phos, Mg, uric acid
- There is a ⬇️in serum bicarbonate & Ca (initially⬇️then⬆️)
7/
The main strategy for 🚫prevention of AKI is:
💧IV volume repletion → target UO of 200-300 cc/hr
💧No difference between IVF solutions
The main strategy for 🚫prevention of AKI is:
💧IV volume repletion → target UO of 200-300 cc/hr
💧No difference between IVF solutions
8/
What other strategies would you use to prevent AKI?
What other strategies would you use to prevent AKI?
9/
The role of bicarbonate for prevention of pigment nephropathy is perhaps one of the most common questions we get asked as nephrologists...
The role of bicarbonate for prevention of pigment nephropathy is perhaps one of the most common questions we get asked as nephrologists...
10/
Based on the mechanisms of AKi, alkalinizing the urine would prevent:
⚡️Precipitation of myoglobin -THP complexes → ⬇️intratubular cast formation
⚡️Reduction-oxidation cycling of myoglobin ---> ⬇️tubular injury
⚡️Metmyoglobin formation (vasoconstrictor) → ⬇️vasoconstriction
Based on the mechanisms of AKi, alkalinizing the urine would prevent:
⚡️Precipitation of myoglobin -THP complexes → ⬇️intratubular cast formation
⚡️Reduction-oxidation cycling of myoglobin ---> ⬇️tubular injury
⚡️Metmyoglobin formation (vasoconstrictor) → ⬇️vasoconstriction
11/
So why don’t we give bicarbonate to everyone❓❓
So why don’t we give bicarbonate to everyone❓❓
12/
It turns out that alkalemia has been associated with higher mortality ☠️
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3589765/

It turns out that alkalemia has been associated with higher mortality ☠️
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3589765/


13/
Some of the downsides of alkalemia include:
🚫Depression of respiratory center
🚫Low iCa
🚫Low Myocardial Contractility
🚫Low Cerebral Blood Flow
Some of the downsides of alkalemia include:
🚫Depression of respiratory center
🚫Low iCa
🚫Low Myocardial Contractility
🚫Low Cerebral Blood Flow
14/
Since alkalemia is detrimental. Is there any evidence behind urine alkalinization❓
An animal model from 1952 by Perri GC and Gorini P showed that animals on an acidifying diet had a urine pH < 6 and developed AKI due to myoglobin precipitation
europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcr…

Since alkalemia is detrimental. Is there any evidence behind urine alkalinization❓
An animal model from 1952 by Perri GC and Gorini P showed that animals on an acidifying diet had a urine pH < 6 and developed AKI due to myoglobin precipitation
europepmc.org/backend/ptpmcr…


15/
In 1984, findings from animal models were reproduced in humans by Ron et.al
⚡️Urine alkalinization (target urine pH > 6.5) was used to treat 7 patients with rhabdomyolysis
⚡️None of them developed AKI by day 5
🚨 No control group
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6696564/
In 1984, findings from animal models were reproduced in humans by Ron et.al
⚡️Urine alkalinization (target urine pH > 6.5) was used to treat 7 patients with rhabdomyolysis
⚡️None of them developed AKI by day 5
🚨 No control group
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6696564/

16/
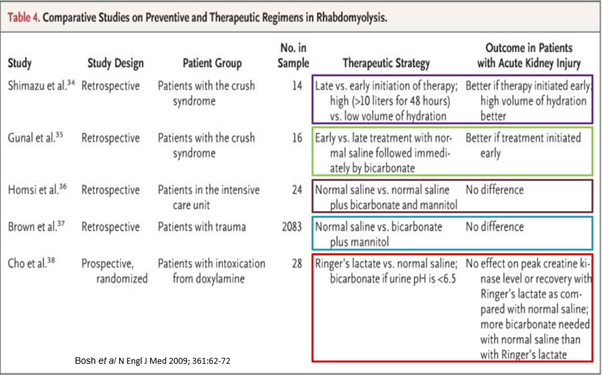
Different studies compared preventive & therapeutic regimens:
⚡️Early initiation of therapy with volume repletion is better
⚡️No difference between NS 🆚 NS +bicarb+mannitol
⚡️No difference between LR 🆚NS.
Both got bicarb if urine pH < 6.5. NS group required more bicarb
Different studies compared preventive & therapeutic regimens:
⚡️Early initiation of therapy with volume repletion is better
⚡️No difference between NS 🆚 NS +bicarb+mannitol
⚡️No difference between LR 🆚NS.
Both got bicarb if urine pH < 6.5. NS group required more bicarb
17/
SUMMARY:
⚡️AKI d/t rhabdo can be d/t vasoconstriction, oxidative injury & intratubular casts
⚡️Acidic urine ⬆️myoglobin toxicity in the proximal tubule AND precipitation of myoglobin-THP casts
⚡️CK levels < 15,000 to 20,000 U/ L on admission usually have a low risk of AKI
SUMMARY:
⚡️AKI d/t rhabdo can be d/t vasoconstriction, oxidative injury & intratubular casts
⚡️Acidic urine ⬆️myoglobin toxicity in the proximal tubule AND precipitation of myoglobin-THP casts
⚡️CK levels < 15,000 to 20,000 U/ L on admission usually have a low risk of AKI
18/
SUMMARY:
⚡️Beware of electrolyte abnormalities!!
⚡️Aggressive IVF repletion is the 🗝️
⚡️A urine pH > 6.5 has been suggested to decrease the risk of AKI (limited data)
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19571284/
SUMMARY:
⚡️Beware of electrolyte abnormalities!!
⚡️Aggressive IVF repletion is the 🗝️
⚡️A urine pH > 6.5 has been suggested to decrease the risk of AKI (limited data)
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19571284/

19/
I hope you enjoyed this overview on the prevention of AKI in rhabdomyolysis 🤓
Special thanks to @NSMCinternship, #GroupofHenle @amyaimei @Nephro_Sparks @docanjuyadav @drM_sudha @jamiekwillows
I hope you enjoyed this overview on the prevention of AKI in rhabdomyolysis 🤓
Special thanks to @NSMCinternship, #GroupofHenle @amyaimei @Nephro_Sparks @docanjuyadav @drM_sudha @jamiekwillows
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





