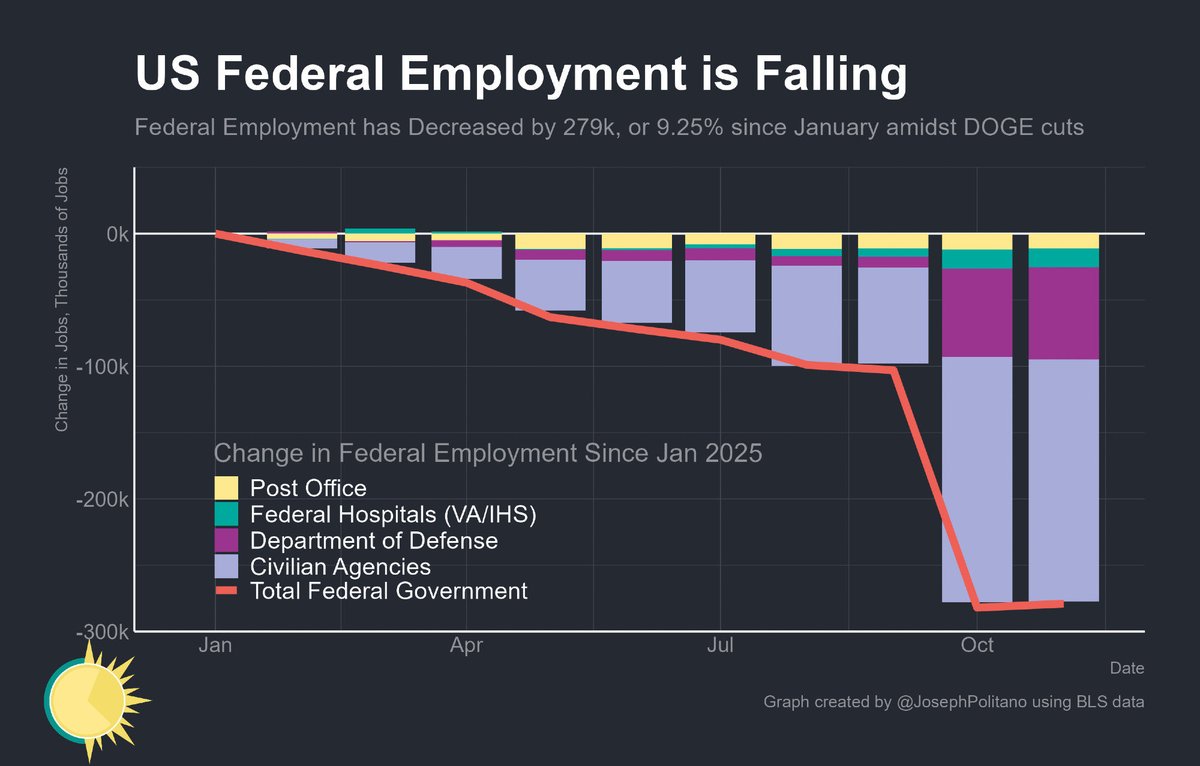
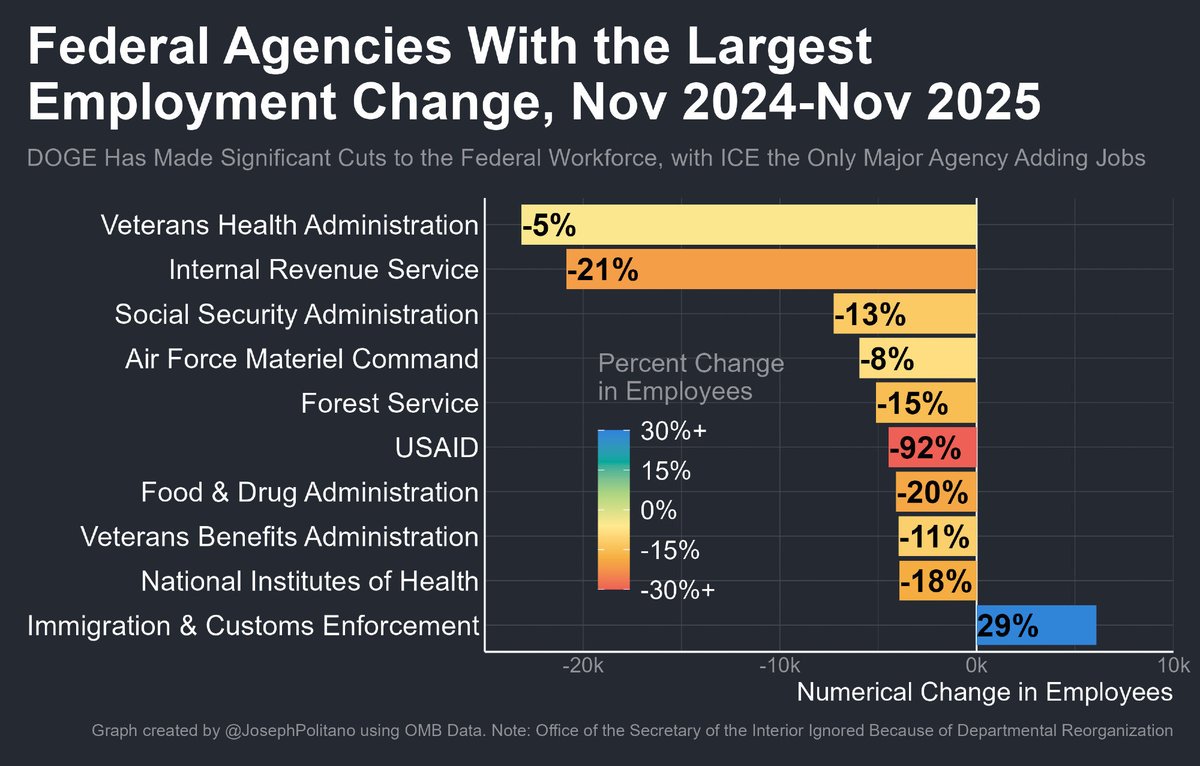
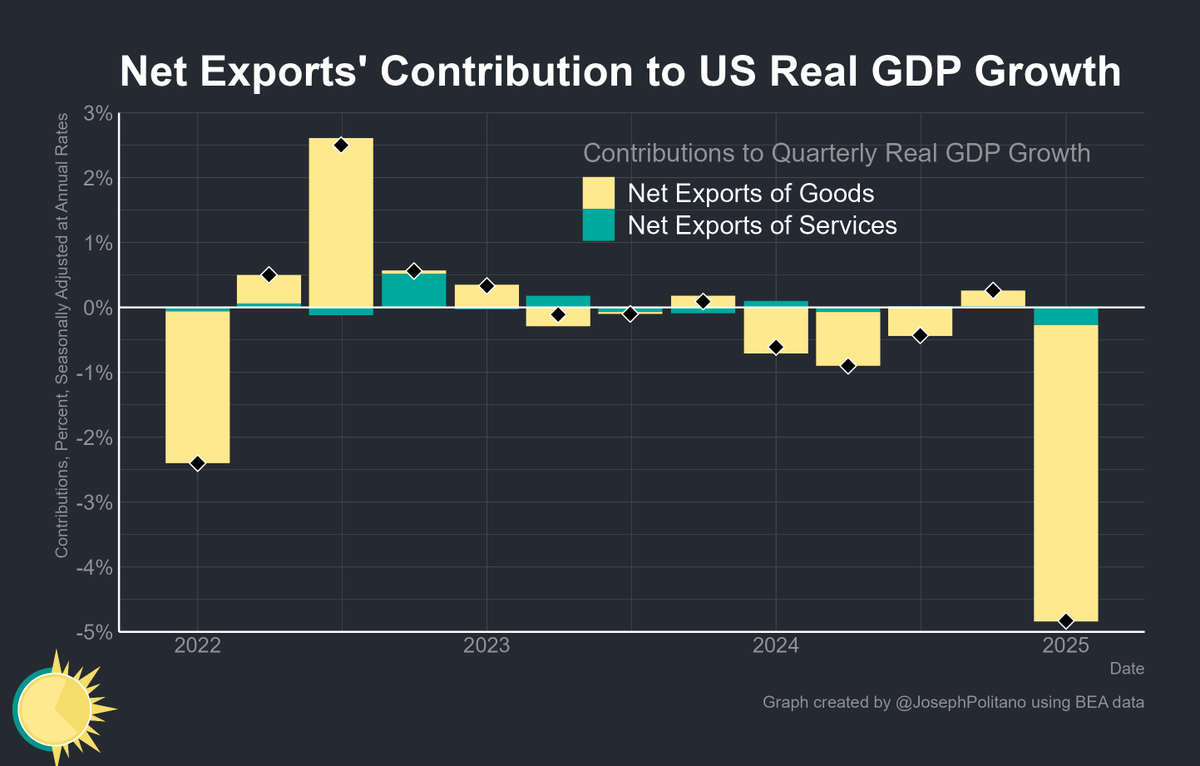
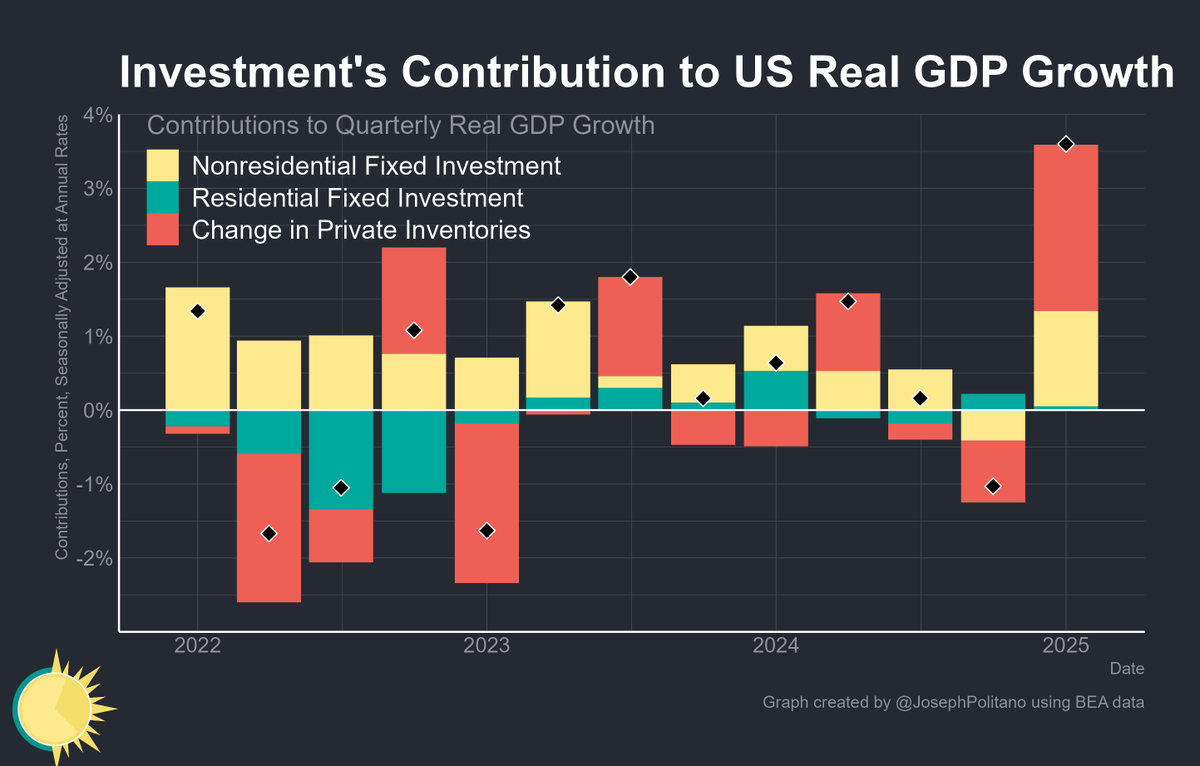
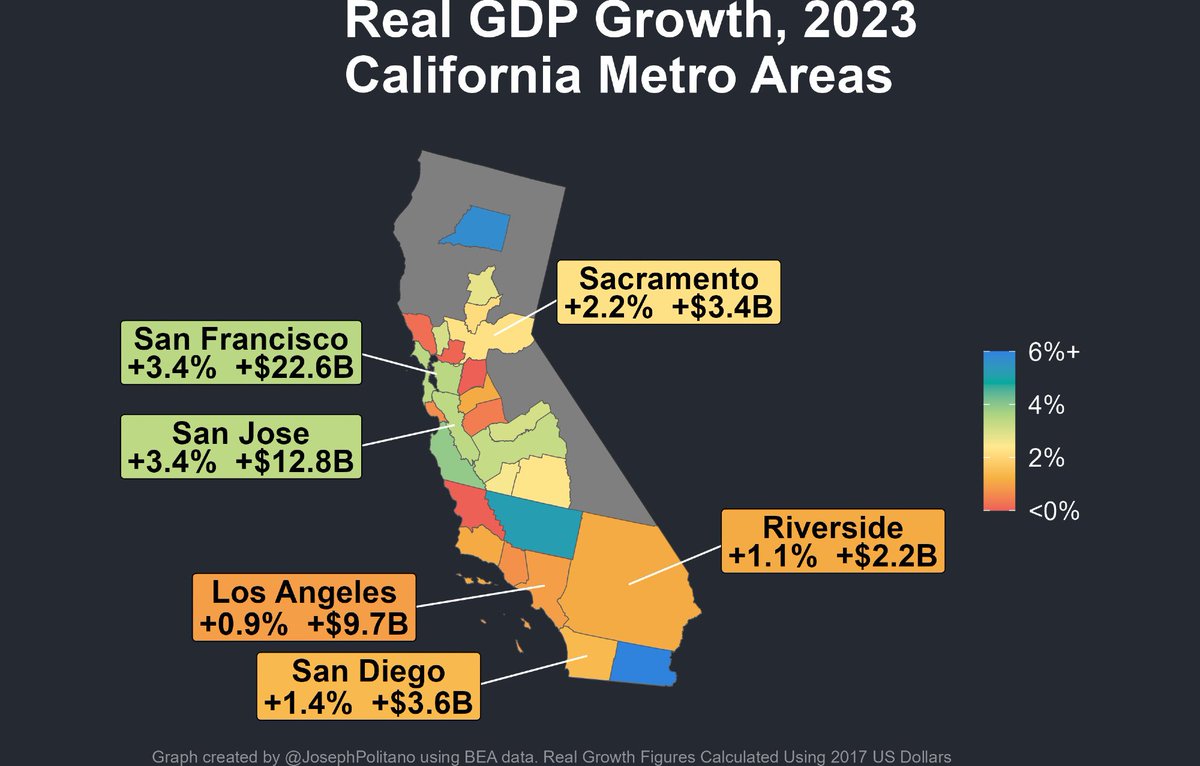
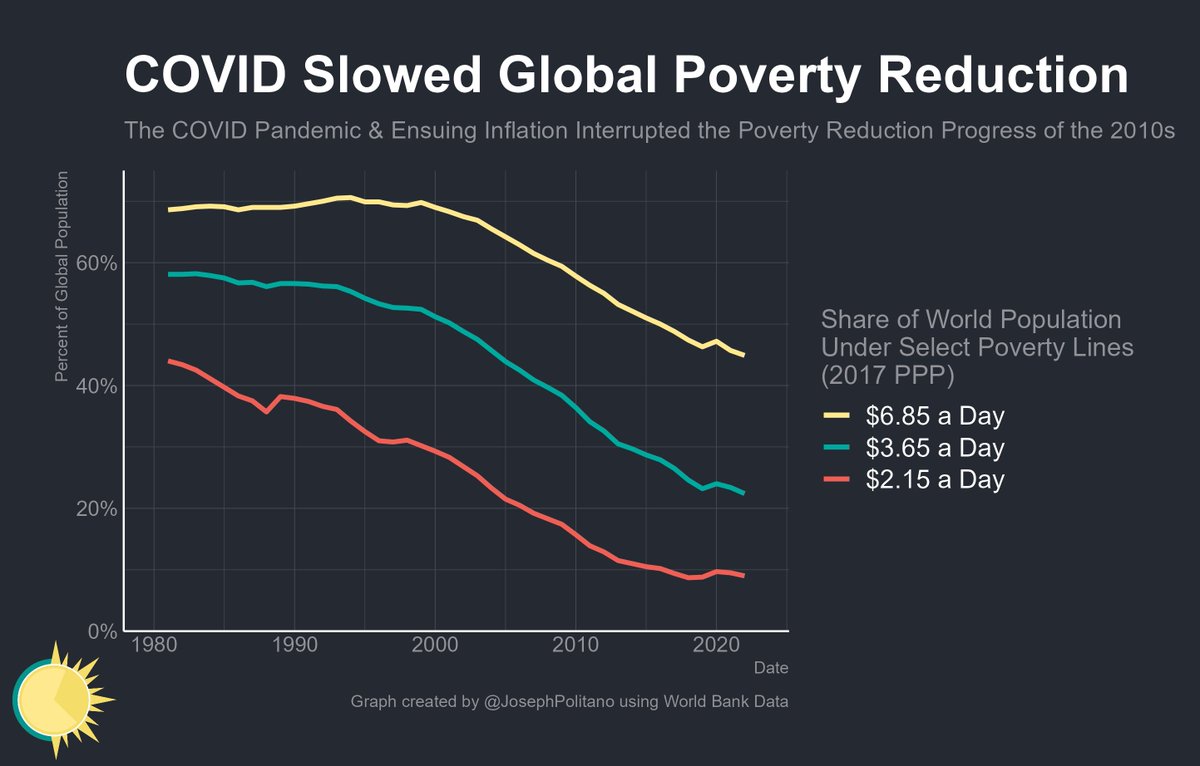
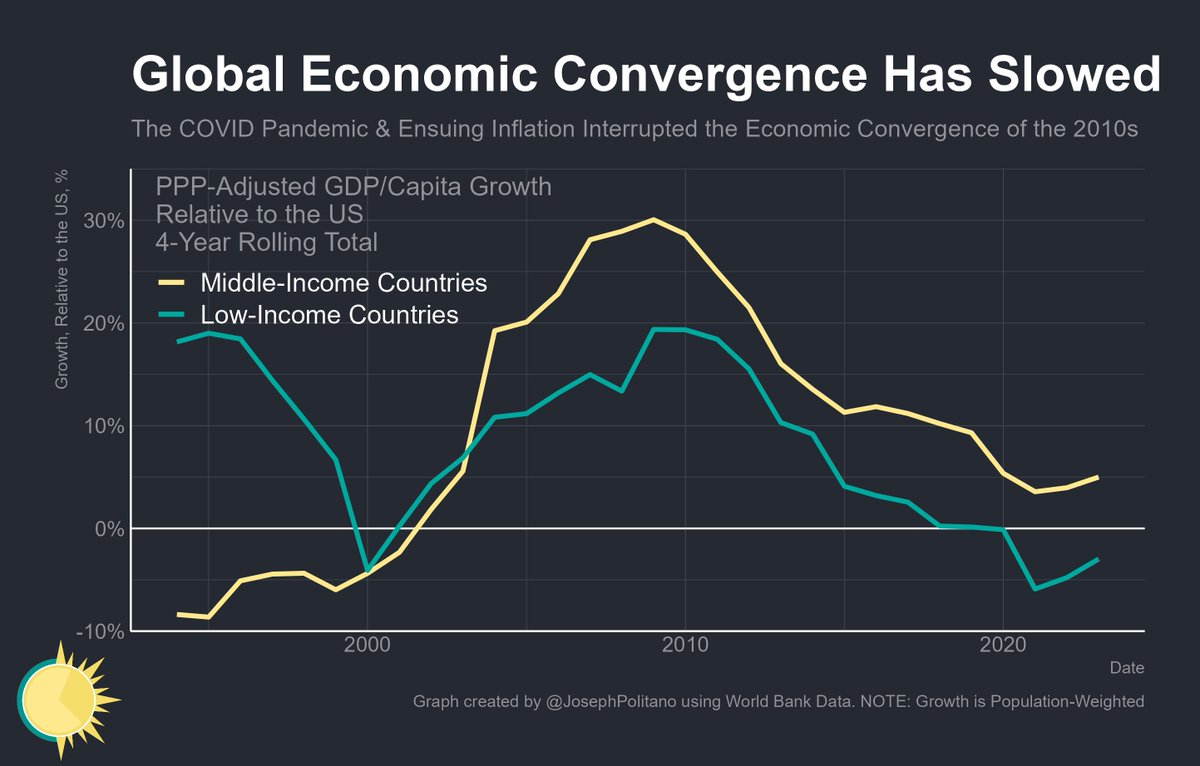
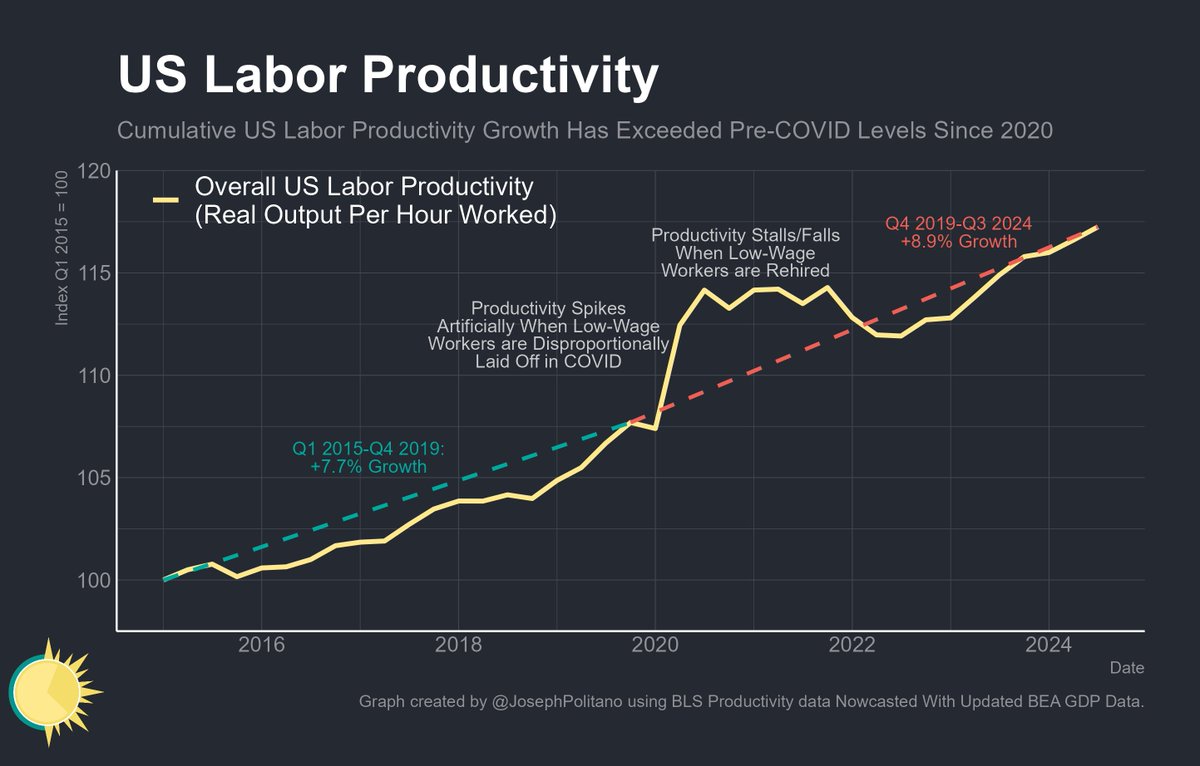
In a great month for the US labor market, October saw 531,000 jobs added and the unemployment rate drop to 4.6%.
I did a full break down of this month's employment data in a the blog post below.
Here's a short 🧵with the important takeaways:
apricitas.substack.com/p/the-october-…
I did a full break down of this month's employment data in a the blog post below.
Here's a short 🧵with the important takeaways:
apricitas.substack.com/p/the-october-…
After stalling out at 78% for 2 months, the prime age employment-population ratio increased significantly to 78.3%. This essentially measures the percent of working-age people who are employed, so it makes for the clearest measure of labor market health. 

The number of people employed part-time for economic reasons held steady at 4.4 million, which is close to pre-pandemic levels. This is down dramatically from the record high of nearly 11 million in April of 2020. 

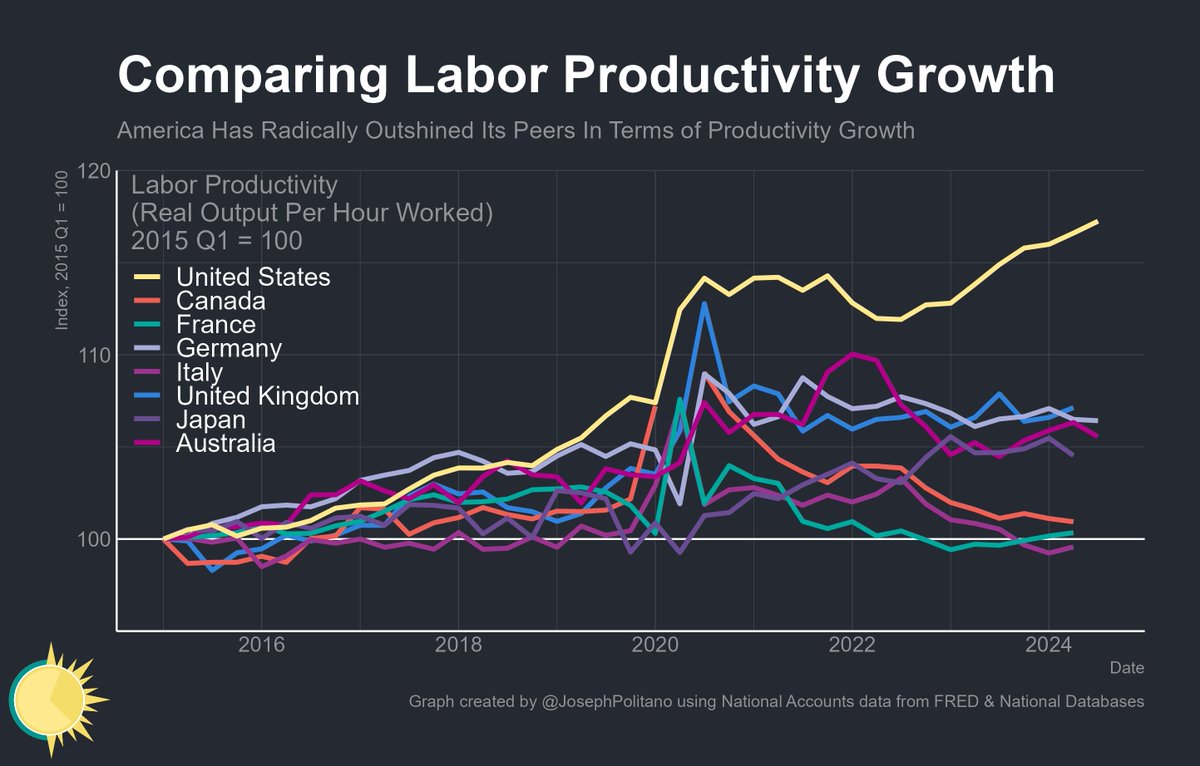
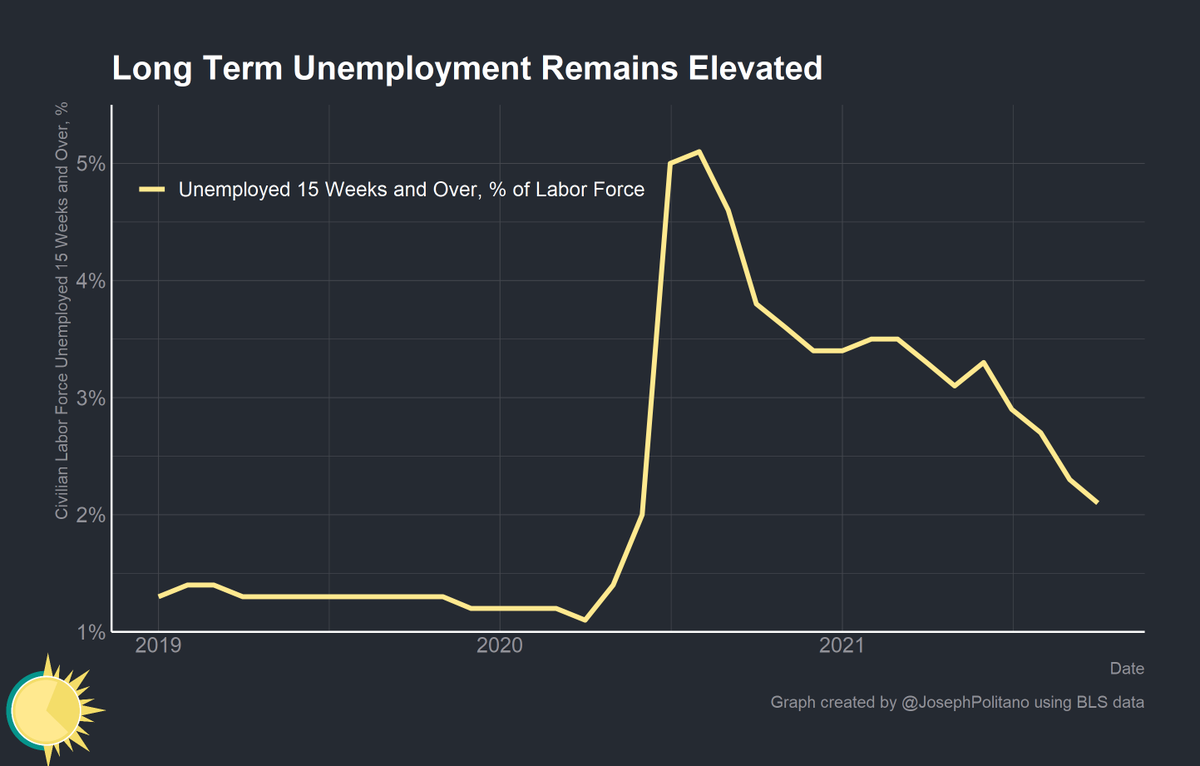
The percent of the workforce experiencing long term unemployment (15 weeks or more) also decreased to 2.1%. Long term unemployment has been on a steady decline since August 2020, when it peaked at 5.1%. 
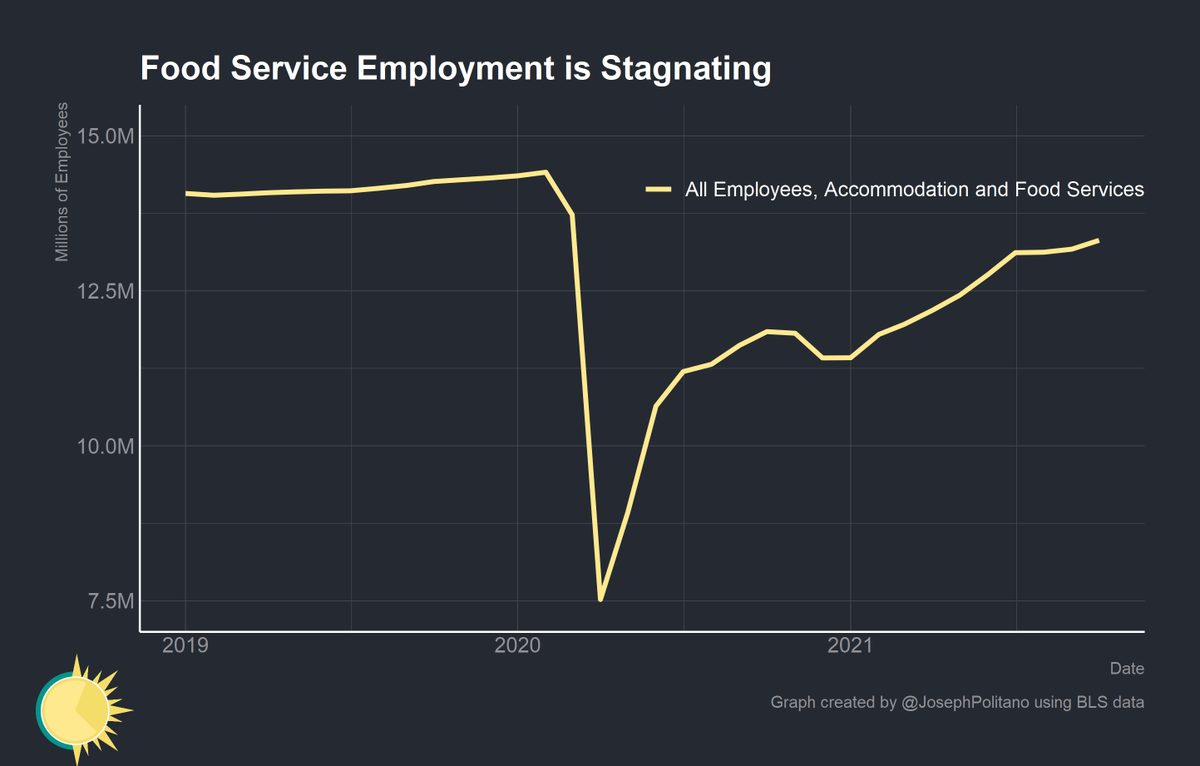
Employment in food services and accommodation, which makes up the majority of employment in leisure and hospitality, jumped up by 142,000. This is still more than 1 million jobs short of the pre-pandemic level. 
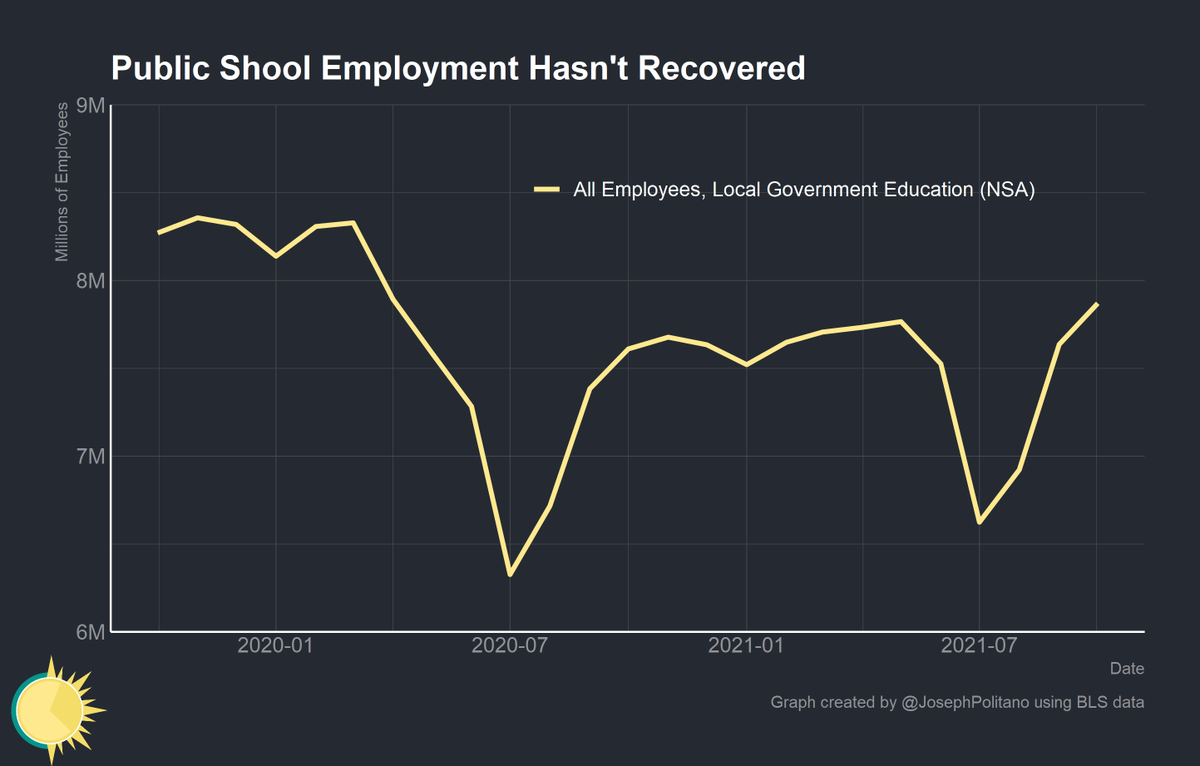
Employment in local government education is also approximately 600k jobs short. Analyzing non-seasonally adjusted (NSA) numbers is crucial, as the seasonal adjustment’s attempts to account for the summer decline in school employment has increased the data’s noise during COVID. 
The jump in demand for goods caused by the pandemic has resulted in a miniature boom in the warehousing and transportation industries. A record-high 5.9 million people are employed in the transportation and warehousing industry, with little signs of a hiring slowdown. 

Bottom line—the virus remains the boss, and there is still significant work to be done in order to get the virus completely under control and reach full employment.
Still, it is worth appreciating the tremendous progress coordinated monetary and fiscal policy has achieved.
Still, it is worth appreciating the tremendous progress coordinated monetary and fiscal policy has achieved.

If you like what I write, consider subscribing! It's free and helps me out a ton.
I'm going to be publishing a piece tomorrow about the Federal Reserve's decision to taper their quantitative easing purchases, so stay tuned!
apricitas.substack.com
I'm going to be publishing a piece tomorrow about the Federal Reserve's decision to taper their quantitative easing purchases, so stay tuned!
apricitas.substack.com
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh